(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
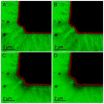
Zoom into the cloudy heart of an active galaxy. This animation shows an artist's rendition of the cloudy structure revealed by a study of data from NASA's Rossi X-Ray Timing...
Click here for more information.
Picture a single cloud large enough to span the solar system from the sun to beyond Pluto's orbit. Now imagine many such clouds orbiting in a vast ring at the heart of a distant galaxy, occasionally dimming the X-ray light produced by the galaxy's monster black hole.
Using data from NASA's Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE) satellite, an international team has uncovered a dozen instances where X-ray signals from active galaxies dimmed as a result of a cloud of gas moving across our line of sight. The new study triples the number of cloud events previously identified in the 16-year archive.
At the hearts of most big galaxies, including our own Milky Way, there lurks a supermassive black hole weighing millions to billions of times the sun's mass. As gas falls toward a black hole, it gathers into a so-called accretion disk and becomes compressed and heated, ultimately emitting X-rays. The centers of some galaxies produce unusually powerful emission that exceeds the sun's energy output by billions of times. These are active galactic nuclei, or AGN.
"One of the great unanswered questions about AGN is how gas thousands of light-years away funnels into the hot accretion disk that feeds the supermassive black hole," said Alex Markowitz, an astrophysicist at the University of California, San Diego and the Karl Remeis Observatory in Bamberg, Germany. "Understanding the size, shape and number of clouds far from the black hole will give us a better idea of how this transport mechanism operates."
The study is the first statistical survey of the environments around supermassive black holes and is the longest-running AGN-monitoring study yet performed in X-rays. In the paper, which will appear in a future issue of Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society and is now published online, the scientists describe various properties of the occulting clouds, which vary in size and shape but average 4 billion miles (6.5 billion km) across – greater than Pluto's distance from the sun -- and twice the mass of Earth. They orbit a few light-weeks to a few light-years from the black hole.
RXTE's instruments measured variations in X-ray emission on timescales as short as microseconds and as long as years across a wide energy span, from 2,000 to 250,000 electron volts. For comparison, the energy of a typical dental X-ray is around 60,000 electron volts. NASA decommissioned the observatory in 2012, following 16 years of successful operation in Earth orbit.
"Because RXTE performed sustained observations of many of these AGN, our research is sensitive to a wide range of cloud events, from those as brief as five hours to as long as 16 years," said co-author Robert Nikutta, a theorist at Andrés Bello University in Santiago, Chile.
For decades, astronomers explained the different observed properties of AGN by suggesting that a relatively uniform "doughnut" of dust and gas surrounds the black hole and extends several light-years away from it. Interference from this material is lowest when we happen to be looking into the doughnut from above or below and greatest when we view it from the side. Now astronomers are moving toward a new generation of models that view the doughnut as a collection of many individual clouds mostly distributed along its central plane, a view supported by the RXTE study.
One of the more unusual events the team turned up occurred in NGC 3783, a barred spiral galaxy located 143 million light-years away toward the constellation Centaurus. "In 2008, the AGN dimmed twice over a period of 11 days and did not reach its typical X-ray brightness within that period," said co-author Mirko Krumpe of the European Southern Observatory in Garching, Germany. "This could be caused by an elongated, filamentary cloud, perhaps one that is in the process of being torn apart by the black hole."
INFORMATION:
RXTE reveals the cloudy cores of active galaxies
2014-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NuSTAR helps untangle how stars explode
2014-02-19
For the first time, an international team of astrophysicists, including Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists, have unraveled how stars blow up in supernova explosions.
Using NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) – a high-energy X-ray observatory - the international collaboration created the first-ever map of radioactive material in a supernova remnant, named Cassiopeia A, or Cas A for short. The findings reveal how shock waves likely rip apart massive dying stars, and ultimately end their lives.
A supernova is the cataclysmic death of a ...
REACT clinical trial supports new approach of accelerated treatment for Crohn's disease
2014-02-19
The final results from an international clinical trial involving nearly 2,000 patients with Crohn's disease support the use of a new management strategy referred to as accelerated step-care as a best practice for the care of active Crohn's disease. The REACT (Randomized Evaluation of an Algorithm for Crohn's Treatment) study, led by Robarts Clinical Trials at Western University (London, Canada) provides valuable new insights for community gastroenterologists which should benefit patients. The results of the study will be presented at the European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation ...
