(Press-News.org) When physicists probe the mysteries of plasma, the fourth state of matter, they often discover phenomena of striking beauty. Much as when the Hubble Space Telescope sent back vivid images from space of ionized gas clouds (an interstellar plasma!), new 3D images of shear Alfvén waves are delighting both scientists and a new generation of science enthusiasts.
Plasmas support a large variety of waves. Some of these are familiar, such as light and sound waves, but a great many exist nowhere else. One of the fundamental waves in magnetized plasma is the shear Alfvén wave, named after Nobel Prize winning scientist Hannes Alfvén, who predicted their existence.
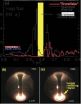
Shear waves of various forms have been a topic of experimental research for more than 15 years in the Large Plasma Device (LAPD) at the University of California, Los Angeles. When the waves were first studied, it was discovered that their creation gives rise to exotic spatial patterns, such as the one shown in Figure 1, all of them Shear Alfvén waves. Three-dimensional data, such as the magnetic field of the wave shown here, will be presented along with relevant theory. Part of the presentation will be in 3D!
It has become apparent that Alfvén waves are important in a wide variety of physical environments. They play a central role in the stability of the magnetic confinement devices used in fusion research, give rise to aurora formation in planets, and are thought to contribute to heating and ion acceleration in the solar corona. Shear waves can also cause particle acceleration over considerable distances in interstellar space.
INFORMATION:
The many faces of the shear Alfvén wave
News from the 52nd annual meeting of the APS Division of Plasma Physics
2010-11-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Plasma as a fast optical switch
2010-11-09
Just like an electrical switch allows the flow of electricity into electrical circuits, relativistic transparency in plasma can act like a fast optical switch allowing the flow of light through otherwise opaque plasma. Modern day lasers, such as the Trident laser in Los Alamos National Laboratory delivers a 200 terawatt power pulse (roughly 400 times the average electrical consumption of the United States) in half a trillionth of a second (picosecond) time. As shown in Fig. 1, when the laser power reaches a threshold limit, relativistic transparency in plasma turns the ...
Scientists unlock the secrets of exploding plasma clouds on the sun
2010-11-09
The Sun sporadically expels trillions of tons of million-degree hydrogen gas in explosions called coronal mass ejections (CMEs). Such clouds—an example is shown in Figure 1a—are enormous in size (spanning millions of miles) and are made up of magnetized plasma gases, so hot that hydrogen atoms are ionized. CMEs are rapidly accelerated by magnetic forces to speeds of hundreds of kilometers per second to upwards of 2,000 kilometers per second in several tens of minutes. CMEs are closely related to solar flares and, when they impinge on the Earth, can trigger spectacular auroral ...
Taming thermonuclear plasma with a snowflake
2010-11-09
Physicists working on the National Spherical Torus Experiment (NSTX) at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory are now one step closer to solving one of the grand challenges of magnetic fusion research—how to reduce the effect that the hot plasma has on fusion machine walls (or how to tame the plasma-material interface). Some heat from the hot plasma core of a fusion energy device escapes the plasma and can interact with reactor vessel walls. This not only erodes the walls and other components, but also contaminates the plasma—all challenges for practical fusion. One method ...
Vacuum arcs spark new interest
2010-11-09
Whenever two pieces of metal at different voltages are brought near each other, as when an appliance is plugged into a live socket, there is a chance there will be an arc between them. Most of the arcs people see are a breakdown of the gas between the metal surfaces, but this type of breakdown can also occur in a vacuum. This vacuum breakdown, which until recently has not been well understood, has implications for applications from particle accelerators to fusion reactors.
As part of an effort to understand the maximum accelerating field in particle accelerators, scientists ...
PIT(-1)ting good and bad outcomes against each other in breast cancer
2010-11-09
The outlook for patients with breast cancer is determined in part by whether or not their tumor has spread to other sites in the body. A team of researchers, led by Roman Perez-Fernandez and colleagues, at the University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain, has now identified in a subset of patients with breast cancer, a marker associated with the occurrence of tumors at distant sites; a finding that they hope might help predict a patient's outlook more accurately. Specifically, the team found that in patients with breast cancer that was accompanied by the presence of tumor ...
JCI online early table of contents: Nov. 8, 2010
2010-11-09
EDITOR'S PICK: PIT(-1)ting good and bad outcomes against each other in breast cancer
The outlook for patients with breast cancer is determined in part by whether or not their tumor has spread to other sites in the body. A team of researchers, led by Roman Perez-Fernandez and colleagues, at the University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain, has now identified in a subset of patients with breast cancer, a marker associated with the occurrence of tumors at distant sites; a finding that they hope might help predict a patient's outlook more accurately. Specifically, the team ...
Research into adolescent sexual habits reveals surprising findings
2010-11-09
Females are more likely to have an unprotected first sexual encounter than their male counterparts.
This finding was a surprise to Nicole Weller, an Arizona State University graduate student working toward her doctoral degree in sociology, who presented preliminary findings on research she is conducting on the relationship between early sex education and the onset of sexual activity at the 138th annual American Public Health Association Social Justice Meeting and Expo in Denver on Monday, Nov. 8. Weller is a student in the School of Social and Family Dynamics in the College ...
PPIs and antiplatelet drugs can be used together after careful consideration of risks and benefits
2010-11-09
Using proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and antiplatelet drugs (thienopyridines) together is an appropriate way of treating patients with cardiovascular (CV) disease who are at high risk of upper gastrointestinal (GI) bleeds, despite recent concerns about an adverse interaction between these two types of drugs, according to an Expert Consensus Document released jointly today by the American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF), the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), and the American Heart Association (AHA).
The potential benefits of antiplatelet therapy for patients ...
Silent vascular disease accompanies cognitive decline in healthy aging
2010-11-09
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — Older people who are leading active, healthy lifestyles often have silent vascular disease that can be seen on brain scans that affect their ability to think, according to a new study led by UC Davis researchers and published online today in the Archives of Neurology, one of the JAMA Archives journals.
"This study shows that silent vascular disease is really common as we get older and it influences our thinking abilities," said Charles DeCarli, professor of neurology in the School of Medicine at UC Davis and director of the UC Davis Alzheimer's ...
Although less prevalent, physician-industry relationships remain common
2010-11-09
A new survey finds that, while the number of physicians who report having relationships with pharmaceutical manufacturers or other industrial companies has dropped in recent years, the vast majority of them still maintain such relationships. The study, conducted by the Mongan Institute for Health Policy (IHP) at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), appears in the Nov. 8 Archives of Internal Medicine and also documents changes in the frequency of particular types of relationships.
"While physician-industry relationships have decreased significantly since 2004, they ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
[Press-News.org] The many faces of the shear Alfvén waveNews from the 52nd annual meeting of the APS Division of Plasma Physics