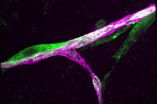
(Press-News.org) A team of French investigators has discovered viruses containing genes for antibiotic resistance in a fossilized fecal sample from 14th century Belgium, long before antibiotics were used in medicine. They publish their findings ahead of print in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
"This is the first paper to analyze an ancient DNA viral metagenome," says Rebecca Vega Thurber of Oregon State University, Corvallis, who was not involved in the research.
The viruses in the fecal sample are phages, which are viruses that infect bacteria, rather than infecting eukaryotic organisms such as animals, plants, and fungi. Most of the viral sequences the researchers found in the ancient coprolite (fossil fecal sample) were related to viruses currently known to infect bacteria commonly found in stools (and hence, in the human gastrointestinal tract), including both bacteria that live harmlessly, and even helpfully in the human gut, and human pathogens, says corresponding author Christelle Desnues of Aix Marseille Université.
The communities of phage within the coprolite were different, taxonomically, from communities seen within modern human fecal samples, but the functions they carry out appear to be conserved, says Desnues. That reinforces the hypothesis that the viral community plays a fundamental role within the human gastrointestinal tract, and one which remains unchanged after centuries, even while the human diet and other human conditions have been changing.
Over the last five years, considerable evidence has emerged that bacteria inhabiting the gut play an important role in maintaining human health, for example, as part of the human metabolic system, says Desnues. Her own research suggests that the bacteriophage infecting the gut bacteria may help maintain these bacteria. Among the genes found in the phage are antibiotic resistance genes and genes for resistance to toxic compounds. Both toxins and antibiotics are common in nature, and Desnues suggests that the resistance genes may simply be protecting the gut bacteria from them.
"Our evidence demonstrates that bacteriophages represent an ancient reservoir of resistance genes and that this dates at least as far back as the Middle Ages," says Desnues.
"We were interested in viruses because these are 100 times more abundant than human cells in our bodies, but their diversity is still largely unexplored," says Desnues. "In the present study, we thus focused on the viral fraction of the coprolite by using, for the first time, a combination of electron microscopy, high-throughput sequencing and suicide PCR approaches."
Desnues and her collaborators are currently conducting further studies on the fungi and parasites in the coprolites, which she says will be of interest not only to microbiologists, but to historians, anthropologists, and evolutionists.
The genesis of the research was an urban renewal project in the city of Namur, Belgium, in which latrines dating back to the 1300s were discovered beneath a square.
INFORMATION:
A copy of the manuscript can be found online at http://bit.ly/asmtip0214g. The final version of the article is scheduled for the May 2014 issue of Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
Applied and Environmental Microbiology is a publication of the American Society for Microbiology (ASM). The ASM is the largest single life science society, composed of over 39,000 scientists and health professionals. Its mission is to advance the microbiological sciences as a vehicle for understanding life processes and to apply and communicate this knowledge for the improvement of health and environmental and economic well-being worldwide.
Fossilized human feces from 14th century contain antibiotic resistance genes
2014-02-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Physicians' stethoscopes more contaminated than palms of their hands
2014-02-27
VIDEO:
A comparative analysis shows that stethoscope diaphragms are more contaminated than the physician's own thenar eminence (group of muscles in the palm of the hand) following a physical examination.
Click here for more information.
Rochester, MN, February 27, 2014 – Although healthcare workers' hands are the main source of bacterial transmission in hospitals, physicians' stethoscopes appear to play a role. To explore this question, investigators at the University of ...
Study reveals mechanisms cancer cells use to establish metastatic brain tumors
2014-02-27
NEW YORK, NY, February 27, 2014 — New research from Memorial Sloan Kettering provides fresh insight into the biologic mechanisms that individual cancer cells use to metastasize to the brain. Published in the February 27 issue of Cell, the study found that tumor cells that reach the brain — and successfully grow into new tumors — hug capillaries and express specific proteins that overcome the brain's natural defense against metastatic invasion.
Metastasis, the process that allows some cancer cells to break off from their tumor of origin and take root in a different tissue, ...
