(Press-News.org) Interim analysis of the intergroup EORTC-LYSA-FIL 20051 H10 trial published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology indicates an increased risk of early relapse when omitting radiotherapy in early PET scan negative patients with stage I/II Hodgkin's lymphoma. Early outcome, however, was excellent in both arms, and the final analysis should reveal whether these initial findings are maintained over time.
Dr. J.M.M. Raemaekers of the Radboud university medical center Nijmegen, The Netherlands, and central coordinator of the study says, "The standard treatment for patients with clinical stage I/II Hodgkin's Lymphoma is ABVD (adriamycin, bleomycin, vinblastin and dacarbazin) chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy. Striking the right balance between initial cure through combined modality treatment and accepting a higher risk of late complications, and a higher recurrence rate after omitting radiotherapy in subsets of patients who will subsequently need intensive salvage treatment, is a matter of unsettled debate."
The main objective of the H10 trial was to evaluate whether involved-node radiotherapy could be omitted without loss of efficacy in terms of progression-free survival in patients with stage I/II Hodgkin's Lymphoma who had a negative earlyPET scan after two cycles of ABVD chemotherapy. This interim trial analysis included a total of 1137 patients with untreated clinical stage I/II Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Of these, 444 patients had favorable and 693 unfavorable prognoses. Patients in each prognostic group were randomized between standard and experimental treatment and first received two cycles of ABVD chemotherapy. Patients in the experimental arm who attained a negative earlyPET scan after the two cycles of ABVD chemotherapy were spared involved-node radiotherapy.
For patients with a favorable prognosis and a negative earlyPET scan, one progression occurred in the standard arm and nine progressions occurred in the experimental arm. For patients with unfavorable prognosis and a negative earlyPET scan, seven events occurred in the standard arm and 16 events occurred in the experimental arm. Even though there were few events and the median follow-up time short, the Independent Data Monitoring Committee concluded it was unlikely that the final results would show non-inferiority for the experimental treatment. They, therefore, advised that randomization should be stopped for earlyPET negative patients.
INFORMATION:
The study was closed for recruitment in June 2011 with a total of 1952 patients.
The intergroup EORTC 20051 H10 trial is coordinated by the EORTC Lymphoma Group in collaboration with the LYmphoma Study Association (LYSA) and the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi (FIL). It is being conducted in 159 sites in eight countries: Belgium, Croatia, Denmark, France, Italy, Slovakia, Switzerland, and The Netherlands.
This randomized intergroup trial is supported by Fonds Cancer (FOCA), Belgium; Institut National du Cancer, France; Dutch Cancer Society, the Netherlands; Fondation contre le Cancer, France; Assistance Publique Hopitaux Paris, France; Societe Française de Medecine Nucleaire et Imagerie Moleculaire, France; Associazone Angela Serra, Italy; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd.
Increased risk of relapse omitting RT in early PET scan negative Hodgkin lymphoma
Interim results of randomized intergroup EORTC-LYSA-FIL 20051 H10 trial
2014-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds forest corridors help plants disperse their seeds
2014-03-19
A forest in South Carolina, a supercomputer in Ohio and some glow-in-the-dark yarn have helped a team of field ecologists conclude that woodland corridors connecting patches of endangered plants not only increase dispersal of seeds from one patch to another, but also create wind conditions that can spread the seeds for much longer distances.
The idea for the study emerged from modern animal conservation practices, where landscape connectivity – the degree to which landscapes facilitate movement – is being used to counteract the impacts of habitat loss and fragmentation ...
Inflammation mobilizes tumor cells
2014-03-19
Researchers of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have discovered a novel feedback mechanism that provides a mechanistic link between chronic inflammation and carcinogenesis.
Malignant tumors pose a major threat to survival largely because they shed mobile cells that can form secondary tumors in other tissues. This process requires a fundamental change in the character of cells within the primary tumor, insofar as members of a localized cell mass must be converted into actively migrating cells that invade into the surrounding tissue and blood vessels, and ...
