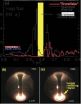
(Press-News.org) The Sun sporadically expels trillions of tons of million-degree hydrogen gas in explosions called coronal mass ejections (CMEs). Such clouds—an example is shown in Figure 1a—are enormous in size (spanning millions of miles) and are made up of magnetized plasma gases, so hot that hydrogen atoms are ionized. CMEs are rapidly accelerated by magnetic forces to speeds of hundreds of kilometers per second to upwards of 2,000 kilometers per second in several tens of minutes. CMEs are closely related to solar flares and, when they impinge on the Earth, can trigger spectacular auroral displays. They also induce strong electric currents in the Earth's plasma atmosphere (i.e., the magnetosphere and ionosphere), leading to outages in telecommunications and GPS systems and even the collapse of electric power grids if the disturbances are very severe.
Since the first observation of a solar flare in 1859, solar eruptions ("explosions") have attracted much attention from scientists around the world and have been studied with a succession of increasingly sophisticated international satellite missions in the past three decades. A major challenge has been that enormous and complicated plasma structures accelerating away from the Sun can only be observed remotely. As a result, it has been difficult to test theoretical models to establish a correct understanding of the mechanisms that cause such eruptions. But in 2006, an international twin-satellite mission called STEREO was launched to continuously observe the erupting plasma structures from the Sun to the Earth.
Now, using the data from STEREO, new research by scientists at the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) in Washington, D.C., demonstrates for the first time that the observed motion of erupting plasma clouds driven by magnetic forces can be correctly explained by a theoretical model. The work will be presented at the 52nd Annual Meeting of the APS Plasma Physics Division.
The theory, controversial when it was first proposed in 1989 by Dr. James Chen of NRL, is based on the concept that an erupting plasma cloud is a giant "magnetic flux rope," a rope of "twisted" magnetic field lines shaped like a partial donut. Chen and Valbona Kunkel, a doctoral student at George Mason University, have applied this model to the new STEREO data of CMEs and shown that the theoretical solutions agree with
the measured trajectories of the ejected clouds within the entire field of view from the Sun to the Earth.
The position of the leading edge (LE) of a CME that erupted on December 24, 2007 were tracked by the STEREO-A spacecraft from the earliest stages of eruption to its arrival at 1 AU approximately five days later. The magnetic field and plasma parameters were measured by the STEREO-B spacecraft. The agreement between theory and data is within 1 percent of the measured position of the LE. Chen and Kunkel's results show that the theoretically predicted magnetic field and plasma properties are in excellent agreement with the measurements aboard STEREO-B. This is the first model that can replicate directly observed quantities near the Sun and the Earth as well as the actual trajectories of CMEs. Prior to STEREO, the motion of CMEs in the region corresponding to HI1 and HI2 data was not observed.
Interestingly, the basic forces acting on solar flux ropes are the same as those in laboratory plasma structures such as tokamaks developed to produce controlled fusion energy. The mechanism described by the theory is also potentially applicable to eruptions on other stars.
INFORMATION:
Scientists unlock the secrets of exploding plasma clouds on the sun
News from the 52nd annual meeting of the APS Division of Plasma Physics
2010-11-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Taming thermonuclear plasma with a snowflake
2010-11-09
Physicists working on the National Spherical Torus Experiment (NSTX) at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory are now one step closer to solving one of the grand challenges of magnetic fusion research—how to reduce the effect that the hot plasma has on fusion machine walls (or how to tame the plasma-material interface). Some heat from the hot plasma core of a fusion energy device escapes the plasma and can interact with reactor vessel walls. This not only erodes the walls and other components, but also contaminates the plasma—all challenges for practical fusion. One method ...
Vacuum arcs spark new interest
2010-11-09
Whenever two pieces of metal at different voltages are brought near each other, as when an appliance is plugged into a live socket, there is a chance there will be an arc between them. Most of the arcs people see are a breakdown of the gas between the metal surfaces, but this type of breakdown can also occur in a vacuum. This vacuum breakdown, which until recently has not been well understood, has implications for applications from particle accelerators to fusion reactors.
As part of an effort to understand the maximum accelerating field in particle accelerators, scientists ...
