(Press-News.org) An analysis of research on peer review finds that studies aimed at improving methods of peer review and reporting of biomedical research are underrepresented and lack dedicated funding, according to a study in the March 12 issue of JAMA.
Mario Malicki, M.D., M.A., of the University of Split School of Medicine, Split, Croatia, and colleagues analyzed research presented at the International Congress on Peer Review and Biomedical Publication (PRC) since 1989. The first PRC was organized to "subject the editorial review process to some of the rigorous scrutiny that editors and reviewers demand of the scientists whose work they are assessing." The researchers collected data on authorship, time to publication, declared funding sources, article availability, and citation counts in Web of Science. The analysis included 614 abstracts.
The researchers found that experimental studies aimed at improving methods of peer review and reporting of biomedical research are still underrepresented on the pages of medical journals. "Although the peer review research community is aware of the consequences of nonpublication of research, 39 percent of studies presented at PRCs have not been fully published. In our cohort, we were unable to determine whether the underreporting was selective [e.g., publication favoring positive results] and were not able to determine its causes."
Peer review and other editorial procedures have the potential to influence the knowledge base of health care, the authors write. "Despite their critical role in biomedical publishing, methods of peer review are still underresearched and lack dedicated funding. Systematic and competitive funding schemes are needed to build and sustain excellence, innovation, and methodological rigor in peer review research."
(doi:10.1001/jama.2014.143; Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
Editorial: Research on Peer Review and Biomedical Publication - Furthering the Quest to Improve the Quality of Reporting
In an accompanying editorial, Drummond Rennie, M.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, and Annette Flanagin, R.N., M.A., of JAMA, Chicago, comment on the studies in this issue of JAMA that examine peer review and the publishing of biomedical research.
"… articles on how to improve research, of which publication is an integral part, are important reminders that no matter how much research on peer review and publication has been presented at the Peer Review Congresses and elsewhere, these studies are but part of a widespread movement to improve the scientific literature. As the reports in this issue of JAMA indicate, discovering the extent of the problems and testing methods to correct them will require a massive and prolonged effort on the part of researchers, funders, institutions, and journal editors."
(doi:10.1001/jama.2014.1362; Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
INFORMATION: END
Study examines development of peer review research in biomedicine
2014-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Discontinuation of randomized clinical trials common
2014-03-11
Approximately 25 percent of about 1,000 randomized clinical trials initiated between 2000 and 2003 were discontinued, with the most common reason cited being poor recruitment of volunteers; and less than half of these trials reported the discontinuation to a research ethics committee, or were ever published, according to a study in the March 12 issue of JAMA.
Conducting high-quality randomized clinical trials (RCTs) is challenging and resource-demanding. Trials are often not conducted as planned or are prematurely discontinued, which poses ethical concerns, particularly ...
Two surgeries for pelvic prolapse found similarly effective, safe
2014-03-11
Two surgical treatments for a form of pelvic hernia affecting women have similar rates of success and safety, scientists in a National Institutes of Health research network have found. A guided exercise therapy to strengthen pelvic muscles did not add to the benefits of either surgery.
The surgical procedures and exercise therapy are used to treat pelvic organ prolapse, an often uncomfortable and sometimes painful weakening of the pelvic organs that may affect women in the years after childbirth. Previous network research suggests that about 3 percent of U.S. women will ...
Incontinence and Prolapse procedures found to be comparable in women
2014-03-11
MAYWOOD – Two common procedures to treat pelvic organ prolapse without vaginal mesh are comparable in safety and efficacy, according to research published in the latest issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association. Researchers also found that behavioral and pelvic floor muscle therapy (BPMT) did not improve urinary incontinence or prolapse symptoms in affected women.
Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the uterus and/or vaginal walls protrude outside of the body. Up to 73 percent of these women report other pelvic floor disorders such as incontinence. More ...
Whole-genome sequencing for clinical use faces many challenges, Stanford study finds
2014-03-11
STANFORD, Calif. — Whole-genome sequencing has been touted as a game-changer in personalized medicine. Clinicians can identify increases in disease risk for specific patients, as well as their responsiveness to certain drugs, by determining the sequence of the billions of building blocks, called nucleotides, that make up their DNA.
Now, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have discovered that although life-changing discoveries can be made, significant challenges must be overcome before whole-genome sequencing can be routinely clinically useful. In ...
Giving dangerous employees socialization, close supervision can avoid problems
2014-03-11
Two UT Arlington management professors argue that employers can prevent workplace violence by keeping dangerous employees positively engaged and closely supervising them to ensure they get the help they need.
James Campbell Quick and M. Ann McFadyen of the College of Business management department analyzed FBI reports, case studies and human resource records to focus on the estimated 1 to 3 percent of employees prone to workplace acts of aggression, such as homicide, suicide or destruction of property.
The team advances the case for "mindfully observing" employees and ...
Long-term warming likely to be significant despite recent slowdown
2014-03-11
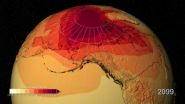
A new NASA study shows Earth's climate likely will continue to warm during this century on track with previous estimates, despite the recent slowdown in the rate of global warming.
This research hinges on a new and more detailed calculation of the sensitivity of Earth's climate to the factors that cause it to change, such as greenhouse gas emissions. Drew Shindell, a climatologist at NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York, found Earth is likely to experience roughly 20 percent more warming than estimates that were largely based on surface temperature observations ...
Acoustic cloaking device hides objects from sound
2014-03-11
VIDEO:
This video demonstrates the difference in how sound waves act with and without the acoustic cloak in their path. The red and blue lines represent the high and low points...
Click here for more information.
DURHAM, N.C. -- Using little more than a few perforated sheets of plastic and a staggering amount of number crunching, Duke engineers have demonstrated the world's first three-dimensional acoustic cloak. The new device reroutes sound waves to create the impression that ...
Scientists 'herd' cells in new approach to tissue engineering
2014-03-11
VIDEO:
Videos show the effect of electric fields on the movement of epithelial cells. The first clip shows the cells migrating normally until the electric field is turned on, causing the...
Click here for more information.
Berkeley -- Sometimes it only takes a quick jolt of electricity to get a swarm of cells moving in the right direction.
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, found that an electrical current can be used to orchestrate the flow of a group ...
Prosocial youth less likely to associate with deviant peers, engage in problem behaviors
2014-03-11
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Prosocial behaviors, or actions intended to help others, remain an important area of focus for researchers interested in factors that reduce violence and other behavioral problems in youth. However, little is known regarding the connection between prosocial and antisocial behaviors. A new study by a University of Missouri human development expert found that prosocial behaviors can prevent youth from associating with deviant peers, thereby making the youth less likely to exhibit antisocial or problem behaviors, such as aggression and delinquency.
"This ...
Finding hiding place of virus could lead to new treatments
2014-03-11
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – March 11, 2014 – Discovering where a common virus hides in the body has been a long-term quest for scientists. Up to 80 percent of adults harbor the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), which can cause severe illness and death in people with weakened immune systems.
Now, researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center's Institute for Regenerative Medicine report that stem cells that encircle blood vessels can be a hiding place, suggesting a potential treatment target.
In the American Journal of Transplantation (online ahead of print), senior scientist ...