(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, PA—Vast amounts of data related to climate change are being compiled by research groups all over the world. Data from these many and various sources results in different climate projections; hence, the need arises to combine information across data sets to arrive at a consensus regarding future climate estimates.
In a paper published last December in the SIAM Journal on Uncertainty Quantification, authors Matthew Heaton, Tamara Greasby, and Stephan Sain propose a statistical hierarchical Bayesian model that consolidates climate change information from observation-based data sets and climate models.
"The vast array of climate data—from reconstructions of historic temperatures and modern observational temperature measurements to climate model projections of future climate—seems to agree that global temperatures are changing," says author Matthew Heaton. "Where these data sources disagree, however, is by how much temperatures have changed and are expected to change in the future. Our research seeks to combine many different sources of climate data, in a statistically rigorous way, to determine a consensus on how much temperatures are changing."
Using a hierarchical model, the authors combine information from these various sources to obtain an ensemble estimate of current and future climate along with an associated measure of uncertainty. "Each climate data source provides us with an estimate of how much temperatures are changing. But, each data source also has a degree of uncertainty in its climate projection," says Heaton. "Statistical modeling is a tool to not only get a consensus estimate of temperature change but also an estimate of our uncertainty about this temperature change."
The approach proposed in the paper combines information from observation-based data, general circulation models (GCMs) and regional climate models (RCMs).
Observation-based data sets, which focus mainly on local and regional climate, are obtained by taking raw climate measurements from weather stations and applying it to a grid defined over the globe. This allows the final data product to provide an aggregate measure of climate rather than be restricted to individual weather data sets. Such data sets are restricted to current and historical time periods. Another source of information related to observation-based data sets are reanalysis data sets in which numerical model forecasts and weather station observations are combined into a single gridded reconstruction of climate over the globe.
GCMs are computer models which capture physical processes governing the atmosphere and oceans to simulate the response of temperature, precipitation, and other meteorological variables in different scenarios. While a GCM portrayal of temperature would not be accurate to a given day, these models give fairly good estimates for long-term average temperatures, such as 30-year periods, which closely match observed data. A big advantage of GCMs over observed and reanalyzed data is that GCMs are able to simulate climate systems in the future.
RCMs are used to simulate climate over a specific region, as opposed to global simulations created by GCMs. Since climate in a specific region is affected by the rest of the earth, atmospheric conditions such as temperature and moisture at the region's boundary are estimated by using other sources such as GCMs or reanalysis data.
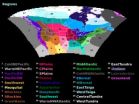
By combining information from multiple observation-based data sets, GCMs and RCMs, the model obtains an estimate and measure of uncertainty for the average temperature, temporal trend, as well as the variability of seasonal average temperatures. The model was used to analyze average summer and winter temperatures for the Pacific Southwest, Prairie and North Atlantic regions (seen in the image above)—regions that represent three distinct climates. The assumption would be that climate models would behave differently for each of these regions. Data from each region was considered individually so that the model could be fit to each region separately.
"Our understanding of how much temperatures are changing is reflected in all the data available to us," says Heaton. "For example, one data source might suggest that temperatures are increasing by 2 degrees Celsius while another source suggests temperatures are increasing by 4 degrees. So, do we believe a 2-degree increase or a 4-degree increase? The answer is probably 'neither' because combining data sources together suggests that increases would likely be somewhere between 2 and 4 degrees. The point is that that no single data source has all the answers. And, only by combining many different sources of climate data are we really able to quantify how much we think temperatures are changing."
While most previous such work focuses on mean or average values, the authors in this paper acknowledge that climate in the broader sense encompasses variations between years, trends, averages and extreme events. Hence the hierarchical Bayesian model used here simultaneously considers the average, linear trend and interannual variability (variation between years). Many previous models also assume independence between climate models, whereas this paper accounts for commonalities shared by various models—such as physical equations or fluid dynamics—and correlates between data sets.
"While our work is a good first step in combining many different sources of climate information, we still fall short in that we still leave out many viable sources of climate information," says Heaton. "Furthermore, our work focuses on increases/decreases in temperatures, but similar analyses are needed to estimate consensus changes in other meteorological variables such as precipitation. Finally, we hope to expand our analysis from regional temperatures (say, over just a portion of the U.S.) to global temperatures."
INFORMATION:
To read other SIAM Nuggets, explaining current high level research involving applications of mathematics in popular science terms, go to http://connect.siam.org/category/siam-nuggets/.
Source article:
Modeling Uncertainty in Climate Using Ensembles of Regional and Global Climate Models and Multiple Observation-Based Data Sets
Matthew J. Heaton, Tamara A. Greasby, and Stephan R. Sain
SIAM/ASA Journal on Uncertainty Quantification, 1(1), 535-559 (Online publish date: December 17, 2013). The source article is available for free access at the link below through December 31, 2014:
http://epubs.siam.org/doi/abs/10.1137/12088505X
About the authors:
Matthew Heaton is currently an assistant professor in the department of statistics at Brigham Young University, but the majority of this work was done while the author was a postgraduate scientist at the National Center for Atmospheric Research. Tamara Greasby is a postdoctoral researcher and Stephan Sain is a scientist at the Institute for Mathematics Applied to the Geosciences (IMAGe) at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR).
