(Press-News.org) For the first time, an international team of astrophysicists, including Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists, have unraveled how stars blow up in supernova explosions.
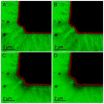
Using NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) – a high-energy X-ray observatory - the international collaboration created the first-ever map of radioactive material in a supernova remnant, named Cassiopeia A, or Cas A for short. The findings reveal how shock waves likely rip apart massive dying stars, and ultimately end their lives.
A supernova is the cataclysmic death of a star, which is extremely luminous and causes a burst of radiation that often briefly outshines an entire galaxy before fading from view. The explosion expels much or all of a star's material at a velocity of 10 percent of the speed of light, driving a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium. This shock wave sweeps up an expanding shell of gas and dust called a supernova remnant.
"Stars are spherical balls of gas, and so you might think that when they end their lives and explode, that explosion would look like a uniform ball expanding out with great power," said Fiona Harrison, the principal investigator of NuSTAR at the California Institute of Technology and one of the lead authors of a new paper. "Our new results show how the explosion's heart, or engine, is distorted, possibly because the inner regions literally slosh around before detonating."
The research appears in the Feb. 20 issue of the journal Nature.
The Cas A remnant was created when a massive star blew up as a supernova more than 11,000 years ago, leaving a dense stellar corpse and its ejected remains. Because the supernova was so far from Earth, the light only reached Earth about 350 years ago, when it may have appeared to be a new, bright star in the sky.
Supernovae seed the universe with many elements, including gold, calcium and iron. While small stars like our sun die less violent deaths, stars with about eight times the mass of our sun or greater blow up in supernova explosions. The high temperatures and particles created in the blast cause fusion of lighter elements into heavier ones.
NuSTAR is the first telescope capable of producing maps of radioactive material in supernova remnants; in this case, titanium-44, an atom with an unstable nucleus produced at the heart of the exploding star.
"Cas A was a mystery for so long but now with the map of radioactive material, we're getting a more complete picture of the core of the explosion," said Bill Craig, an LLNL scientist now at UC Berkeley and co-author of the paper.
The NuSTAR map of Cas A, which shows the titanium concentrated in clumps at the remnant's center, points to a possible solution to the mystery of how the star met its demise. When researchers simulate supernova blasts with computers, the main shock wave stalls out and the star fails to shatter.
"For NuSTAR, Cas A is special," said Mike Pivovaroff, an LLNL physicist and a co-author on the new paper. "One of NuSTAR's science goals is to map recently synthesized material in young supernova remnants, and Cas A is one of the youngest supernova remnants we know of."
The latest findings strongly suggest the exploding star literally sloshed around, reenergizing the stalled shock wave and allowing the star to blast off its outer layers.
NuSTAR, a NASA Explorer-class mission launched in June of 2012, is uniquely designed to detect the highest-energy X-ray light in great detail. For Livermore, the predecessor to NuSTAR was a balloon-borne instrument known as HEFT (the High Energy Focusing Telescope) that was funded, in part, by a Laboratory Directed Research and Development investment beginning in 2001. NuSTAR takes HEFT's X-ray focusing abilities and sends them beyond Earth's atmosphere on a satellite. The optics principles and the fabrication approach for NuSTAR are based on those developed under the HEFT project. Craig serves as the NuSTAR instrument manager while Pivovaroff and LLNL scientist Julia Vogel are part of the optics team.
INFORMATION:
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory provides solutions to our nation's most important national security challenges through innovative science, engineering and technology. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
NuSTAR helps untangle how stars explode
2014-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
REACT clinical trial supports new approach of accelerated treatment for Crohn's disease
2014-02-19
The final results from an international clinical trial involving nearly 2,000 patients with Crohn's disease support the use of a new management strategy referred to as accelerated step-care as a best practice for the care of active Crohn's disease. The REACT (Randomized Evaluation of an Algorithm for Crohn's Treatment) study, led by Robarts Clinical Trials at Western University (London, Canada) provides valuable new insights for community gastroenterologists which should benefit patients. The results of the study will be presented at the European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation ...
ORNL microscopy system delivers real-time view of battery electrochemistry
2014-02-19
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Feb. 19, 2014 -- Using a new microscopy method, researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory can image and measure electrochemical processes in batteries in real time and at nanoscale resolution.
Scientists at ORNL used a miniature electrochemical liquid cell that is placed in a transmission electron microscope to study an enigmatic phenomenon in lithium-ion batteries called the solid electrolyte interphase, or SEI, as described in a study published in Chemical Communications.
