Can-do plan gets women trimmer, healthier, and cuts hot flashes
Program shows potential to fit into today's healthcare environment
2014-02-13
(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND, Ohio (Thursday, February 13, 2014)—A woman can beat middle-aged spread, her disease risks, and her hot flashes with the help of her healthcare provider. And even a short term program can spell success for women and fit into a busy provider's practice, shows a demonstration obesity-fighting and health risk reduction program detailed in an article just published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Making lifestyle changes can take a lot of work. Programs that have successfully helped women lose weight and reduce their other heart disease risks have been long and intensive—and they work as long as the program goes on. Most first-line women's healthcare providers, such as obstetrician-gynecologists or primary care providers, don't have the time and might not be reimbursed for so many consultations.
But this pilot program, called WAIPointes (WAI stands for "who am I"), took only five visits that all were reimbursed by insurance. And it kept the participants engaged in achieving their health goals by showing them that they could reduce their menopause symptoms, in addition to their long-term disease risks, with healthy lifestyle changes.
The 83 women who completed the 6-month program ranged from 35 to 55 years old, and most were in perimenopause or menopause. At an orientation, the women learned about menopause and the health risks that come with it and were told they have the opportunity to get their personal health risks assessed if they joined the program. At the first visit, they answered questionnaires and got assessments of body weight and fat and menopause status and went home with a pedometer and a health diary, educational materials, and goal-setting worksheets to develop their personal health goals. From the second to the fifth visit, each woman had health assessments including waist measurement, blood pressure, menopause symptoms, mammograms and bone density tests if needed, and blood tests to look for inflammation, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
Once a woman had her goals set, she discussed with the healthcare providers how to reach those goals, what obstacles stood in the way, and how to overcome them. If distressing menopause symptoms were obstacles, the providers offered the women treatment options, such as lifestyle modifications or medications, to overcome them.
"Empowerment through education is a cornerstone of our intervention," wrote the authors. Their surveys of the participants and the health assessments showed that approach was working.
By the end of the program, the women understood their health risks better, and they had already made significant progress toward achieving their health goals. They trimmed their waistlines by an average of an inch and a half and lowered their diastolic blood pressure by 2 points. What's more, their hot flashes and other menopause symptoms, such as energy, libido, mood, and vaginal dryness, had all improved significantly. And each woman had a "life action plan," with personalized recommendations, to continue working toward their health goals.
INFORMATION:
Founded in 1989, The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) is North America's leading nonprofit organization dedicated to promoting the health and quality of life of all women during midlife and beyond through an understanding of menopause and healthy aging. Its multidisciplinary membership of 2,000 leaders in the field—including clinical and basic science experts from medicine, nursing, sociology, psychology, nutrition, anthropology, epidemiology, pharmacy, and education—makes NAMS uniquely qualified to serve as the definitive resource for health professionals and the public for accurate, unbiased information about menopause and healthy aging. To learn more about NAMS, visit http://www.menopause.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Immunologists from the University of Bonn topple dogma
2014-02-13
An international team of scientists under the leadership of the University of Bonn disproves a dogma: To date, immunologists have assumed that the macrophages functioning as "scavenger cells" can be classified into two different forms. In an extensive search, the researchers have now discovered that these immune cells turn into far more different manifestations. These findings also give rise to completely new therapeutic approaches for many widespread diseases. The results are now being published in the renowned journal Immunity.
In the body, macrophages go on patrol ...
Books rate more negatively after winning award, study finds
2014-02-13
Looking for a good book? Stay away from the award-winning section of the bookstore or library.
New research from Amanda Sharkey of the University of Chicago Booth School of Business finds that a book read after winning a prestigious award will likely be judged more negatively than if it's read in its pre-award days.
In "The Paradox of Publicity: How Awards Can Negatively Affect the Evaluation of Quality," to be published in the March issue of Administrative Science Quarterly, Sharkey and colleague Balázs Kovács of the University of Lugano analyze thousands of reader ...