Statistics research could build consensus around climate predictions
2014-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Smellizing -- imagining a product's smell -- increases consumer desire, study finds
2014-02-19
Seeing is believing, but smellizing – a new term for prompting consumers to imagine the smell of a product – could be the next step toward more effective advertising.
Researchers came to this conclusion through four studies of products most of us would like to smellize: cookies and cake.
Professor of Marketing Maureen Morrin of Temple University's Fox School of Business co-authored Smellizing Cookies and Salivating: A Focus on Olfactory Imagery to examine the impact imagining what a food smells like would have on consumer behavior.
"Before we started this project, ...
Discovery by Baylor University researchers sheds new light on the habitat of early apes
2014-02-19
WACO, Texas (Feb. 18, 2014)-- Baylor University researchers, in collaboration with an international team of scientists, have discovered definitive evidence of the environment inhabited by the early ape Proconsul on Rusinga Island, Kenya. The groundbreaking discovery provides additional information that will help scientists understand and interpret the connection between habitat preferences and the early diversification of the ape-human lineage.
Their research findings--published this month in Nature Communications--demonstrate that Proconsul and its primate relative Dendropithecus ...
Graduate student makes major discovery about seal evolution
2014-02-19
Ottawa, February, 19, 2014—In the world of science, one of the most exciting things a researcher can do is pin down an answer to a widely asked question. This experience came early for Carleton University graduate Thomas Cullen, who made a discovery about pinnipeds—the suborder that makes up seals, sea lions and walruses—while doing research for his Master's degree under the supervision of Canadian Museum of Nature palaeontologist Dr. Natalia Rybczynski.
His discovery, published the journal Evolution, relates to sexual dimorphism (a large variance in size between males ...
Huntington's disease: Hot on the trail of misfolded proteins' toxic modus operandi
2014-02-19
WASHINGTON D.C. Feb. 19, 2014 -- Proteins are the workhorses of the cell, and their correctly folded three-dimensional structures are critical to cellular functions. Misfolded structures often fail to properly perform these vital jobs, leading to cellular stress and devastating neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's disease.
In comparison with the mysteries of Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease has a seemingly simple culprit: an expansion in the polyglutamine (polyQ) tract of a protein called "Huntingtin" (Htt). ...
Rutgers scientists identify structure of virus that could lead to hepatitis C vaccine
2014-02-19
Rutgers University scientists have determined the structure of a hepatitis C surface protein, a finding that could assist in the development of a vaccine to halt the spread of the the deadly disease that has infected 3.2 million Americans.
Joseph Marcotrigiano, associate professor of chemistry and chemical biology, says this new research – published online today in Nature – describes an outer region of hepatitis C that enables the virus to evade the body's natural immune system response, causing persistent, chronic infection.
Hepatitis C is constantly mutating, allowing ...
The ups and downs of early atmospheric oxygen
2014-02-19
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — A team of biogeochemists at the University of California, Riverside, give us a nontraditional way of thinking about the earliest accumulation of oxygen in the atmosphere, arguably the most important biological event in Earth history.
A general consensus asserts that appreciable oxygen first accumulated in Earth's atmosphere around 2.3 billion years ago during the so-called Great Oxidation Event (GOE). However, a new picture is emerging: Oxygen production by photosynthetic cyanobacteria may have initiated as early as 3 billion years ago, with oxygen ...
NuSTAR telescope takes first peek into core of supernova
2014-02-19
Astronomers for the first time have peered into the heart of an exploding star in the final minutes of its existence.
The feat is one of the primary goals of NASA's NuSTAR mission, launched in June 2012 to measure high-energy X-ray emissions from exploding stars, or supernovae, and black holes, including the massive black hole at the center of our Milky Way Galaxy.
The NuSTAR team reported in this week's issue of the journal Nature the first map of titanium thrown out from the core of a star that exploded in 1671. That explosion produced the beautiful supernova remnant ...
Managed honeybees linked to new diseases in wild bees
2014-02-19
Diseases that are common in managed honeybee colonies are now widespread in the UK's wild bumblebees, according to research published in Nature. The study suggests that some diseases are being driven into wild bumblebee populations from managed honeybees.
Dr Matthias Fürst and Professor Mark Brown from Royal Holloway University of London (who worked in collaboration with Dr Dino McMahon and Professor Robert Paxton at Queen's University Belfast, and Professor Juliet Osborne working at Rothamsted Research and the University of Exeter) say the research provides vital information ...
Gene sequencing project discovers common driver of a childhood brain tumor
2014-02-19
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – February 19, 2014) The St. Jude Children's Research Hospital-Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome Project has identified the most common genetic alteration ever reported in the brain tumor ependymoma and evidence that the alteration drives tumor development. The research appears February 19 as an advanced online publication in the scientific journal Nature.
The results provide a foundation for new research to improve diagnosis and treatment of ependymoma, the third most common brain tumor in children. St. Jude has begun work to translate the ...
Managing chronic bone and joint pain
2014-02-19
ROSEMONT, Ill.—Musculoskeletal pain of the bone, joint and muscles is one of the most common reasons for primary care visits in the United States. According to a literature review appearing in a recent issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (JAAOS), chronic pain, or pain that persists beyond an expected period of healing, is estimated to affect 100 million Americans.
The majority of chronic pain complaints concern the musculoskeletal system, but they also include headaches and abdominal pain. "As orthopaedic surgeons, we are experts in the ...