The SEI is a nanometer-scale film that forms ...
Many Texans struggling to pay for health service as Affordable Care Act is about to launch
2014-02-19
HOUSTON – (Feb. 19, 2014) – Many Texans were struggling to pay for basic health services on the eve of the launch of the Affordable Care Act's Health Insurance Marketplace, according to a report released today by Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy and the Episcopal Health Foundation. The report also found that even those with health insurance reported dissatisfaction with the cost and availability of services. Most Texans expect more of the same in 2014.
The Health Reform Monitoring Survey (HRMS)-Texas report is based on the HRMS, a national project that ...
Molecular aberration signals cancer
2014-02-19
Several scientists, including one at Simon Fraser University, have made a discovery that strongly links a little understood molecule, which is similar to DNA, to cancer and cancer survival.
EMBO Reports, a life sciences journal published by the European Molecular Biology Organization, has just published online the scientists' findings about small non-coding RNAs.
While RNA is known to be key to our cells' successful creation of proteins, the role of small non-coding RNAs, a newly discovered cousin of the former, has eluded scientific understanding for the most part. ...
Cell therapy shows remarkable ability to eradicate cancer in clinical study
2014-02-19
NEW YORK, February 19, 2014 — Investigators from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center have reported more encouraging news about one of the most exciting methods of cancer treatment today. The largest clinical study ever conducted to date of patients with advanced leukemia found that 88 percent achieved complete remissions after being treated with genetically modified versions of their own immune cells. The results were published today in Science Translational Medicine.
"These extraordinary results demonstrate that cell therapy is a powerful treatment for patients who ...
LGBT youth face greater cancer risks, CCNY-led study
2014-02-19
A new study led by City College of New York psychologist Margaret Rosario found that youths of same-sex orientation are more likely to engage in behaviors associated with cancer risk than heterosexuals. The peer-reviewed findings appear in the February 2014 issue of the American Journal of Public Health.
Titled "Sexual Orientation Disparities in Cancer-Related Risk Behaviors of Tobacco, Alcohol, Sexual Behaviors, and Diet and Physical Activity: Pooled Youth Risk Behavior Surveys," the study pooled YRBS (Youth Risk Behavior Survey) data from 2005 and 2007. The YRBS is ...
Using holograms to improve electronic devices
2014-02-19
RIVERSIDE, Calif. (http://www.ucr.edu) — A team of researchers from the University of California, Riverside Bourns College of Engineering and Russian Academy of Science have demonstrated a new type of holographic memory device that could provide unprecedented data storage capacity and data processing capabilities in electronic devices.
The new type of memory device uses spin waves – a collective oscillation of spins in magnetic materials – instead of the optical beams. Spin waves are advantageous because spin wave devices are compatible with the conventional electronic ...
Statistics research could build consensus around climate predictions
2014-02-19
Philadelphia, PA—Vast amounts of data related to climate change are being compiled by research groups all over the world. Data from these many and various sources results in different climate projections; hence, the need arises to combine information across data sets to arrive at a consensus regarding future climate estimates.
In a paper published last December in the SIAM Journal on Uncertainty Quantification, authors Matthew Heaton, Tamara Greasby, and Stephan Sain propose a statistical hierarchical Bayesian model that consolidates climate change information ...
Smellizing -- imagining a product's smell -- increases consumer desire, study finds
2014-02-19
Seeing is believing, but smellizing – a new term for prompting consumers to imagine the smell of a product – could be the next step toward more effective advertising.
Researchers came to this conclusion through four studies of products most of us would like to smellize: cookies and cake.
Professor of Marketing Maureen Morrin of Temple University's Fox School of Business co-authored Smellizing Cookies and Salivating: A Focus on Olfactory Imagery to examine the impact imagining what a food smells like would have on consumer behavior.
"Before we started this project, ...
Discovery by Baylor University researchers sheds new light on the habitat of early apes
2014-02-19
WACO, Texas (Feb. 18, 2014)-- Baylor University researchers, in collaboration with an international team of scientists, have discovered definitive evidence of the environment inhabited by the early ape Proconsul on Rusinga Island, Kenya. The groundbreaking discovery provides additional information that will help scientists understand and interpret the connection between habitat preferences and the early diversification of the ape-human lineage.
Their research findings--published this month in Nature Communications--demonstrate that Proconsul and its primate relative Dendropithecus ...