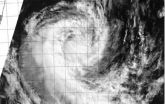
(Press-News.org) NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Cyclone Guito as it exited the Mozambique Channel and moved into the open waters of the Southern Indian Ocean.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Cyclone Guito on Feb. 21 at 07:05 UTC/2:05 a.m. EST and took a visible image of the storm exiting the Mozambique Channel. The image showed bands of thunderstorms were still wrapping around the western quadrant of the storm.
At 0900 UTC/4 a.m. EST, Guito still had maximum sustained winds near 60 knots/69.0 mph/111.1 kph. It was located just south of the Mozambique Channel (the waterway between Mozambique and the island nation of Madagascar. Guito had moved into the open waters of the Southern Indian Ocean and was moving south at 12 knots/13.8 mph/22.2 kph.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that animated multispectral satellite imagery also showed a tightly-wrapped, partially-exposed low-level circulation center. The strongest thunderstorms were located over the western and southern quadrants. Microwave satellite imagery showed an eye feature still existed.
Guito is expected to drift south and start to weaken on Feb. 22, becoming extra-tropical over the next several days.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Guito exit the Mozambique Channel
2014-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Current ice melt rate in Pine Island Glacier may go on for decades
2014-02-21
A study of the Pine Island Glacier could provide insight into the patterns and duration of glacial melt.
The Pine Island Glacier, a major outlet of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, has been undergoing rapid melting and retreating for the past two decades. But new research by an international team including researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory shows that this same glacier also experienced rapid thinning about 8,000 years ago.
Using LLNL's Center for Accelerator Mass Spectrometry to measure beryllium-10 produced by cosmic rays in glacially transported ...
Will plug-in cars crash the electric grid?
2014-02-21
Selecting a Chevy Volt, Tesla Model S, Nissan Leaf — or one of many other new models — shoppers in the United States bought more than 96,000 plug-in electric cars in 2013. That's a tiny slice of the auto market, but it's up eighty-four percent from the year before. By 2020, the International Energy Agency forecasts, there will be 20 million electric vehicles on the world's roads, many of them plug-ins.
This is good news in terms of oil consumption and air pollution. But, of course, every plug-in has to be, well, plugged in. And this growing fleet will put a lot of new ...
Reducing HIV transmission among drug injectors lowers AIDS mortality in heterosexuals
2014-02-21
Although community network studies show that sexual relationships occur between members of "risk groups" -- men who have sex with other men (MSM), people who inject drugs (PWID), non-injection drug users (NIDU) -- and heterosexuals, researchers at New York University's Center for Drug Use and HIV Research (CDUHR) note that little research has been done to help explain how HIV epidemics and programs in one population affect others and how to reduce the risks of transmission.
A recent study conducted by researchers from CDUHR, led by Samuel R. Friedman, Director of both ...
Promising cervical cancer study
2014-02-21
(Phoenix , Ariz. Feb 21, 2014) -- Research on cervical cancer performed by a physician at the University of Arizona Cancer Center at St. Joseph's Hospital and Medical Center has been published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The multi-site research project by Bradley J. Monk, MD, is expected to change the standard of care for women with advanced cervical cancer.
The featured research revealed that women with advanced cervical cancer live about four months longer with the combined use of bevacizumab (Avastin®) and chemotherapy compared to chemotherapy alone. ...
Tracking catalytic reactions in microreactors
2014-02-21
A pathway to more effective and efficient synthesis of pharmaceutical drugs and other flow reactor chemical products has been opened by a study in which for the first time the catalytic reactivity inside a microreactor was mapped in high resolution from start-to-finish. The results not only provided a better understanding of the chemistry behind the catalytic reactions, they also revealed opportunities for optimization, which resulted in better catalytic performances. The study was conducted by a team of scientists with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley ...
Air Force aircraft returned from Vietnam identified as postwar source of Agent Orange contamination
2014-02-21
Amsterdam, February 21, 2014 – From 1971-1982 Air Force reservists, who flew in about 34 dioxin-contaminated aircraft used to spray Agent Orange and returned to the US following discontinuation of the herbicide spraying operations in the Vietnam War, were exposed greater levels of dioxin than previously acknowledged, according to a study published today in Environmental Research.
"These findings are important because they describe a previously unrecognized source of exposure to dioxin that has health significance to those who engaged in the transport work using these ...
Kessler Foundation MS researchers find task meaningfulness influences learning and memory
2014-02-21
West Orange, NJ. February 21, 2014. Kessler Foundation researchers have found that among persons with multiple sclerosis, self-generation may be influenced by variables such as task meaningfulness during learning and memory. They also found that type of task (functional versus laboratory) had a significant effect on memory.
This is the first controlled investigation of therapeutic and patient-specific factors that supports the inclusion of self-generation in cognitive rehabilitation. The study was published in the January issue of Neuropsychological Rehabilitation: An ...
If you think you have Alzheimer's, you just might be right, study suggests
2014-02-21
Lexington, Ky. -- (Feb. 20, 2014) -- a recent study suggests that self-reported memory complaints might predict clinical memory impairment later in life.
Erin Abner, Ph.D, an assistant professor at the University of Kentucky's Sanders-Brown Center on Aging, asked 3,701 men aged 60 and higher a simple question: "Have you noticed any change in your memory since you last came in?"
That question led to some interesting results. "It seems that subjective memory complaint can be predictive of clinical memory impairment," Abner said. "Other epidemiologists have seen similar ...
Researchers look to reduce hep C infections for injecting drug user
2014-02-21
Despite a number of social/behavioral intervention and educational programs, the spread of hepatitis C (HCV) in people who inject drugs (PWIDs) remains a chronic problem. Now, researchers affiliated with New York University's Center for Drug Use and HIV Research (CDUHR) are focusing on intervention strategies that highlight the lesser-known dangers of HCV transmission through the sharing of other injection equipment such as cookers, filters, drug-dilution water and water containers.
Their article, "The Staying Safe Intervention: Training People Who Inject Drugs in ...
Optimizing custody is child's play for physicists
2014-02-21
Physics can provide insights into societal trends. Problems involving interactions between people linked in real-life networks can be better understood by using physical models. As a diversion from his normal duties as a theoretical physicist, Andrés Gomberoff from the Andres Bello University in Santiago, Chile, set out to resolve one of his real-life problems: finding a suitable weekend for both partners in his recomposed family to see all their children at the same time. He then joined forces with a mathematician and a complex systems expert. This resulted in a study ...