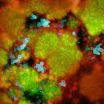
(Press-News.org) Early childhood caries, a highly aggressive and painful form of tooth decay that frequently occurs in preschool children, especially from backgrounds of poverty, may result from a nefarious partnership between a bacterium and a fungus, according to a paper published ahead of print in the journal Infection and Immunity.
The resulting tooth decay can be so severe that treatment frequently requires surgery—in the operating room, says corresponding author Hyun (Michel) Koo of the University of Pennsylvania.
"Our data will certainly open the way to test agents to prevent this disease, and even more intriguing, the possibility of preventing children from acquiring this infection," says Koo.
In the study the investigators showed that infection by S. mutans and C. albicans together doubled the number of cavities, and boosted their severity several-fold in rats.
Koo, of U. Penn's School of Dental Medicine, has spent 15 years studying how microbes construct the biofilms, also known as plaque, that have plagued teeth since H. sapiens invented agriculture, bringing large quantities of starch into the diet. (Caries are common in Neolithic skeletons, but virtually absent from our Paleolithic ancestors.)
The bacterium Streptococcus mutans has long been assumed to be the sole microbial culprit, but Koo and collaborators—as well as other investigators—noticed that the fungus, Candida albicans, was almost always present in plaque from cases of early childhood caries. S. mutans sticks to the surfaces of teeth by converting sugars to a sticky glue-like material called extracellular polysaccharide (EPS.) In the mouth, Candida adheres mainly to cheek and tongue, but had rarely been seen in dental plaque.
"However, we and others noticed that Candida was very frequently observed in plaque from patients who have early childhood caries," says Koo. "We were puzzled! Candida usually does not associate with S. mutans, nor does it colonize teeth very effectively."
The investigators discovered that the "exoenzyme" which S. mutans uses to react with sugar to produce EPS, also enables Candida to produce a glue-like polymer in the presence of sugar, allowing it to adhere to teeth, and to bind S. mutans, two abilities it otherwise lacks. Under these circumstances, the fungus now contributes the bulk of the plaque.
"The combination of the two organisms led to a greatly enhanced production of the glue-like polymer, drastically boosting the ability of the bacterium and the fungus to colonize the teeth, increasing the bulk of the biofilms and the density of the infection," says Koo. All that led to greatly elevated accumulation next to the teeth of the acid that dissolves enamel, leading to cavity formation.
"This represents a truly unique physical interaction where a bacterially-produced product attaches to and functions on the surface of an organism from another kingdom, converting this normally innocuous (with respect to teeth) fungus into a fierce stimulator of cariogenic biofilm formation," says Koo. That observation, he says, supports his hypothesis that early childhood caries in toddlers results from infection by both organisms, with frequent exposure to sucrose.
INFORMATION:
A copy of the manuscript can be found online at http://bit.ly/asmtip0314b. The final version of the article is scheduled for the May 2014 issue of Infection and Immunity.
Infection and Immunity is a publication of the American Society for Microbiology (ASM). The ASM is the largest single life science society, composed of over 39,000 scientists and health professionals. Its mission is to advance the microbiological sciences as a vehicle for understanding life processes and to apply and communicate this knowledge for the improvement of health and environmental and economic well-being worldwide.
Bacterium and fungus team up to cause virulent tooth decay in toddlers
2014-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Majority of transgender patients report negative experiences in emergency departments
2014-03-12
A new study out of Western University (London, Canada) has found the majority of transgender patients have had a negative experience when it comes to receiving emergency department (ED) care. The findings, by first author Greta Bauer, PhD, is in press at the Annals of Emergency Medicine, the official publication of the American College of Emergency Physicians, and is now posted online.
The study used respondent-driven sampling, a methodology developed to specifically address the challenge of studying hard-to-reach populations. It relies on a snowball sampling, using ...
Metallurgical challenges in microelectronic 3-D IC packaging technology
2014-03-12
Mobile hand-held consumer electronic products have a rapid growing market today, witnessed by the popularity of Apple products. Most people make their first contact to internet, not by a PC, rather by a smart phone. The phone is no longer a phone, but it provides various functions for communication and for entertainment. Not only we can have recorded information such as books, images, songs, and movies from the phone or i-pad, but also we can have instant information such as traffic jam when we drive home, as well as breaking news at the last moment. It is expected that ...
