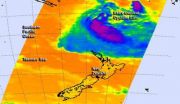
(Press-News.org) NASA's Aqua satellite caught an infrared picture of Tropical Cyclone Lusi after it transitioned into an extra-tropical storm, north of New Zealand. Gale Warnings are in effect in Northern New Zealand.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Lusi on March 13 at 13:41 UTC/9:41 a.m. EDT and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument captured infrared data on the storm that revealed it had become a cold-core system. When a storm becomes extra-tropical and its core changes from warm to cold, the strongest winds spread out and the storm expands.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued their final bulletin on Lusi on March 13 at 2100 UTC/5 p.m. EDT. At that time, Lusi's maximum sustained winds were still near 50 knots/57.5 mph/92.6 kph. Lusi was centered near 26.7 south and 173.2 east, about 476 nautical miles/547.8 miles/881.6 km southwest of Suva, Fiji and the extra-tropical storm was moving to the south-southwest at 15 knots/17.2 mph/27.7 kph.
On March 14, the New Zealand Meteorological Service noted that Lusi had picked up speed to 35 kph. Lusi's current track is expected to bring the storm just to the northwest of North Cape around midday Saturday, March 15.
The Brett coastal forecast issued at 4:25 a.m. on Saturday, March 15 (local time) includes a Gale Warning as the Met service expects "southeast winds of 45 knots/51.7 mph/83.3 kph turning northeast late morning and easing to 35 knots/40.2 mph/64.8 kph this evening. High sea easing. Northeast swell rising to 4 meters/13.1 feet. Poor visibility in heavy rain. "
The Met Service expects Lusi to move southward over the ocean west of the North Island on March 15 and early on March 16 (local time) then cross the South Island to just east of Canterbury Sunday night . For updates on the extra-tropical storm, visit: http://www.metservice.com/national/home
INFORMATION:
NASA sees an extra-tropical Lusi north of New Zealand
2014-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Salad at concession stands!?
2014-03-14
Pep-rallies, the marching band, cheers and chants, and savory, indulgent foods sold at the concession stand are all beloved features of the American high school sports tradition.
In contrast to the nutrition requirements on breakfast and lunches sold in school cafeterias, foods sold at concession stands do not follow the standard nutrition guidelines because they are typically sold for fundraising purposes. Is there something that can be done to improve the healthful features of concession stand food, and preserve the profits they generate? According to this new study ...
Older age at onset of Type 1 diabetes associated with lower brain connectivity
2014-03-14
SAN FRANCISCO, March 14, 2014 – Children and adolescents older than age 8 at the onset of type 1 diabetes had weaker brain connectivity when tested later in life relative to those who had earlier ages of diagnosis, University of Pittsburgh Schools of the Health Sciences researchers discovered.
The findings, presented today at the American Psychosomatic Society's annual meeting, were made by analyzing the brain scans of 44 middle-age adults diagnosed with type 1 diabetes as children.
"Adolescence is a time when the brain matures and makes connections in networks responsible ...
Study: Losing or gaining weight after joint replacement affects how well patients do
2014-03-14
While many overweight patients have the best intentions to lose weight after joint replacement, a study at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) finds that although some are able to achieve this goal, equal numbers of patients actually gain weight after hip or knee replacement. Researchers also determined that patients who lose weight do better in terms of function and activity level two years down the road.
"Our findings represent the first report to present evidence that weight loss is associated with improved clinical outcomes, while weight gain is associated with inferior ...
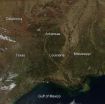
Southeastern fires consist of prescribed and wild
2014-03-14
According to the Southern Area Coordination Center, which monitors and coordinates response to incidents throughout the Southeast, there are currently seven large fires burning in this area of the country. Six of them are located in the state of Oklahoma and the seventh is in the Gulf area of Louisiana. These fires currently have burned over 7,600 acres. The majority of the fires on this image, though, are not wildfires, but are prescribed fires. The Chicasaw Journal of Mississippi wrote this regarding prescribed fires: "Prescribed fire, also known as controlled burning, ...
Researchers find significant increase in painkillers prescribed to US adults in the ER
2014-03-14
WASHINGTON (March 14, 2014) —George Washington University (GW) researchers report dramatic increases in prescriptions of opioid analgesics, such as Percocet, Vicodin, oxycodone and Dilaudid, during U.S. emergency department visits from 2001 to 2010. These findings were not explained by higher visit rates for painful conditions, which only increased modestly during the time period. This report was published today in the journal Academic Emergency Medicine.
"This trend is especially concerning given dramatic increases in opioid-related overdoses and fatalities in recent ...
In the lab, scientists coax E. coli to resist radiation damage
2014-03-14
MADISON, Wis. – Capitalizing on the ability of an organism to evolve in response to punishment from a hostile environment, scientists have coaxed the model bacterium Escherichia coli to dramatically resist ionizing radiation and, in the process, reveal the genetic mechanisms that make the feat possible.
The study, published in the online journal eLife, provides evidence that just a handful of genetic mutations give E. coli the capacity to withstand doses of radiation that would otherwise doom the microbe. The findings are important because they have implications for better ...
Researchers find high acceptability of 3-colored raspberry jelly
2014-03-14
CHICAGO—Raspberries are among the most popular berries in the world and are high in antioxidants that offer significant health benefits to consumers. The red raspberry is most commonly used in processed products like juices, jams, jellies and preserves because of its short shelf life. A new study in the Journal of Food Science, published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), found that the production of a mixed raspberry jelly with black and yellow raspberries could be a good alternative to just one-colored jelly.
Black raspberries, which produce clusters of ...
Gluten-free crackers made with hemp flour and decaffeinated green tea leaves
2014-03-14
CHICAGO—The market for gluten-free foods with functional properties is growing immensely across virtually all food categories on a global level. The need to replace wheat proteins, fibers, and minerals is very important in order to provide a better selection and more nutritious food for consumers that belong to this segment of the population. At the same time, the use of by-products of the food processing industry as a source of functional ingredients such as antioxidants, phenols, fibers and proteins is on the rise, which supports global sustainability.
A team of food ...
Genes may thwart seniors' exercise gains
2014-03-14
Bethesda, Md. (March 14, 2014)—Keeping strong and physically fit is crucial to maintaining independence among the elderly. Exercise has repeatedly been shown to reduce or slow age-related declines in physical function and is a widely recommended for seniors, but the way that older people respond to exercise varies widely. A new study by Thomas W. Buford et al. examines the ACE I/D gene and whether its variations—the ID, DD, and II genotypes—impact some seniors' ability to fully reap the benefits of exercise.
Researchers followed 424 sedentary, mobility-limited seniors ...
Brighter inks, without pigment
2014-03-14
Cambridge, Mass. – March 14, 2014 – Among the taxidermal specimens in Harvard's Museum of Comparative Zoology, past centuries-old fur coats, arises a flicker of brilliant blue. This is the spangled cotinga. Surprisingly, the cotinga is about as old as everything in the room, but its color is still as dazzling as the day it was brought to the museum. The cotinga—or rather its feathers—achieve this effect through structural color.
Unlike color that we usually think of, which arises from paints and dyes absorbing certain wavelengths of light and reflecting the remainder, ...