(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO, March 11, 2014 -- In the global aftershock zone that followed the major April 2012 Indian Ocean earthquake, seismologists noticed an unusual pattern – a dynamic "stress shadow," or period of seismic silence when some faults near failure were temporarily rendered incapable of a large rupture.
The magnitude (M) 8.6 earthquake, a strike-slip event at intraoceanic tectonic plates, caused global seismic rates of M≥4.5 to spike for several days, even at distances tens of thousands of kilometers from the mainshock site. But beginning two weeks after the mainshock, the rate of M≥6.5 seismic activity subsequently dropped to zero for the next 95 days.
Why did this rare period of quiet occur?
In a paper published today in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America (BSSA), Fred Pollitz of the U.S. Geological Survey and co-authors suggests that the Indian Ocean earthquake caused short-term dynamic stressing of a global system of faults. Across the planet, there are faults that are "close to failure" and ready to rupture. It may be, suggests Pollitz and his colleagues, that a large quake encourages short-term triggering of these close-to-failure faults but also relieves some of the stress that has built up along these faults. Large magnitude events would not occur until tectonic movement loads stress back on to the faults at the ready-to-fail levels they reached before the main shock.
Using a statistical model of global seismicity, Pollitz and his colleagues show that a transient seismic perturbation of the size of the April 2012 global aftershock would inhibit rupture in 88 percent of their possible M≥6.5 earthquake fault sources over the next 95 days, regardless of how close they were to failure beforehand.
This surprising finding, say the authors, challenges the previously held notion that dynamic stresses can only increase earthquake rates rather than inhibit them. But there are still mysteries about this process; for example, the global rate of M≥4.5 and M≥5.5 shocks did not decrease along with the larger shocks.
INFORMATION:
"The profound reach of the M8.6 11 April 2012 Indian Ocean earthquake: short-term global triggering followed by a longer-term global shadow" is co-authored by Fred Pollitz, Ross Stein and Volkan Sevilgen of the U. S. Geological Survey, and Roland Burgmann of University of California, Berkeley. The paper is published online on March 11, 2014 by BSSA and will appear in the journal's April print edition.
Dynamic stressing of a global system of faults results in rare seismic silence
2014-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Timid jumping spider uses ant as bodyguard
2014-03-11
A timid jumping spider uses the scent of ants as a secret weapon to save itself from becoming the somewhat soggy prey of the predatory spitting spider. The downside to this plan is that jumping spiders are also a favorite snack of its very own saviors. To overcome this additional hazard, the spider has made yet another plan in the form of an ant-proof nest, writes Ximena Nelson of the University of Canterbury in New Zealand and Robert Jackson of the University of Canterbury and the International Centre of Insect Physiology and Ecology in Kenya, in Springer's journal Behavioral ...
Magnet hospitals have higher quality of care, NYU researcher finds
2014-03-11
Magnet recognition is considered a leading source for measuring organizational success in nursing. Magnet hospitals show higher job satisfaction and lower odds of patient mortality than non-Magnet hospitals. However, only nine percent of American hospitals are recognized as Magnet. Currently, there is little research into the causes of the differences between Magnet and non-Magnet hospitals, research that could create an infrastructure for positive change in nurse and patient outcomes.
Now research from New York University College of Nursing (NYUCN) and the University ...
Some galaxies in the early universe grew up quickly
2014-03-11
Pasadena, CA— Some galaxies grew up in a hurry. Most of the galaxies that have been observed from the early days of the universe were young and actively forming stars. Now, an international team of astronomers, including Carnegie's Eric Persson and Andy Monson, have discovered galaxies that were already mature and massive in the early days. Fifteen mature galaxies were found at a record-breaking average distance of 12 billion light years, when the universe was just 1.6 billion years old. Their existence at such an early time raises new questions about what forced them to ...
Why antisocial youths are less able to take the perspective of others
2014-03-11
This news release is available in German. Adolescents with antisocial personality disorder inflict serious physical and psychological harm on both themselves and others. However, little is yet known about the underlying neural processes. Researchers at the University of Leiden and the Max Planck Institute for Human Development have pinpointed a possible explanation: Their brain regions responsible for social information processing and impulse control are less developed.
The study focused on incarcerated delinquent adolescents from the Netherlands aged between 15 and ...
How Twitter shapes public opinion
2014-03-11
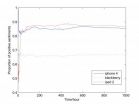
WASHINGTON D.C., March 11, 2014 -- How exactly does Twitter, with its 241 million users tweeting out 500 million messages daily, shape public opinion?
That question was tackled by a group of researchers in China who investigated how opinions evolve on Twitter by gathering about 6 million 140-character-or-less messages that were tweeted out over a six month period in the first half of 2011. They ran these messages through computer algorithms that sorted them by topic ("iPhone 4" or "blackberry," for instance), and they analyzed the underlying sentiments of the authors ...
Soil microbes shift as shrubs invade remnant hill prairies
2014-03-11
URBANA, Ill. – Perched high on the bluffs of the big river valleys in the Midwest are some of the last remnants of never-farmed prairie grasslands. These patches, edged by forest, are slowly being taken over by shrubs. A recent University of Illinois study examined the soil microbes on nine patches, also called "balds," that had varying degrees of shrub invasion and found an interesting shift in the composition of the microbial community.
"When we looked at the soil samples from a lightly encroached hill prairie remnant, it was very clear that there was a set of fungi ...
Tracking neighborhood eating habits to promote healthier diets
2014-03-11
Poor food choices, such as overconsumption of carbonated soft drinks, are an important factor driving the global obesity epidemic and have been linked directly to diabetes and heart disease. While public health agencies are working to help people to make healthier choices, monitoring the effectiveness of these efforts has been costly and difficult. But now, using the same digital data employed by marketers to promote food products, McGill University's David Buckeridge has developed a way for health agencies to track Montreal consumers' food choices, neighborhood by neighborhood. ...
NASA saw some power in Tropical Cyclone Gillian before making landfall
2014-03-11
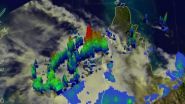
VIDEO:
The TRMM Satellite's Precipitation Radar data was used to create this 3-D flyby over Tropical Cyclone Gillian on March 10. Some powerful storms within Gillian reached heights above 16 km/~9.9...
Click here for more information.
NASA's TRMM satellite saw some towering thunderstorms in Tropical Cyclone Gillian before it made landfall over the Western Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia. Gillian has been staying over land since, and is now a remnant low pressure area. ...
Higher levels of CSF alpha-synuclein predict faster cognitive loss in Parkinson disease
2014-03-11
Philadelphia, PA, March 11, 2014 – The course of Parkinson disease (PD) can vary from gradual deterioration to precipitous decline in motor or cognitive function. Therefore identifying predictors of progression can benefit understanding of PD disease progression and impact management. Data from 304 PD patients followed for up to 8 years indicate that patients with higher cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) alpha-synuclein levels experienced faster cognitive decline in the following months, although no associations were found between alpha-synuclein levels and motor changes. The results ...
Cellular alchemy: Penn study shows how to make insulin-producing cells from gut cells
2014-03-11
PHILADELPHIA — Destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas is at the heart of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. "We are looking for ways to make new beta cells for these patients to one day replace daily insulin injections," says Ben Stanger, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Transplanting islet cells to restore normal blood sugar levels in patients with severe type 1 diabetes is one approach to treating the disease, and using stem cells to create beta cells ...