(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON (March 14, 2014) —George Washington University (GW) researchers report dramatic increases in prescriptions of opioid analgesics, such as Percocet, Vicodin, oxycodone and Dilaudid, during U.S. emergency department visits from 2001 to 2010. These findings were not explained by higher visit rates for painful conditions, which only increased modestly during the time period. This report was published today in the journal Academic Emergency Medicine.
"This trend is especially concerning given dramatic increases in opioid-related overdoses and fatalities in recent years," said Maryann Mazer-Amirshahi, M.D., co-author of the study and adjunct instructor of emergency medicine at the GW School of Medicine and Health Sciences (SMHS). "Using prescription opioids to treat acute painful conditions in emergency departments and hospitals might do more harm than good, as they can potentially lead to misuse and addiction. More needs to be done to monitor opioid prescriptions in emergency departments — having recommended standard approaches may be a good starting point."
Mazer-Amirshahi and colleagues found that between 2001 and 2010, the percentage of overall emergency department visits where an opioid analgesic was prescribed increased from 20.8 percent to 31 percent. For some opioids, prescription rates increased dramatically; Dilaudid, one of the most potent yet addictive medications, went up 668.2 percent. The percentage of visits for painful conditions during the period only increased by four percent, from 47.1 percent in 2001 to 51.1 percent in 2010.
"Emergency department providers are often caught in a difficult position because some have their pay incentivized based on how patients report their satisfaction with their experience. The intention is always to provide appropriate pain relief, but many patients have come to expect opioids," said Jesse Pines, M.D., co-author of the study and director of the Office of Clinical Practice Innovation at GW SMHS. "When patients in pain want opioids, but don't get them — which is common — they may report a poor experience. We need to carefully consider how to balance these issues when it comes to national policy, particularly local and national payment policies, in this country."
The study analyzed data from the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey, exploring which demographic groups, medications, and reasons for visiting the emergency room may account for this change in prescribing rates. In their analysis, the authors found the following over the ten-year study period:
Opioid prescribing increases across all age groups, including those over 65 years
Increases in opioid use in both blacks and whites; however, blacks were consistently prescribed fewer opioids than whites
Significant increases in opioid use in all categories of payer
Largest proportional increase in opioid prescriptions in Midwestern states; Highest overall frequency of opioids prescribed in Western states; Lowest rates of opioid utilization in Northeast states
Opioids more commonly prescribed in urban emergency departments and in nonprofit hospitals
Increases in prescription rates for all opioid analgesics, except codeine and meperidine
Greatest relative increases in use of hydromorphone (known as Dilaudid) and morphine; Hydromorphone and oxycodone had the greatest relative increases from 2005-2010
INFORMATION:
Additional authors of the study include John van den Anker, M.D., professor of pediatrics, and Irit Rasooly, 4th year medical student, both at GW SMHS.
The paper, titled "Rising Opioid Prescribing in Adult U.S. Emergency Department Visits: 2001-2010," is available at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/acem.12328/abstract.
Media: For more information or to interview an author of the study, please contact Lisa Anderson at lisama2@gwu.edu or 202-994-3121.
About the GW School of Medicine and Health Sciences:
Founded in 1825, the GW School of Medicine and Health Sciences (SMHS) was the first medical school in the nation's capital and is the 11th oldest in the country. Working together in our nation's capital, with integrity and resolve, the GW SMHS is committed to improving the health and well-being of our local, national and global communities. smhs.gwu.edu
Researchers find significant increase in painkillers prescribed to US adults in the ER
Researchers at GW found a dramatic increase in opioid prescriptions during emergency department visits over the last decade, while only a modest increase in pain-related complaints
2014-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In the lab, scientists coax E. coli to resist radiation damage
2014-03-14
MADISON, Wis. – Capitalizing on the ability of an organism to evolve in response to punishment from a hostile environment, scientists have coaxed the model bacterium Escherichia coli to dramatically resist ionizing radiation and, in the process, reveal the genetic mechanisms that make the feat possible.
The study, published in the online journal eLife, provides evidence that just a handful of genetic mutations give E. coli the capacity to withstand doses of radiation that would otherwise doom the microbe. The findings are important because they have implications for better ...
Researchers find high acceptability of 3-colored raspberry jelly
2014-03-14
CHICAGO—Raspberries are among the most popular berries in the world and are high in antioxidants that offer significant health benefits to consumers. The red raspberry is most commonly used in processed products like juices, jams, jellies and preserves because of its short shelf life. A new study in the Journal of Food Science, published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), found that the production of a mixed raspberry jelly with black and yellow raspberries could be a good alternative to just one-colored jelly.