ORNL microscopy system delivers real-time view of battery electrochemistry
2014-02-19
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Feb. 19, 2014 -- Using a new microscopy method, researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory can image and measure electrochemical processes in batteries in real time and at nanoscale resolution.
Scientists at ORNL used a miniature electrochemical liquid cell that is placed in a transmission electron microscope to study an enigmatic phenomenon in lithium-ion batteries called the solid electrolyte interphase, or SEI, as described in a study published in Chemical Communications.
The SEI is a nanometer-scale film that forms ...
Many Texans struggling to pay for health service as Affordable Care Act is about to launch
2014-02-19
HOUSTON – (Feb. 19, 2014) – Many Texans were struggling to pay for basic health services on the eve of the launch of the Affordable Care Act's Health Insurance Marketplace, according to a report released today by Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy and the Episcopal Health Foundation. The report also found that even those with health insurance reported dissatisfaction with the cost and availability of services. Most Texans expect more of the same in 2014.
The Health Reform Monitoring Survey (HRMS)-Texas report is based on the HRMS, a national project that ...
Molecular aberration signals cancer
2014-02-19
Several scientists, including one at Simon Fraser University, have made a discovery that strongly links a little understood molecule, which is similar to DNA, to cancer and cancer survival.
EMBO Reports, a life sciences journal published by the European Molecular Biology Organization, has just published online the scientists' findings about small non-coding RNAs.
While RNA is known to be key to our cells' successful creation of proteins, the role of small non-coding RNAs, a newly discovered cousin of the former, has eluded scientific understanding for the most part. ...
Cell therapy shows remarkable ability to eradicate cancer in clinical study
2014-02-19
NEW YORK, February 19, 2014 — Investigators from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center have reported more encouraging news about one of the most exciting methods of cancer treatment today. The largest clinical study ever conducted to date of patients with advanced leukemia found that 88 percent achieved complete remissions after being treated with genetically modified versions of their own immune cells. The results were published today in Science Translational Medicine.
"These extraordinary results demonstrate that cell therapy is a powerful treatment for patients who ...
LGBT youth face greater cancer risks, CCNY-led study
2014-02-19
A new study led by City College of New York psychologist Margaret Rosario found that youths of same-sex orientation are more likely to engage in behaviors associated with cancer risk than heterosexuals. The peer-reviewed findings appear in the February 2014 issue of the American Journal of Public Health.
Titled "Sexual Orientation Disparities in Cancer-Related Risk Behaviors of Tobacco, Alcohol, Sexual Behaviors, and Diet and Physical Activity: Pooled Youth Risk Behavior Surveys," the study pooled YRBS (Youth Risk Behavior Survey) data from 2005 and 2007. The YRBS is ...
Using holograms to improve electronic devices
2014-02-19
RIVERSIDE, Calif. (http://www.ucr.edu) — A team of researchers from the University of California, Riverside Bourns College of Engineering and Russian Academy of Science have demonstrated a new type of holographic memory device that could provide unprecedented data storage capacity and data processing capabilities in electronic devices.
The new type of memory device uses spin waves – a collective oscillation of spins in magnetic materials – instead of the optical beams. Spin waves are advantageous because spin wave devices are compatible with the conventional electronic ...
Statistics research could build consensus around climate predictions
2014-02-19
Philadelphia, PA—Vast amounts of data related to climate change are being compiled by research groups all over the world. Data from these many and various sources results in different climate projections; hence, the need arises to combine information across data sets to arrive at a consensus regarding future climate estimates.
In a paper published last December in the SIAM Journal on Uncertainty Quantification, authors Matthew Heaton, Tamara Greasby, and Stephan Sain propose a statistical hierarchical Bayesian model that consolidates climate change information ...
Smellizing -- imagining a product's smell -- increases consumer desire, study finds
2014-02-19
Seeing is believing, but smellizing – a new term for prompting consumers to imagine the smell of a product – could be the next step toward more effective advertising.
Researchers came to this conclusion through four studies of products most of us would like to smellize: cookies and cake.
Professor of Marketing Maureen Morrin of Temple University's Fox School of Business co-authored Smellizing Cookies and Salivating: A Focus on Olfactory Imagery to examine the impact imagining what a food smells like would have on consumer behavior.
"Before we started this project, ...