(Press-News.org) Identification of factors that influence breast cancer metastasis to bone
One of the more serious and frequent complications of advanced breast cancer is bone metastasis, which is exacerbated by TGF-β signaling; however, it is not clear how TGF-β production is regulated prior to and during metastasis. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Guohong Hu and colleagues at the Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences evaluated murine models of invasive breast cancer and determined that cancer cells lacking the putative tumor suppressor DLC1 have a greater propensity toward infiltrating bone, while overexpression of DLC1 inhibited bone colonization. DLC1 knockdown increased TGF-β signaling, resulting in elevated levels of parathyroid hormone-like hormone (PTHLH) and increased metastasis, and pharmacological inhibition of PTHLH production prevented spread to bone. Furthermore, evaluation of clinical breast tumor samples revealed a correlation between reduced DLC1, elevated PTHLH, and bone metastasis.
TITLE:
DLC1-dependent parathyroid hormone–like hormone inhibition suppresses breast cancer bone metastasis
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Guohong Hu
Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, , CHN
Phone: 86-21-63844516; E-mail: ghhu@sibs.ac.cn
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/71812
CELL BIOLOGY
TITLE:
Assembly of the cochlear gap junction macromolecular complex requires connexin 26
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Kazusaku Kamiya
Juntendo University Faculty of Medicine, Tokyo, JPN
Phone: +81-3-5802-1229; Fax; E-mail: kkamiya@juntendo.ac.jp
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/67621
TITLE:
Disrupting hedgehog and WNT signaling interactions promotes cleft lip pathogenesis
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Paul Trainor
Stowers Institute for Medical Research, Kansas City, MO, USA
Phone: 816-926-4414; E-mail: pat@stowers.org
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/72688
ONCOLOGY
TITLE:
SPARC promotes leukemic cell growth and predicts acute myeloid leukemia outcome
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Guido Marcucci
The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH, USA
Phone: 614-366-2261; E-mail: guido.marcucci@osumc.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/70921
TITLE:
SOX2 and p63 colocalize at genetic loci in squamous cell carcinomas
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Adam Bass
Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, USA
Phone: 6176322477; E-mail: Adam_Bass@dfci.harvard.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/71545
NEPHROLOGY
TITLE:
Endothelial mitochondrial oxidative stress determines podocyte depletion in segmental glomerulosclerosis
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Erwin Bottinger
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA
Phone: 212.241.0800; Fax: 212.849.2643 ; E-mail: erwin.bottinger@mssm.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/71195
NEUROSCIENCE
TITLE:
Dysregulation of ubiquitin homeostasis and β-catenin signaling promote spinal muscular atrophy
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Thomas Gillingwater
University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UNK, GBR
Phone: +44 131 6503724; E-mail: T.Gillingwater@ed.ac.uk
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/71318
PULMONOLOGY
TITLE:
Fibrotic extracellular matrix activates a pro-fibrotic positive feedback loop
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Matthew Parker
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA
Phone: 612-205-2514; E-mail: park0523@umn.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/71386
INFORMATION: END
JCI online ahead of print table of contents for March 3, 2014
2014-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Youngest kindergarteners most likely to be held back, MU study finds
2014-03-04
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- For some parents, the decision of when to enroll their children into kindergarten can result in costly consequences such as another year of daycare expenses. In general, children must be five years old to be eligible to be enrolled in kindergarten. However, the developmental differences between a young kindergartener who barely qualifies for the state-mandated age cutoff date compared to a child who is almost year older, may have implications. Now, a University of Missouri researcher has found that the youngest kindergartners are about five times more likely ...
UC research tests which nano system works best in killing cancer cells
2014-03-04
In current research related to improving cancer treatments, one promising area of research is the effort to find ways to selectively pinpoint and target cancer cells while minimizing effects on healthy cells.
In that effort, it's already been found in lab experiments that iron-oxide nanoparticles, when heated and then applied specifically to cancer cells, can kill those cells because cancer cells are particularly susceptible to changes in temperature. Increasing the temperature of cancer cells to over 43 degrees Celsius (about 109 degrees Fahrenheit) for a sufficient ...