Higher levels of CSF alpha-synuclein predict faster cognitive loss in Parkinson's disease
2014-03-12
Philadelphia, PA, March 11, 2014 – The course of Parkinson disease (PD) can vary from gradual deterioration to precipitous decline in motor or cognitive function. Therefore identifying predictors of progression can benefit understanding of PD disease progression and impact management. Data from 304 PD patients followed for up to 8 years indicate that patients with higher cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) alpha-synuclein levels experienced faster cognitive decline in the following months, although no associations were found between alpha-synuclein levels and motor changes. The results ...
Hasbro Children's Hospital study finds texting program good option for teen girls' health
2014-03-12
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – Megan Ranney, M.D., M.P.H., an emergency medicine attending physician at Hasbro Children's Hospital, recently led a study that found a text-message program may be an effective violence prevention tool for at-risk teen girls. The study has been published online in the Journal of Adolescent Health.
"Mobile health, or 'mHealth,' is increasingly being used as a way to improve people's health, via text-messaging or phone-based applications," said Ranney. "However, few people have studied whether teens are interested in mHealth, especially for prevention-type ...
Wishing to be another gender: Links to ADHD and autism spectrum disorders
2014-03-12
Children and teenagers with an autism spectrum disorder or those who have attention deficit and hyperactivity problems are much more likely to wish to be another gender. So says John Strang of the Children's National Medical Center in Washington, DC, USA, leader of the first study to compare the occurrence of such gender identity issues among children and adolescents with and without specific neurodevelopmental disorders. The paper is published in Springer's journal Archives of Sexual Behavior.
Children between 6 and 18 years old were part of the study. They either had ...
Lawns across America: Is the US becoming 1 shade of green?
2014-03-12
Boston and Baltimore. Miami and Minneapolis. Phoenix and Los Angeles.
Fanned across the United States and in locations from coast to prairie to desert, what do these cities have in common?
How their human residents manage that icon of America, the urban lawn, or so hypothesized a team of scientists. However, when they conducted a study comparing residential landscapes in these six cities, they discovered that lawn care practices had fewer similarities than they expected.
Ecologists Colin Polsky of Clark University in Worcester, Mass., Peter Groffman of the Cary Institute ...
Climate of Genghis Khan's ancient time extends long shadow over Asia of today
2014-03-12
Climate was very much on Genghis Khan's side as he expanded his Mongol Empire across northeastern Asia.
That link between Mongolia's climate and its human history echoes down the centuries, according to findings reported in this week's issue of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
But climate may no longer be the boon it was during the latter, wetter part of Genghis Khan's reign. The early years were marked by drought.
Mongolia's current drought conditions could have serious consequences for the Asia region's human and other inhabitants.
The ...
NASA sees remnants of Tropical Cyclone Hadi in So. Pacific
2014-03-12
Tropical Cyclone Hadi is now a remnant low pressure area in the Southern Pacific Ocean. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the storm and captured a visible image of it on March 12.
When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Hadi's remnants, the MODIS instrument aboard captured a visible image that showed the strongest thunderstorms associated with the low appeared south of the center of circulation. The center was located near 15.1 south and 156.1 east, about 585 nautical miles/673.2 miles/ 1,083 km west of Vanuatu.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center or JTWC noted that animated ...
Skating to the puck or avoiding the penalty box in health care?
2014-03-12
LEBANON, NH (March 12, 2014) – In a Viewpoint published in the March issue of JAMA, Researcher Jeremiah Brown of The Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy & Clinical Practice and colleagues, Hal Sox and David Goodman, question whether the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services' use of financial penalties is the right tack for changing the behavior of hospitals.
The researchers examine the pros and cons of the hospital readmissions reduction policy in the Affordable Care Act as an example of similar CMS initiatives.
"Using financial incentives to change practice ...
The immune system's redesigned role in fighting cancerous tumors
2014-03-12
LOS ANGELES (March 11, 2014) – Researchers in the Cedars-Sinai Samuel Oschin Comprehensive Cancer Institute eradicated solid tumors in laboratory mice using a novel combination of two targeted agents. These two synergistic therapies stimulate an immune response, ultimately allowing solid tumors to act as their own cancer-fighting vaccine.
The study's findings, published in the journal Cancer Research, are the first to use these combined agents as an immune stimulator and may have the potential to kill cancerous cells in solid tumors, including some of the most aggressive ...