(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH—British mathematician Alan Turing's accomplishments in computer science are well known—he's the man who cracked the German Enigma code, expediting the Allies' victory in World War II. He also had a tremendous impact on biology and chemistry. In his only paper in biology, Turing proposed a theory of morphogenesis, or how identical copies of a single cell differentiate, for example, into an organism with arms and legs, a head and tail.
Now, 60 years after Turing's death, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh and Brandeis University have provided the first experimental evidence that validates Turing's theory in cell-like structures.
The team published their findings in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on March 10.
Turing, in 1952, was the first to offer an explanation of morphogenesis through chemistry. He theorized that identical biological cells differentiate and change shape through a process called intercellular reaction-diffusion. In this model, chemicals react with each other and diffuse across space—say between cells in an embryo. These chemical reactions are managed by the interaction of inhibitory and excitatory agents. When this interaction plays out across an embryo, it creates patterns of chemically different cells. Turing predicted six different patterns could arise from this model.
At Brandeis, Seth Fraden, professor of physics, and Irv Epstein, professor of chemistry, created rings of synthetic, cell-like structures with activating and inhibiting chemical reactions to test Turing's model. Pitt's G. Bard Ermentrout, University Professor of Computational Biology and professor of mathematics, undertook mathematical analysis of the experiments.
The researchers observed all six patterns plus a seventh unpredicted by Turing.
In addition, they noticed that, as Turing theorized in the 1950s, the once identical cell-like structures—now chemically different—also began to change in size due to osmosis. This may explain how some cells, further down the development assembly line, become large egg cells or tiny sperm cells.
The research "tells you how a zebra gets its stripes," says Ermentrout. Turing's theory underlies pattern formation in every biological area from pigmentation of seashells to the shapes of flowers and leaves and to the geometric structures seen in drug-induced hallucinations, he adds. Thus, validating Turing's theory could have an impact on future research in fields ranging from embryology to neurology to cardiology. This research could impact not only the study of biological development but the study of materials science as well. For example, Turing's model could help grow soft robots with certain patterns and shapes.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded in part by grants from the National Science Foundation Material Research Science and Engineering Center (DM-0820492 and CHE-1012428). Nathan Tompkins, Ning Li, Camille Girabawe, and Michael Heymann, all from Brandeis University, also contributed to the paper, titled "Testing Turing's theory of morphogenesis in chemical cells."
Turing's theory of morphogenesis validated 60 years after his death
2014-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Large study identifies the exact gut bacteria involved in Crohn's disease
2014-03-12
While the causes of Crohn's disease are not well understood, recent research indicates an important role for an abnormal immune response to the microbes that live in the gut. In the largest study of its kind, researchers have now identified specific bacteria that are abnormally increased or decreased when Crohn's disease develops. The findings, which appear in the March 12 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Host & Microbe, suggest which microbial metabolites could be targeted to treat patients with this chronic and currently incurable inflammatory bowel disease.
Twenty-eight ...
Newly diagnosed Crohn's disease patients show imbalance in intestinal microbial population
2014-03-12
A multi-institutional study led by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the Broad Institute has identified how the intestinal microbial population of newly diagnosed Crohn's disease patients differs from that of individuals free of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In their paper in the March 12 issue of Cell Host and Microbe, the researchers report that Crohn's patients showed increased levels of harmful bacteria and reduced levels of the beneficial bacteria usually found in a healthy gastrointestinal tract.
Several studies have suggested that ...
Missing link in plant immunity identified
2014-03-12
After a 30-year search, scientists have uncovered how an enzyme critical to plants' rapid immune response against microbes is activated.
"The insights will open up new ways to improve disease resistance and stress tolerance in plants," says Professor Cyril Zipfel of The Sainsbury Laboratory in Norwich.
The enzyme, the NAPDH oxidase RBOHD, triggers a rapid generation of signalling molecules derived from oxygen that are believed to be detrimental to microbial growth. The newly-discovered way this enzyme is activated, by a protein (called BIK1) fills a gap in how plants ...
Microbes help to battle infection
2014-03-12
The human relationship with microbial life is complicated. At almost any supermarket, you can pick up both antibacterial soap and probiotic yogurt during the same shopping trip. Although there are types of bacteria that can make us sick, Caltech professor of biology and biological engineering Sarkis Mazmanian and his team are most interested in the thousands of other bacteria—many already living inside our bodies—that actually keep us healthy. His past work in mice has shown that restoring populations of beneficial bacteria can help alleviate the symptoms of inflammatory ...
Study finds increased gender variance in children with autism and ADHD
2014-03-12
Washington, DC— John F. Strang, PsyD, a pediatric neuropsychologist at Children's National Health System, and colleagues, found that children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) were more likely to exhibit gender variance, the wish to be the other gender, than children with no neurodevelopmental disorder, or a medical neurodevelopmental disorder such as epilepsy or neurofibromatosis.
The study, titled "Increased Gender Variance in Autism Spectrum Disorders and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder" was published ...
Can material rivaling graphene be mined out of rocks? Yes, if...
2014-03-12
Will one-atom-thick layers of molybdenum disulfide, a compound that occurs naturally in rocks, prove to be better than graphene for electronic applications? There are many signs that might prove to be the case. But physicists from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw have shown that the nature of the phenomena occurring in layered materials are still ill-understood and require further research.
Graphene has already been hailed as the future of electronics. Built of six-atom carbon rings arranged in a honeycomb-like structure, it forms extremely resilient ...
Transition to ICD-10 may cause information, financial losses for providers
2014-03-12
Health providers may experience information and financial loss during the mandated conversion from the current International Classification of Diseases to its new and improved version, report researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
The study, appearing in the March issue of the Journal of Oncology Practice, looked at coding ambiguity for hematology-oncology diagnoses to anticipate challenges all providers may face during the transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM.
The researchers chose to look at hematology-oncology because prior research suggested that, ...
Two definitions for chronic multisymptom illness afflicting gulf war vets should guide treatment
2014-03-12
WASHINGTON – Two existing definitions of chronic multisymptom illness (CMI) -- one by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and another from a study of Kansas Gulf War veterans -- should be used by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs to guide research and treatment of Gulf War veterans, says a new report from the Institute of Medicine. Determining which definition to use in different circumstances should be based on specific needs. Furthermore, the term "Gulf War illness" should replace "chronic multisymptom illness" to reflect the group in which the illness ...
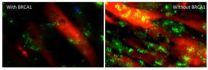
Breast cancer gene could play critical role in obesity and diabetes
2014-03-12
College Park, Md. -- The gene known to be associated with breast cancer susceptibility, BRCA 1, plays a critical role in the normal metabolic function of skeletal muscle, according to a new study led by University of Maryland School of Public Health researchers. Dr. Espen Spangenburg, associate professor of kinesiology, and his laboratory team are the first to identify that the BRCA1 protein is expressed in the skeletal muscle of both mice and humans, and that it plays a key role in fat storage, insulin response and mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle cells. The research ...
Large waist linked to poor health, even among those in healthy body mass index ranges
2014-03-12
ROCHESTER, Minn. — March 12, 2014 — Having a big belly has consequences beyond trouble squeezing into your pants. It's detrimental to your health, even if you have a healthy body mass index (BMI), a new international collaborative study led by a Mayo Clinic researcher found. Men and women with large waist circumferences were more likely to die younger, and were more likely to die from illnesses such as heart disease, respiratory problems, and cancer after accounting for body mass index, smoking, alcohol use and physical activity. The study is published in the March edition ...