The chemistry (and fascinating history) of pepper, the spice that changed the world
2014-03-04
WASHINGTON, March 3, 2014 — Pepper is one of the most plentiful condiments in the world today, but it used to be more valuable than gold. In the American Chemical Society's (ACS') latest Reactions video, we examine how pepper's delectable chemistry made it a key player in the global spice trade. The sought-after spice helped usher in the "Age of Discovery," which bridged the gap between the Middle Ages and the Modern era. And because we're celebrating our second month of existence, it's a Reactions double feature this week. In our second video, we examine the science behind ...
Team models photosynthesis and finds room for improvement
2014-03-04
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Teaching crop plants to concentrate carbon dioxide in their leaves could increase photosynthetic efficiency by 60 percent and yields by as much as 40 percent, researchers report in a new study.
The team used a computer model to simulate how adding genes from a type of photosynthetic algae known as cyanobacteria might influence photosynthetic efficiency in plants. Cyanobacteria contain small structures, called carboxysomes, which concentrate carbon dioxide at the site of photosynthesis.
"Photosynthesis is the most studied of all plant processes, so ...
Scientists identify protein linked to most common movement disorder
2014-03-04
Quebec City, March 3rd, 2014—A team of researchers from Université Laval and CHU de Québec identified unusually high levels of a certain protein in the brains of people suffering from essential tremor (ET), a movement disorder that affects 4% of the adult population. The discovery, the details of which were published in the most recent edition of the journal Movement Disorders, could lead to an effective treatment for this neurological condition, which is 10 times more prevalent than Parkinson's disease.
As its name suggests, ET causes tremors in various parts of the ...
UC research tests range of electrical frequencies that help heal chronic wounds
2014-03-04
Naturally occurring electricity in our cells is key to how our bodies function, and that includes the healing of wounds.
And externally applied low-amplitude electric fields have been shown to help hard-to-heal chronic wounds, like those associated with diabetes, where there is insufficient blood supply and drug treatments are not effective. The externally applied electric field manipulates the body's naturally occurring electricity, such that the new vessels are formed, and blood supply to the wound is increased.
University of Cincinnati physics and biomedical engineering ...
Cigarette smoking may cause physical changes in brains of young smokers, UCLA study shows
2014-03-04
The young, it turns out, smoke more than any other age group in America. Unfortunately, the period of life ranging from late adolescence to early adulthood is also a time when the brain is still developing.
Now, a small study from UCLA suggests a disturbing effect: Young adult smokers may experience changes in the structures of their brains due to cigarette smoking, dependence and craving. Even worse, these changes can occur in those who have been smoking for relatively short time. Finally, the study suggests that neurobiological changes that may result from smoking ...
Pitt public health analysis provides guidance on hospital community benefit programs
2014-03-04
PITTSBURGH, March 3, 2014 – A new analysis led by the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health offers insights for nonprofit hospitals in implementing community health improvement programs.
In a special issue of the Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Underserved that focuses on the Affordable Care Act (ACA), a multidisciplinary team of Pitt researchers explore published research on existing community benefit programs at U.S. hospitals and explain how rigorous implementation of such programs could help hospitals both meet federal requirements and ...
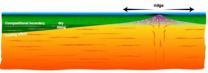
New study reveals insights on plate tectonics, the forces behind earthquakes, volcanoes
2014-03-04
The Earth's outer layer is made up of a series of moving, interacting plates whose motion at the surface generates earthquakes, creates volcanoes and builds mountains. Geoscientists have long sought to understand the plates' fundamental properties and the mechanisms that cause them to move and drift, and the questions have become the subjects of lively debate.
A study published online Feb. 27 by the journal Science is a significant step toward answering those questions.
Researchers led by Caroline Beghein, assistant professor of earth, planetary and space sciences ...
Novel drug treatment protects primates from deadly Marburg virus
2014-03-04
For the first time, scientists have demonstrated the effectiveness of a small-molecule drug in protecting nonhuman primates from the lethal Marburg virus. Their work, published online in the journal Nature, is the result of a continuing collaboration between Army scientists and industry partners that also shows promise for treating a broad range of other viral diseases.
According to senior author Sina Bavari, the drug, known as BCX4430, protected cynomolgous macaques from Marburg virus infection when administered by injection as long as 48 hours post-infection. Bavari ...