(Press-News.org) Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have released an updated version of a computer system testing tool that can cut costs by more efficiently finding flaws. A tutorial on using the tool accompanies the new release.
Catching software "bugs" before a program is released enhances computer security because hackers often exploit these flaws to introduce malware, including viruses, to disrupt or take control of computer systems. But it's difficult. A widely cited 2002 study prepared for NIST* reported that even though 50 percent of software development budgets go to testing, flaws in software still cost the U.S. economy $59.5 billion annually.
Exhaustive checking of all possible combinations of input actions that could cause software failure is not practical, explained NIST's Raghu Kacker, because of the huge number of possibilities, but it's also not necessary. Based on studies of software crashes in applications, including medical devices and Web browsers, NIST's Rick Kuhn and other researchers determined that between 70 and 95 percent of software failures are triggered by only two variables interacting and practically 100 percent of software failures are triggered by no more than six. "Testing every combination up to six variables can be as good as exhaustive testing," said Kacker.
Working with researcher Jeff Yu Lei and his students from the University of Texas at Arlington, NIST designed Advanced Combinatorial Testing System (ACTS), a freely distributed software tool to generate plans for efficiently testing combinations of two to six interacting variables. The method goes beyond the commonly used "pairwise" approach to software testing, which tests combinations of two variables, so it can detect more obscure flaws. (See "'Combinatorial' Approach Squashes Software Bugs Faster, Cheaper" in NIST Tech Beat, Dec. 12, 2007, at www.nist.gov/itl/math/bugs_121207.cfm.)
Kuhn describes the process "as packing as many combinations into a set of tests as efficiently as we know how." For example, testing all possible interactions for a product with 34 on and off switches would require 17 billion tests. Using ACTS, all three-way interactions can be evaluated using only 33 tests and all six-way combinations with just 522 tests, instead of 17 billion.
The first version of ACTS was released in 2008. Since then, it has been distributed at no cost to 465 organizations and individuals in industry, academia and government. "About half of our users are in IT, but other heavy users are in the financial, defense and telecommunications sectors," said Kuhn. In August, NIST and Lockheed Martin initiated a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement to study the application of ACTS in the company's large and complex software applications. The two groups will jointly publish the results.
NIST released the latest update of ACTS in October. The new version includes an improved user interface and a better method of specifying relationships between parameters for testing. This can eliminate the problem, for example, of spending time on tests for invalid combinations, such as using Internet Explorer on a Linux system. Information for requesting ACTS is available at http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/SNS/acts/index.html.
Just released is a new tutorial, Practical Combinatorial Testing, that introduces key concepts and methods along with explaining the use of software tools for generating combinatorial tests. Cost and other practical considerations are addressed. The tutorial is designed to be accessible to undergraduate students in computer science or engineering and includes extensive references. NIST Special Publication 800-142 (link to http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/SNS/acts/documents/SP800-142-101006.pdf) can be downloaded at crsc.nist.gov/acts.
INFORMATION:
* Research Triangle Institute, The Economic Impacts of Inadequate Infrastructure for Software Testing, NIST Planning Report 02-3, May 2002.
Updated NIST software uses combination testing to catch bugs fast and easy
2010-11-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
U of M researchers find learning in the visual brain
2010-11-11
A team of researchers from the University of Minnesota's College of Liberal Arts and College of Science and Engineering have found that an early part of the brain's visual system rewires itself when people are trained to perceive patterns, and have shown for the first time that this neural learning appears to be independent of higher order conscious visual processing.
The researchers' findings could help shape training programs for people who must learn to detect subtle patterns quickly, such as doctors reading X-rays or air traffic controllers monitoring radars. In addition, ...
New NIST dietary supplement reference materials could be 'berry' useful
2010-11-11
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) researchers have developed new certified reference materials for measuring amounts of organic acids in dietary supplements formulated with Vaccinium berries—cranberries, blueberries and bilberries. As described in a recent paper,* manufacturers and researchers can use this new suite of standard reference materialsTM (SRMs) as quality assurance tools.
berry SRMs
Dietary supplement manufacturers often include health claims on products made with Vaccinium berries. Suggested benefits include prevention of urinary tract ...
