(Press-News.org) Most of us draw roughly 25,000 breaths a day without any thought. But for patients with pulmonary hypertension, a life-threatening increase in blood pressure in the lungs, even the smallest task can leave them gasping for air. A new study by researchers at Yale School of Medicine offers insight into the function of cells linked to this incurable and often fatal illness.
Published Feb. 27 in Cell Reports, the study is the first to explore the cellular mechanisms behind the changes in the way cells are organized in pulmonary arteries in pulmonary hypertension, which leaves patients short of breath and fatigued, and ultimately results in heart failure and death. Almost half of patients die within three years of diagnosis.
Up until now, these mechanisms were not well understood, leaving clinicians with little guidance on how to prevent or reverse them. Scientists believe the fate of these patients could be improved if treatments were designed to address the abnormal changes in the pulmonary artery structure.
"For the first time, we understand which cells are responsible and the cellular processes underlying their recruitment," said senior author Daniel Greif, M.D., assistant professor of internal medicine (cardiology), who conducted the study with Yale colleagues Abdul Sheikh and Janet Lighthouse. "We looked at the mechanism involved in how these cells migrate along blood vessels."
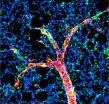
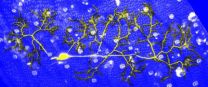
Excess smooth muscle accumulation is a key component of pulmonary hypertension and other vascular disorders such as atherosclerosis. Vascular structures in the lung have patterns reminiscent of tree branches, and the smallest blood vessels normally lack a muscular coating; however, in pulmonary hypertension they become muscularized.
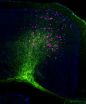
Greif and colleagues used genetic tools to map the fate of smooth muscle cells in mice with pulmonary hypertension. They focused on specific small vessels and determined that the smooth muscle coating comes from smooth muscle cells of larger vessels. "We also discovered the process by which smooth muscle cells differentiate, migrate to small blood vessels, and then re-differentiate, thereby muscularizing vessels that normally lack a smooth muscle cell coating," said Greif.
"Now that the culprit cell population in pulmonary hypertension is identified, we can turn our attention to tailoring therapies to target these cell," he added.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded in part by a Senior Research Fellowship from the American Lung Association; the National Institute of Health under the Ruth L. Kirschstein NRSA Institutional Training Grant (2T32HL007950); the March of Dimes (Basil O'Connor Award, 5-FY13-208); the Pulmonary Hypertension Association (Clinical Scientist Development Award); and National Institute of Health (5K08HL093362, and CTSA 5UL1RR024139-08 through the National Center for Advancing Translational Science (NCATS).
Citation: Cell Reports doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.01.042 (Feb. 27, 2014)
Yale study provides a breath of hope for pulmonary hypertension patients
2014-02-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Internal logic: 8 distinct subnetworks in mouse cerebral cortex
2014-02-27
The mammalian cerebral cortex, long thought to be a dense single interrelated tangle of neural networks, actually has a "logical" underlying organizational principle, reveals a study appearing Feb. 27 in the journal Cell.
Researchers have identified eight distinct neural subnetworks that together form the connectivity infrastructure of the mammalian cortex, the part of the brain involved in higher-order functions such as cognition, emotion and consciousness.
"This study is the first comprehensive mapping of the most developed region of the mammalian brain: the cerebral ...
New discovery paves the way for medicine for people with hearing disabilities
2014-02-27
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have identified a biological circadian clock in the hearing organ, the cochlea. This circadian clock controls how well hearing damage may heal and opens up a new way of treating people with hearing disabilities.
Important body functions, such as sleep, the immune system, and hormone levels are controlled by a biological circadian clock. A team of researchers at Karolinska Institutet have now discovered that there is also a biological clock in the ear, controlled by genes known to regulate circadian rhythms. One of these ...
