(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – By literally looking below the surface and digging up the dirt, Cornell researchers have discovered that a burgeoning deer population forever alters the progression of a forest's natural future by creating environmental havoc in the soil and disrupting the soil's natural seed banks.
The study, "Deer Browsing Delays Succession by Altering Aboveground Vegetation and Belowground Seed Banks," was published online March 7 in PLOS ONE.
"Deer are slowing down forest succession or natural establishment. In fact, the deer are preventing forests from establishing," says Anurag Agrawal, Cornell professor of ecology and evolutionary biology, a co-author on the paper.
Deer typically prefer to eat native, woody plants and rebuff invasive species. The study showed that when deer consume native plants, the non-native species are left to flourish, dropping seed in the soil.
As forests normally mature, their grasses give way to herbs and shrubs, and then new trees eventually take root. Expanding deer populations in the Northeast, however, stall forest development and promote the growth of thorny thickets of buckthorn, viburnum and multiflora rose bushes. If deer leave the forests alone, such trees as cottonwood, locust and sumac can sprout and grow unimpeded.
The researchers found that the impacts of deer grazing on vegetation were severe and resulted in bare soil and reduced plant biomass, less recruitment of woody species and relatively fewer native species. And the deer's negative impact on seed banks resulted in significantly decreased overall species richness and relatively more short-lived species of both annual and biennial plants.
Co-author Antonio DiTommaso, Cornell associate professor of weed ecology and management, and research technician Scott Morris gathered soil cores – from both within and outside of fenced "deer exclosures" – and germinated the seed. They found the soil cores from outside of the exclosures contained many more seeds from non-native species.
Deer select forests for their trees but in doing so disrupt forest system growth trajectories, concludes the study.
"It's obvious that the deer are affecting the above-ground species, but it's like an iceberg. There are major effects below the soil surface. We are seeing a divergence of seeds contained within the soil from what should be there," says DiTommaso. "We are not seeing the seeds of woody plants. Instead, we're seeing an escalation of non-native seed and the virtual elimination of woody plant seeds."
INFORMATION:
The multiyear study was conducted on Cornell land near Freese Road in Ithaca, where the deer density is about 39 animals per square kilometer – about 10 times greater than it was before European settlement in the late 1700s.
Cornell University has television, ISDN and dedicated Skype/Google+ Hangout studios available for media interviews.
Deer proliferation disrupts a forest's natural growth
2014-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New guidelines employ a team approach to autism diagnosis and care
2014-03-08
Improving diagnosis and treatment for individuals with autism has been the focus of a growing body of research. New information from these studies led the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry to revise key parameters for evaluating and treating autism. Researchers led by Yale Child Study Center director Fred Volkmar, M.D., have published the new practice parameters in the Feb. issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
"Early diagnosis of children with autism spectrum disorders means treatments will be introduced that ...
Research on 3D scaffolds sets new bar in lung regeneration
2014-03-07
In end-stage lung disease, transplantation is sometimes the only viable therapeutic option, but organ availability is limited and rejection presents an additional challenge. Innovative research efforts in the field of tissue regeneration, including pioneering discoveries by University of Vermont (UVM) Professor of Medicine Daniel Weiss, M.D., Ph.D., and colleagues, holds promise for this population, which includes an estimated 12.7 million people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD), the third leading cause of death in the U.S.
In the past year alone, Weiss ...
New NASA Van Allen Probes observations helping to improve space weather models
2014-03-07
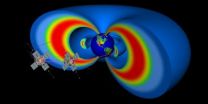
Using data from NASA's Van Allen Probes, researchers have tested and improved a model to help forecast what's happening in the radiation environment of near-Earth space -- a place seething with fast-moving particles and a space weather system that varies in response to incoming energy and particles from the sun.
When events in the two giant doughnuts of radiation around Earth – called the Van Allen radiation belts -- cause the belts to swell and electrons to accelerate to 99 percent the speed of light, nearby satellites can feel the effects. Scientists ultimately want ...
NASA satellites see double tropical trouble for Queensland, Australia
2014-03-07
There are two developing areas of tropical low pressure that lie east and west of Queensland, Australia. System 96P and System 98P, respectively. The MODIS instrument that flies aboard both NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites captured images of both tropical trouble-makers as each satellite passed overhead on March 7.
In the Coral Sea, part of the Southwestern Pacific Ocean, System 96P was just 125 nautical miles/143.8 miles/231.5 km north-northeast of Willis Island, Australia. It was centered near 14.3 south latitude and 150.6 east longitude. System 96P is moving in south-southwesterly ...
The dark side of fair play
2014-03-07
We often think of playing fair as an altruistic behavior. We're sacrificing our own potential gain to give others what they deserve. What could be more selfless than that? But new research from Northeastern University assistant professor of philosophy Rory Smead suggests another, darker origin behind the kindly act of fairness.
Smead studies spite. It's a conundrum that evolutionary biologists and behavioral philosophers have been mulling over for decades, and it's still relatively unclear why the seemingly pointless behavior sticks around. Technically ...
Service is key to winery sales
2014-03-07
ITHACA, N.Y. – To buy, or not to buy? That is the question for the more than 5 million annual visitors to New York's wineries. Cornell University researchers found that customer service is the most important factor in boosting tasting room sales, but sensory descriptions of what flavors consumers might detect were a turn-off.
The findings stem from two studies on how the tasting room experience affects customer purchases and what wineries can do to create satisfied sippers, published in the current issue of the International Journal of Wine Business Research.
"On average, ...
Ever-so-slight delay improves decision-making accuracy
2014-03-07
NEW YORK, NY (March 7, 2014) — Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) researchers have found that decision-making accuracy can be improved by postponing the onset of a decision by a mere fraction of a second. The results could further our understanding of neuropsychiatric conditions characterized by abnormalities in cognitive function and lead to new training strategies to improve decision-making in high-stake environments. The study was published in the March 5 online issue of the journal PLoS One.
"Decision making isn't always easy, and sometimes we make errors ...
Notre Dame chemists discover new class of antibiotics
2014-03-07
A team of University of Notre Dame researchers led by Mayland Chang and Shahriar Mobashery have discovered a new class of antibiotics to fight bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and other drug-resistant bacteria that threaten public health. Their research is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society in an article titled "Discovery of a New Class of Non-beta-lactam Inhibitors of Penicillin-Binding Proteins with Gram-Positive Antibacterial Activity."
The new class, called oxadiazoles, was discovered in silico (by computer) ...
New theory on cause of endometriosis
2014-03-07
Changes to two previously unstudied genes are the centerpiece of a new theory regarding the cause and development of endometriosis, a chronic and painful disease affecting 1 in 10 women.
The discovery by Northwestern Medicine scientists suggests epigenetic modification, a process that enhances or disrupts how DNA is read, is an integral component of the disease and its progression. Matthew Dyson, research assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and and Serdar Bulun, MD, chair of obstetrics and gynecology ...
Bone turnover markers predict prostate cancer outcomes
2014-03-07
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) —Biomarkers for bone formation and resorption predict outcomes for men with castration-resistant prostate cancer, a team of researchers from UC Davis and their collaborators have found. Their study, published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, also found that the markers identified a small group of patients who responded to the investigational drug atrasentan. The markers' predictive ability could help clinicians match treatments with individual patients, track their effectiveness and affect clinical trial design.
Castration-resistant ...