IU, Regenstrief study: New noninvasive colorectal cancer screening tool highly accurate
2014-03-19
INDIANAPOLIS -- An Indiana University and Regenstrief Institute study of nearly 10,000 average-risk, asymptomatic men and women from 90 sites across the United States reports that a multi-target stool DNA test -- a new noninvasive colorectal cancer screening tool that has not yet been approved for sale by the Food and Drug Administration -- detects 92.3 percent of colon cancers, compared to only 73.8 percent of cancers detected by a fecal immunochemical test, the most commonly used noninvasive test today.
Study results were published online March 19 and in the April ...
Earliest evidence of limb bone marrow in the fin of a 370 million year old fish
2014-03-19
This week in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, a team of French and Swedish researchers present the earliest fossil evidence for the presence of bone marrow in the fin of a 370 million-year-old fish.
Long bones, which are found in the limb of tetrapods, are not only important for locomotion and supporting the weight of the body, but also host the bone marrow. The latter plays a major role in haematopoiesis, i.e. the formation of blood cells. In a healthy adult human, about a hundred billion to one trillion new blood cells are produced every day to maintain ...
Internists must play a larger role in managing menopausal symptoms
2014-03-19
New Rochelle, NY, March 19, 2014—The number of menopausal women is projected to reach 50 million by 2020. With changing views on appropriate therapies to control symptoms and new treatments available and on the horizon, most internists lack the core competencies and experience to meet the needs of women entering menopause, according to a provocative Commentary published in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://www.liebertpub.com/jwh.
The ...
Genetic test could improve colon cancer screening
2014-03-19
A non-invasive test that includes detection of the genetic abnormalities related to cancer could significantly improve the effectiveness of colon cancer screening, according to research published by a team of scientists including David Ransohoff, MD, professor of medicine at the UNC School of Medicine and UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center member. The large-scale, cross-sectional study was published online today in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The study compared two different types of tests used for screening colorectal cancer: a non-invasive, multitarget ...
Strategies for teaching common core to teens with autism show promise
2014-03-19
Scientists at UNC's Frank Porter Graham Child Development Institute (FPG) report that high school students with autism can learn under Common Core State Standards (CCSS), boosting their prospects for college and employment. Newly published recommendations from FPG's team also provide strategies for educating adolescents with autism under a CCSS curriculum.
"The number of students with autism who enter high school settings continues to grow," said Veronica P. Fleury, lead author and postdoctoral research associate with FPG's Center on Secondary Education for Students with ...
New technique makes LEDs brighter, more resilient
2014-03-19
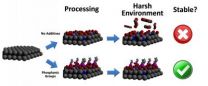
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new processing technique that makes light emitting diodes (LEDs) brighter and more resilient by coating the semiconductor material gallium nitride (GaN) with a layer of phosphorus-derived acid.
"By coating polar GaN with a self-assembling layer of phosphonic groups, we were able to increase luminescence without increasing energy input," says Stewart Wilkins, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the work. "The phosphonic groups also improve stability, making the GaN less likely ...
Chemo-free treatment a possibility for leukemia/lymphoma
2014-03-19
Patients with terminal forms of leukaemia and lymphoma who have run out of treatment options could soon benefit from a new drug, which not only puts an end to chemotherapy and has virtually no side effects but also improves a patient's life expectancy and quality of life.
It has been described as a breakthrough in cancer treatment by a leading professor in haematology, who presented the findings of the Phase 1 trial at an international conference in New Orleans in December 2013.
Professor Simon Rule, Consultant Haematologist at Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust and researcher ...
Neuroscience 'used and abused'
2014-03-19
Influential policy-informing 'evidence' that children's brains are irreversibly 'sculpted' by parental care is based on questionable evidence.
The researchers warn that the success that advocates of 'brain-based' parenting have had in influencing government policy could undermine parent-child relationships.
The study identified that although there is a lack of scientific foundation to many of the claims of 'brain-based' parenting, the idea that years 0-3 are neurologically critical is now repeated in policy documents and has been integrated into professional training ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Increased risk of relapse omitting RT in early PET scan negative Hodgkin lymphomaInterim results of randomized intergroup EORTC-LYSA-FIL 20051 H10 trial