Disease-causing bacterial invaders aided by failure of immune system switch
2014-02-27
Immune system defenses against dangerous bacteria in the gut can be breached by turning off a single molecular switch that governs production of the protective mucus lining our intestinal walls, according to a study led by researchers at Yale, the University of British Columbia, and the Weizmann Institute of Science.
"This gut microbiota has been linked to the inflammation that triggers obesity, diabetes, metabolic disease, and most of chronic health problems of the Western World," said Yale's Richard Flavell, Sterling Professor of Immunobiology, Howard Hughes Medical ...
Fruit fly's pruning protein could be key to treating brain injury
2014-02-27
DURHAM, NC -- A protein that controls the metamorphosis of the common fruit fly could someday play a role in reversing brain injuries, said Duke University researchers.
This protein directs both the early development and regrowth of the tiny branches that relay information from neuron to neuron. Known as dendrites, these thin structures that resemble tree branches are responsible for receiving electrical impulses that flash throughout the body.
Incorrect dendrite development or injury has been linked to neurodevelopmental or psychiatric diseases in humans, such as autism, ...
An ancient 'Great Leap Forward' for life in the open ocean
2014-02-27
It has long been believed that the appearance of complex multicellular life towards the end of the Precambrian (the geologic interval lasting up until 541 million years ago) was facilitated by an increase in oxygen, as revealed in the geological record. However, it has remained a mystery as to why oxygen increased at this particular time and what its relationship was to 'Snowball Earth' – the most extreme climatic changes the Earth has ever experienced – which were also taking place around then.
This new study shows that it could in fact be what was happening to nitrogen ...
Discoveries point to more powerful cancer treatments, fewer side effects
2014-02-27
What if there were a way to make chemotherapy and radiation more effective as cancer treatments than they are today, while also getting rid of debilitating side effects that patients dread? A new study led by Alexey Ryazanov, a professor of pharmacology at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School and member of the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey, suggests the day that happens could be getting closer.
Side effects such as heart damage, nausea and hair loss occur when cancer therapy kills healthy cells along with the malignant cells that are being targeted. It ...
A world free from cancers: Probable, possible, or preposterous?
2014-02-27
ALEXANDRIA, Va. – February 27, 2014 – A panel of leading health, economics and policy experts today discussed the prospects for a future where cancers are rendered manageable or even eradicated and the variables affecting progress toward that goal so that cancer patients are able to lead normal, productive lives – and thus be "free from" their cancers. The forum was hosted by Research!America and the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. The event, titled, "A World Free from Cancers: Probable, Possible, or Preposterous?" was held at the New York Academy of Sciences.
Medical ...
Math anxiety factors into understanding genetically modified food messages
2014-02-27
People who feel intimidated by math may be less able to understand messages about genetically modified foods and other health-related information, according to researchers.
"Math anxiety, which happens when people are worried or are concerned about using math or statistics, leads to less effort and decreases the ability to do math," said Roxanne Parrott, Distinguished Professor of Communication Arts and Sciences and Health Policy and Administration. "Math anxiety also has been found to impair working memory."
The researchers found that math anxiety led to a decrease ...
Google Glass could help stop emerging public health threats around the world
2014-02-27
The much-talked-about Google Glass — the eyewear with computer capabilities — could potentially save lives, especially in isolated or far-flung locations, say scientists. They are reporting development of a Google Glass app that takes a picture of a diagnostic test strip and sends the data to computers, which then rapidly beam back a diagnostic report to the user. The information also could help researchers track the spread of diseases around the world. The study appears in the journal ACS Nano, a publication of the American Chemical Society, the world's largest scientific ...
Faster anthrax detection could speed bioterror response
2014-02-27
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Shortly following the 9/11 terror attack in 2001, letters containing anthrax spores were mailed to news outlets and government buildings killing five people and infecting 17 others. According to a 2012 report, the bioterrorism event cost $3.2 million in cleanup and decontamination. At the time, no testing system was in place that officials could use to screen the letters. Currently, first responders have tests that can provide a screen for dangerous materials in about 24-48 hours. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have worked with a private ...