Academies of science call for amendments to impracticable Genetic Diagnostics Act
2010-11-11
Many aspects of the German Genetic Diagnostics Act (Gendiagnostikgesetz) are out of touch with the latest technology, almost impossible to implement in clinical practice, or even detrimental to the success of recognised screening tests, such as newborn screening. The Act, which came into force in February 2010, is in desperate need of amendment. This was the conclusion reached by the Academy Workgroup "Predictive genetic diagnostics as an instrument of disease prevention" of the German Academy of Sciences Leopoldina, the Berlin-Brandenburg Academy of Sciences and Humanities ...
NIST pings key material in sonar, closes gap on structural mystery
2010-11-11
Using a neutron beam as a probe, researchers working at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have begun to reveal the crystal structure of a compound essential to technologies ranging from sonar to computer memory. Their recent work* provides long-sought insight into just how a widely used material of modern technology actually works.
The compound is a "piezoelectric," a material capable of changing one kind of energy into another—mechanical to electrical, or vice versa. Long employed in sonar systems to detect sound waves, more recently piezoelectrics ...
Looking for wireless? Try a local farm
2010-11-11
VIDEO:
Wireless. For most, the word conjures images quaint coffee shops or busy airport lobbies -- places where people drop in to check on business or check in with other people.
But...
Click here for more information.
BEAUMONT – Wireless. For most, the word conjures images quaint coffee shops or busy airport lobbies – places where people drop in to check on business or check in with other people.
But increasingly "wireless" is showing up on the farm to help produce better ...
AFM positioning: Shining light on a needle in a haystack
2010-11-11
The researchers characterize their new technique as a neat solution to the "needle in a haystack" problem of nanoscale microscopy, but it's more like the difference between finding the coffee table in a darkened room either by walking around until you fall over it, or using a flashlight. In a new paper,* a group from JILA—a joint venture of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Colorado—finds tiny assemblies of biomolecules for subsequent detailed imaging by combining precision laser optics with atomic force microscopy.
The ...
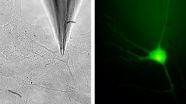
Synapses recycle proteins for the release of neurotransmitters
2010-11-11
Neurons communicate via chemical transmitters which they store in the bubble-like synaptic vesicles and release as required. To be able to react reliably to stimulation, neurons must have a certain number of "acutely releasable" vesicles. With the help of a new method, neuroscientists at the Max Planck Institute of Experimental Medicine in Göttingen have now discovered that neurons systematically recycle the protein components necessary for transmitter release and in this way guarantee the reliability of signal transmission in the brain. If this process is disrupted, the ...
Portrait of gambling behavior in Quebec
2010-11-11
Montreal, November 10, 2010 – The initial findings of a survey on the prevalence of gambling in Quebec have been released. The study also deals with behavior problems associated with gambling. The study reveals that nearly 70 percent of Quebec adults report having bet or spent money on gambling during the previous 12 months. It also found Quebecers spend an average of $483 annually on gambling activities.
This survey was conducted between June and September 2009 throughout the province among 11,888 non-institutionalized adults over the age of 18. It constitutes the first ...
Army-funded technology detects bacteria in water
2010-11-11
November 10, 2010 -- To keep soldiers in the battlefield healthy, the U.S. Army is exploring new ways to detect harmful bacteria in water.
Current techniques for analyzing water in the field can take as long as 24 hours to complete, according to Bart Lipkens of Western New England College in Springfield, Massachusetts and his colleagues at Physical Sciences in Andover, Ma.
They are working on an alternative technology that uses sound waves to accelerate the process.
"The goal of our project is to speed up the detection of bacteria in water supplies," said Lipkens. ...
Evolutionary bestseller in image processing
2010-11-11
The eye is not just a lens that takes pictures and converts them into electrical signals. As with all vertebrates, nerve cells in the human eye separate an image into different image channels once it has been projected onto the retina. This pre-sorted information is then transmitted to the brain as parallel image sequences. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology in Martinsried have now discovered that fruit flies process optical information in a similar way. The evidence suggests that this type of wiring is an effective energy-saving mechanism and is therefore ...