Black raspberries, which produce clusters of ...
Gluten-free crackers made with hemp flour and decaffeinated green tea leaves
2014-03-14
CHICAGO—The market for gluten-free foods with functional properties is growing immensely across virtually all food categories on a global level. The need to replace wheat proteins, fibers, and minerals is very important in order to provide a better selection and more nutritious food for consumers that belong to this segment of the population. At the same time, the use of by-products of the food processing industry as a source of functional ingredients such as antioxidants, phenols, fibers and proteins is on the rise, which supports global sustainability.
A team of food ...
Genes may thwart seniors' exercise gains
2014-03-14
Bethesda, Md. (March 14, 2014)—Keeping strong and physically fit is crucial to maintaining independence among the elderly. Exercise has repeatedly been shown to reduce or slow age-related declines in physical function and is a widely recommended for seniors, but the way that older people respond to exercise varies widely. A new study by Thomas W. Buford et al. examines the ACE I/D gene and whether its variations—the ID, DD, and II genotypes—impact some seniors' ability to fully reap the benefits of exercise.
Researchers followed 424 sedentary, mobility-limited seniors ...
Brighter inks, without pigment
2014-03-14
Cambridge, Mass. – March 14, 2014 – Among the taxidermal specimens in Harvard's Museum of Comparative Zoology, past centuries-old fur coats, arises a flicker of brilliant blue. This is the spangled cotinga. Surprisingly, the cotinga is about as old as everything in the room, but its color is still as dazzling as the day it was brought to the museum. The cotinga—or rather its feathers—achieve this effect through structural color.
Unlike color that we usually think of, which arises from paints and dyes absorbing certain wavelengths of light and reflecting the remainder, ...
Patients should wait 6 to 12 weeks before driving after shoulder surgery
2014-03-14
NEW ORLEANS--More than 53,000 Americans have total shoulder joint replacement (SJR) surgery each year, and yet the effects of this surgery on a patient's ability to safely drive a vehicle, and the appropriate recovery time before patients should return to driving, have yet to be determined. In a new study, "Driving Performance after Total Shoulder Arthroplasty," presented today at the 2014 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), the driving skills of 28 shoulder replacement patients, with a mean age of 65 ±10 years, were tested at four distinct ...
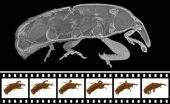
3-D X-ray film: Rapid movements in real time
2014-03-14
This news release is available in German. How does the hip joint of a crawling weevil move? A technique to record 3D X-ray films showing the internal movement dynamics in a spatially precise manner and, at the same time, in the temporal dimension has now been developed by researchers at ANKA, KIT's Synchrotron Radiation Source. The scientists applied this technique to a living weevil. From up to 100,000 two-dimensional radiographs per second, they generated complete 3D film sequences in real time or slow motion. The results are now published in the Proceedings of the ...
Patient requests for specific drugs have major impact on prescribing, reports study in Medical Care
2014-03-14
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 14, 2014) – Patient requests for specific medications—including requests for brand-name drugs spurred by direct-to-consumer (DTC) advertising—have a substantial impact on doctors' prescribing decisions, suggests a study in the April issue of Medical Care. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"A patient request for a specific medication dramatically increases the rate at which physician s prescribe that medication," according to the new research led by John B. McKinlay, PhD, of New England ...
Lurking in the darkness of Chinese caves 5 new species of armored spiders come to light
2014-03-14
Armored spiders are medium to small species that derive their name from the complex pattern of the plates covering their abdomen strongly resembling body armor. Lurking in the darkness of caves In Southeast China, scientists discover and describe five new species of these exciting group of spiders. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
The common name armored spiders is given to the engaging family Tetrablemmidae. Distinguished by their peculiar armor-like abdominal pattern, these tropical and subtropical spiders are mainly collected from litter ...
Dartmouth researchers develop new approach to chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment
2014-03-14
March 14, 2014 Lebanon, NH - Dartmouth researchers have developed a novel and unique approach to treating Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), a form of blood cancer that often requires repeated chemotherapy treatments to which it grows resistant. The researchers, led by Alexey V. Danilov, MD, PhD, assistant professor at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth and Hematologist-Oncologist at the Norris Cotton Cancer Center, modeled the lymph node microenvironment where CLL cells are found in the laboratory. They were able to disrupt the activity of a pathway (NF-kappaB) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
[Press-News.org] Researchers find significant increase in painkillers prescribed to US adults in the ERResearchers at GW found a dramatic increase in opioid prescriptions during emergency department visits over the last decade, while only a modest increase in pain-related complaints