PIT(-1)ting good and bad outcomes against each other in breast cancer
2010-11-09
The outlook for patients with breast cancer is determined in part by whether or not their tumor has spread to other sites in the body. A team of researchers, led by Roman Perez-Fernandez and colleagues, at the University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain, has now identified in a subset of patients with breast cancer, a marker associated with the occurrence of tumors at distant sites; a finding that they hope might help predict a patient's outlook more accurately. Specifically, the team found that in patients with breast cancer that was accompanied by the presence of tumor ...
JCI online early table of contents: Nov. 8, 2010
2010-11-09
EDITOR'S PICK: PIT(-1)ting good and bad outcomes against each other in breast cancer
The outlook for patients with breast cancer is determined in part by whether or not their tumor has spread to other sites in the body. A team of researchers, led by Roman Perez-Fernandez and colleagues, at the University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain, has now identified in a subset of patients with breast cancer, a marker associated with the occurrence of tumors at distant sites; a finding that they hope might help predict a patient's outlook more accurately. Specifically, the team ...
Research into adolescent sexual habits reveals surprising findings
2010-11-09
Females are more likely to have an unprotected first sexual encounter than their male counterparts.
This finding was a surprise to Nicole Weller, an Arizona State University graduate student working toward her doctoral degree in sociology, who presented preliminary findings on research she is conducting on the relationship between early sex education and the onset of sexual activity at the 138th annual American Public Health Association Social Justice Meeting and Expo in Denver on Monday, Nov. 8. Weller is a student in the School of Social and Family Dynamics in the College ...
PPIs and antiplatelet drugs can be used together after careful consideration of risks and benefits
2010-11-09
Using proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and antiplatelet drugs (thienopyridines) together is an appropriate way of treating patients with cardiovascular (CV) disease who are at high risk of upper gastrointestinal (GI) bleeds, despite recent concerns about an adverse interaction between these two types of drugs, according to an Expert Consensus Document released jointly today by the American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF), the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), and the American Heart Association (AHA).
The potential benefits of antiplatelet therapy for patients ...
Silent vascular disease accompanies cognitive decline in healthy aging
2010-11-09
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — Older people who are leading active, healthy lifestyles often have silent vascular disease that can be seen on brain scans that affect their ability to think, according to a new study led by UC Davis researchers and published online today in the Archives of Neurology, one of the JAMA Archives journals.
"This study shows that silent vascular disease is really common as we get older and it influences our thinking abilities," said Charles DeCarli, professor of neurology in the School of Medicine at UC Davis and director of the UC Davis Alzheimer's ...
Although less prevalent, physician-industry relationships remain common
2010-11-09
A new survey finds that, while the number of physicians who report having relationships with pharmaceutical manufacturers or other industrial companies has dropped in recent years, the vast majority of them still maintain such relationships. The study, conducted by the Mongan Institute for Health Policy (IHP) at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), appears in the Nov. 8 Archives of Internal Medicine and also documents changes in the frequency of particular types of relationships.
"While physician-industry relationships have decreased significantly since 2004, they ...
Alternative treatment for preventing relapse of certain type of vasculitis appears less effective
2010-11-09
In a comparison of treatments for maintaining remission of a certain type of vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), the immunosuppressant mycophenolate mofetil, regarded as an alternative to the drug often used to prevent relapse, azathioprine, was less effective, according to a study that will appear in the December 1 print edition of JAMA. The study is being released early online to coincide with its presentation at the American College of Rheumatology annual scientific meeting.
"Relapses of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) ...
Survey suggests that many physicians still have relationships with industry
2010-11-09
Relationships with drug manufacturers, device companies and other medical companies appear to be have decreased since 2004 but remain common among physicians, according to a report in the November 8 issue of Archives of Internal Medicine, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
"The medical profession has embraced the importance of placing patient welfare ahead of financial benefits to physicians in clinical decision making," the authors write as background information in the article. "One tenet of medical professionalism is managing conflicts of interest related to physician-industry ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
[Press-News.org] Scientists unlock the secrets of exploding plasma clouds on the sunNews from the 52nd annual meeting of the APS Division of Plasma Physics