Methane leaks from palm oil wastewater are a climate concern, CU-Boulder study says
2014-02-27
In recent years, palm oil production has come under fire from environmentalists concerned about the deforestation of land in the tropics to make way for new palm plantations. Now there is a new reason to be concerned about palm oil's environmental impact, according to researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder.
An analysis published Feb. 26 in the journal Nature Climate Change shows that the wastewater produced during the processing of palm oil is a significant source of heat-trapping methane in the atmosphere. But the researchers also present a possible solution: ...
Famed Milwaukee County Zoo orangutan's death caused by strange infection
2014-02-27
MADISON – Mahal, the young orangutan who became a star of the Milwaukee County Zoo and an emblem of survival for a dwindling species, led an extraordinary life.
It turns out, the young ape died an extraordinary death, too.
Rejected by his biological mother at the Cheyenne Mountain Zoo in Colorado Springs, Colo., and eventually flown to Milwaukee aboard a private jet to live with a surrogate mother, Mahal became one of the Milwaukee County Zoo's star attractions. His unexpected death at age 5 in late December 2012 was a shock to the community that came to know him through ...
Scientists describe deadly immune 'storm' caused by emergent flu infections
2014-02-27
LA JOLLA, CA—February 26, 2014—Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have mapped key elements of a severe immune overreaction—a "cytokine storm"—that can both sicken and kill patients who are infected with certain strains of flu virus.
Their findings, published in this week's online Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, also clarify the workings of a potent new class of anti-inflammatory compounds that prevent this immune overreaction in animal models.
"We show that with this type of drug, we can quiet the storm enough to ...
Livestock found ganging up on pandas at the bamboo buffet
2014-02-27
VIDEO:
A panda in the Wolong Nature Reserve munches on bamboo -- which comprises 99 percent of the endangered species' diet in the wild.
Click here for more information.
Pandas, it turns out, aren't celebrating the Year of the Horse.
Livestock, particularly horses, have been identified as a significant threat to panda survival. The reason: They're beating the pandas to the bamboo buffet. A paper by Michigan State University panda habitat experts published in this week's Journal ...
Making treatment of rare blood disorder more affordable and effective
2014-02-27
PHILADELPHIA — A University of Pennsylvania research team has defined a possible new way to fight a disease that is currently treatable only with the most expensive drug available for sale in the United States. In a study published this month in Blood, the Penn team describes the strategy, based on the oldest part of the human immune system – called "complement" -- that could turn out to be less costly and more effective for the majority of patients with a rare blood disorder.
Complement is a network of more than 50 proteins in the blood and on cell surfaces that quietly ...
International study shows majority of children unaware of cigarette warning labels
2014-02-27
College Park, Md. -- An international study of children's perceptions of cigarette package warning labels found that the majority of children are unaware that they exist. Children in countries where larger warning labels are used, and which include a compelling graphic image of the negative health impacts of smoking, were more likely to be aware of and understand the health risks of tobacco products.
The study, led by Dina Borzekowski, Ed.D, in the University of Maryland School of Public Health (UMD SPH), and Joanna Cohen, PhD, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public ...
AGU: A 'shark's eye' view: Witnessing the life of a top predator
2014-02-27
HONOLULU – Instruments strapped onto and ingested by sharks are revealing novel insights into how one of the most feared and least understood ocean predators swims, eats and lives.
For the first time, researchers at the University of Hawaii and the University of Tokyo outfitted sharks with sophisticated sensors and video recorders to measure and see where they are going, how they are getting there, and what they are doing once they reach their destinations. (Go to http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UHDOAmXRw-0&feature=youtu.be for video).
Scientists are also piloting ...
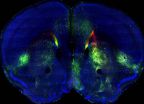
Mouse brain atlas maps neural networks to reveal how brain regions interact
2014-02-27
Different brain regions must communicate with each other to control complex thoughts and behaviors, but relatively little is known about how these areas organize into broad neuronal networks. In a study published by Cell Press February 27th in the journal Cell, researchers developed a mouse whole-brain atlas that reveals hundreds of neuronal pathways in a brain structure called the cerebral cortex. The online, open access, interactive image database, called the Mouse Connectome Project, provides an invaluable resource for researchers interested in studying the anatomy and ...