(Press-News.org) Montreal November 9, 2010 – Potential investors might wish to examine the fingers of their financial advisor prior to signing over any savings. A new study from Concordia University has found the length between the second and fourth finger is an indicator of high levels of prenatal testosterone, risk-taking and potential financial success in men. The findings, published in the journal of Personality and Individual Differences, suggest that alpha males may take greater risks in relationships, on the squash court and in the financial market.
"Previous studies have linked high testosterone levels with risky behaviour and financial success," says senior researcher Gad Saad, Concordia University Research Chair in Evolutionary Behavioral Sciences and Darwinian Consumption as well as a marketing professor at the John Molson School of Business. "We investigated the relationship between prenatal testosterone and various risk proclivities. Our findings show an association between high testosterone and risk-taking among males in three domains: recreational, social and financial."
"Since women tend to be attracted to men who are fit, assertive and rich, men are apt to take risks with sports, people and money to be attractive to potential mates. What's interesting is that this tendency is influenced by testosterone exposure – more testosterone in the womb can lead to more risks in the rink, the bar and the trading floor in later in life," says first author and Concordia doctoral student, Eric Stenstrom.
Link only observed in men
Saad and his team analyzed risk-taking among 413 male and female students using a survey. "Prenatal testosterone exposure not only influences fetal brain development," adds study co-author and graduate student, Zack Mendenhall, "but it also slows the growth of the index finger relative to the sum of the four fingers excluding the thumb."
The change in finger length produced by testosterone provides a handy measure of prenatal testosterone exposure. The study compared the length of the index finger with all four digits (known as the rel2 ratio) and found that those with lower ratios were more likely to engage in risk-taking. These findings were further confirmed by the additional measurement of the ratio between the index and ring finger. These correlations were only observed in men.
"A possible explanation for the null effects in women is that they do not engage in risky behaviour as a mating signal, whereas men do," says Professor Saad.
INFORMATION:
About the study:
Testosterone and domain-specific risk: Digit ratios (2D:4D and rel2) as predictors of recreational, financial, and social risk-taking behaviors, published in the journal Personality and Individual Differences, was authored by Eric Stenstrom, Gad Saad, Marcelo V. Nepomuceno and Zack Mendenhall from Concordia University.
On the Web:
Concordia University: www.concordia.ca
Concordia's John Molson School of Business: http://johnmolson.concordia.ca
Cited Personality and Individual Differences study: www.elsevier.com/wps/find/journaldescription.cws_home/603/description#description
Media contact:
Sylvain-Jacques Desjardins
Senior advisor, media relations
University Communications Services
Concordia University
Phone: 514-848-2424, ext. 5068
Email: s-j.desjardins@concordia.ca
Twitter: http://twitter.com/concordianews
Concordia news: http://now.concordia.ca
END
Infrared and visible imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite today hinted that the low pressure area formerly known as Cyclone Jal may have new life soon. Jal has emerged into the warm waters of the Arabian Sea after crossing India this past weekend.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies onboard Aqua captured infrared and visible images of Jal's remnants on Nov. 9 at 1:30 p.m. local time/India.
Today's AIRS imagery hints that circulation is still occurring in Jal's remnants. The circulation was particularly apparent in the AIRS visible image. The ...
The amount of time parents spend talking about numbers has a much bigger impact on how young children learn mathematics than was previously known, researchers at the University of Chicago have found.
For example, children whose parents talked more about numbers were much more likely to understand the cardinal number principle--which states that the size of a set of objects is determined by the last number reached when counting the set (e.g., a set of 10 items is larger than a set of seven items).
"By the time children enter preschool, there are marked individual differences ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Depression affects approximately 30 to 40 percent of nursing home residents, but it often goes unrecognized, according to American Geriatrics Society, which can lead to lower quality of life or even suicide. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have found a series of indicators, other than changes in mood that are associated with the development of depression in nursing home residents.
"Prompt diagnosis and treatment of depression is essential to improve the quality of life for nursing home residents," said Lorraine Phillips, assistant professor ...
AURORA, Colo. (Nov. 9, 2010) – As dog bites become an increasingly major public health concern, a new study shows that unsupervised children are most at risk for bites, that the culprits are usually family pets and if they bite once, they will bite again with the second attack often more brutal than the first.
The study, the largest of its kind, was done by Vikram Durairaj, MD, of the University of Colorado School of Medicine, who found that dogs usually target a child's face and eyes and most often it's a breed considered `good' with children, like a Labrador retriever.
"People ...
Killing microorganisms has become a national obsession. A pair of antimicrobial compounds known as triclosan and triclocarban are lately the weapons of choice in our war of attrition against the microbial world. Both chemicals are found in an array of personal care products like antimicrobial soaps, and triclosan also is formulated into everyday items ranging from plastics and toys to articles of clothing.
But are these antimicrobial chemicals, as commonly used by people across the nation, really safe for human health and the environment? More pointedly, do they even ...
Between 20 and 30 percent of women who undergo in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedures suffer from significant symptoms of depression. Many practitioners believe that the hormone therapy involved in IVF procedures is primarily responsible for this. But new research from Tel Aviv University shows that, while this is true, other factors are even more influential.
According to Dr. Miki Bloch of Tel Aviv University's Sackler Faculty of Medicine and the Sourasky Medical Center in Tel Aviv, stress, pre-existing depression, and anxiety are more likely than hormone therapy ...
U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists in West Virginia are finding ways to improve soil on degraded land so it can be used for sports fields and other uses.
Researchers with USDA's Agricultural Research Service (ARS) at the agency's Appalachian Farming Systems Research Center (AFSRC) in Beaver, W.Va., are developing constructed or replacement subsoils and topsoils to build better and less-costly sports fields, raingardens and lawns on former landfills, mine lands and other degraded land. ARS is USDA's principal intramural scientific research agency.
The constructed ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---Some scholars estimate that presenteeism, a relatively recent buzzword that applies to people who are less productive at work because of health issues, costs employers as much as three times the dollar amount as absenteeism in terms of lost productivity.
But researchers at University of Michigan believe those numbers may be inaccurate. A new opinion paper suggests that the tools for measuring and quantifying hours of lost productivity and translating those hours to dollars are unreliable and don't capture the entire presenteeism picture, said Susan ...
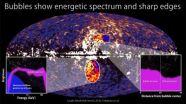
WASHINGTON -- NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has unveiled a previously unseen structure centered in the Milky Way. The feature spans 50,000 light-years and may be the remnant of an eruption from a supersized black hole at the center of our galaxy.
"What we see are two gamma-ray-emitting bubbles that extend 25,000 light-years north and south of the galactic center," said Doug Finkbeiner, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Mass., who first recognized the feature. "We don't fully understand their nature or origin."
The ...
DALLAS – Nov. 9, 2010 – A hormone already responsible for increasing blood pressure by prompting the kidneys to retain salt appears to moonlight as a major stimulator of the brain centers that control the vascular system and blood pressure.
Researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center studied patients who overproduce aldosterone to see whether the hormone had any effect on sympathetic nerve activity responsible for blood pressure increases.
"Between 10 percent and 20 percent of patients with high blood pressure who are resistant to treatment have elevated aldosterone ...