Study: Beauty not disease motivates teens to wear sunscreen
2014-02-13
After offering information about UV light and sun-protective behaviors, the two health-ed
videos diverge: one describes the increased skin cancer risk of UV exposure and the other
describes effects on appearance including wrinkles and premature aging. Which of these two
videos do you think caused teenagers to use more sunscreen six weeks after it was shown? A
University of Colorado Cancer Center study shows that while teens who watched both videos
learned and retained the same amount of knowledge about UV light and sun-protective behaviors,
only the teens who ...
Air pollution increases risk for hypertension in pregnant women
2014-02-13
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — Breathing the air outside their homes may be just as toxic to pregnant women — if not more so — as breathing in cigarette smoke, increasing a mom-to-be's risk of developing deadly complications such as preeclampsia, according to findings from a new University of Florida study.
UF researchers compared birth data with Environmental Protection Agency estimates of air pollution, finding that heavy exposure to four air pollutants led to a significantly increased risk for developing a high blood pressure disorder during pregnancy. The research was published ...
Light-induced degradation in amorphous silicon thin film solar cells
2014-02-13
This news release is available in German. Researchers at the Helmholtz Center Berlin (HZB) have taken a leap forward towards a deeper
understanding of an undesired effect in thin film solar cells based on amorphous silicon – one
that has puzzled the scientific community for the last 40 years. The researchers were able to
demonstrate that tiny voids within the silicon network are partly responsible for reducing solar
cell efficiency by some 10 to 15 percent as soon as you start using them. Their work has now
been published in Physical Review Letters (DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.066403).
Amorphous ...
Two new weapons in the battle against bacteria
2014-02-13
This news release is available in German.
Proteins are made up of a chain of amino acids and are vital for all cell processes. Proteases are among the most important types of protein. Like "molecular scissors", they cut other proteins at given positions and thereby execute important cell functions. By cutting the amino acid chains to the right length or breaking proteins apart they, for example, activate or deactivate proteins, decompose defective ones or switch signal sequences that serve to transport proteins to their proper position within a cell.
But proteases ...
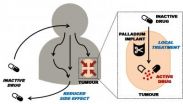
Metal implants may cut chemotherapy side effects, study suggests
2014-02-13
Cancer patients could one day experience fewer side effects from chemotherapy following a discovery that opens the door for more targeted treatments.
Researchers have identified a possible way of treating tumours that would see doctors place harmless metal implants at the cancer site.
The discovery could make treatment more targeted than existing therapies, avoiding unwanted side effects, such as hair loss, tiredness and nausea. These occur when chemotherapy drugs carried in the blood kill healthy cells as well as cancer cells.
The scientists found that they could ...
Deutsche eMark (DEM) - Could be second cryptocurrency coin after Bitcoin
2014-02-13
Deutsche eMark is an open source peer-to-peer digital Internet currency. Deutsche eMark stands for fast and secure payments to anyone around the world, who has an eMark Wallet. Therefore no banks are required and the fees are low and simple to understand. Today price on Cryptsy Exchange is 0.00012, but experts says, that it could fast reach 0.002 DEM/BTC.
Sleep apnea common among stroke-related brainstem injuries
2014-02-13
People whose brainstems are affected by their stroke have a significantly higher prevalence of sleep apnea than those who have stroke-related injury elsewhere in the brain, according to research presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2014.
Sleep apnea is marked by interrupted breathing during sleep and can lead to serious health problems including heart disease and stroke.
"This is the largest population-based study to address the issue of the location of the brain injury and its relationship to sleep apnea in post-stroke patients," ...
ADHD drugs not linked to increased stroke risk among children
2014-02-13
Children who take medication to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) don't appear to be at increased stroke risk, according to a study presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2014.
In a study of 2.5 million 2- to 19-year-olds over a 14-year period, researchers compared stimulant medication usage in children diagnosed with ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke to stimulant usage in children without stroke.
Researchers found no association between stroke risk and the use of ADHD stimulant medications at the time of stroke ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
Can Europe be climate-neutral by 2050? New monitor tracks the pace of the energy transition
Major heart attack study reveals ‘survival paradox’: Frail men at higher risk of death than women despite better treatment
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
[Press-News.org] Can-do plan gets women trimmer, healthier, and cuts hot flashesProgram shows potential to fit into today's healthcare environment