(Press-News.org) In a study published today (19/3/2014) in the scientific journal Neuron, neuroscientists at the Champalimaud Foundation, in collaboration with neuroscientists from Harvard University, describe the first activity maps at the resolution of single cells and throughout the entire brain of behaving zebrafish.
"This opens up new possibilities for studying neural circuits in the brain," says Michael Orger, principal investigator at the Champalimaud Neuroscience Programme. "In order to understand how the brain works, it is imperative that we can record the activity of the cells of the brain – the neurons, and at the same time be able to relate that to an animal's behaviour". Until recently, available methods allowed researchers to monitor activity in only a small fraction of the neurons in the brain, but "Now, we can systematically record activity through the whole brain of the zebrafish, which contains about one hundred thousand neurons, while at the same time we are monitoring its movements using high speed video."
Claudia Feierstein, a postdoctoral fellow in the lab of Dr. Orger explains, "by watching the brain while the fish tries to follow rotating visual patterns by moving its eyes and tail, we were able to identify the specific brain structures that are involved in these behaviours, and how different patterns of activity reflect the different aspects of sensory and motor processing."
One of the strengths of this method is that, because whole brain activity maps are recorded from a single fish, rather than pieced together across multiple experiments, it is possible to compare the neural circuit organization across different individuals. "When we talk about brain activity maps," says Dr. Orger "an important question is to what extent the circuits in different animals are similar. How precisely can we predict where we will find particular neurons from one brain to another?".
Surprisingly, the study revealed that, while the network of neurons mediating simple visual-motor behaviours is widely distributed across the brain, the pattern can be highly stereotyped between individuals. "If you identify a region with a particular pattern of activity in one fish, you can typically find neurons with the same activity within a few micrometers in the brain of another fish." says Ruben Portugues, a scientist from the group of Professor Florian Engert at Harvard, who coauthored the study. This has important practical consequences, because it makes it possible to build a detailed functional atlas of the brain, which allows researchers to locate and target specific groups of neurons. This map of functional "blocks" can also be aligned with existing maps of gene expression to assign behavioural roles to different cell types in the brain.
This systematic approach to mapping activity also enables researchers to discover rare cell populations that might have stayed hidden for decades. "We found a handful of neurons in the main visual processing area of the fish brain, called the optic tectum, that integrate motion information from both eyes. This was surprising since this area only gets direct information from one eye." Says Dr. Orger. "These cells are few in number, but may play an important role in the behaviour of the animal, since they allow him to decode how he is moving through the water." According to the researchers, the next step is to use optical and genetic targeting of interesting subpopulations of neurons, such as this one, and apply specific manipulations that will ultimately reveal how the brain processes sensory information to generate appropriate movements.
INFORMATION: END
Study describes first maps of neural activity in behaving zebrafish
Champalimaud Foundation neuroscientists publish in the scientific journal Neuron
2014-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers uncover allergy-cancer connection
2014-03-19
While many are stocking up on allergy medicine in preparation for spring, a new study from researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center has uncovered a new connection between allergy and cancer that could potentially lead to therapies involving common antihistamines.
Recently published in the Journal of Leukocyte Biology, the study was led by Daniel H. Conrad, Ph.D., member of the Cancer Cell Signaling research program at Massey and professor of microbiology and immunology at the VCU School of Medicine, with substantial contributions from Ph.D. ...
Growing rice the sustainable way: LEGATO holds its 3rd annual conference
2014-03-19
In a world facing the challenges of climate change, demographic boom and deficit in food resources, the word "sustainable" and the concept behind it become increasingly relevant. Sustainability in the way humanity uses available resources is key to a brighter and greener future.
In the context of sustainable food production, there is a clear need for crop productivity increases and diversification. Optimising rice ecosystem functions and services in Southeast Asia and their stabilisation under future land use and climate change, is the main focus of the project LEGATO ...
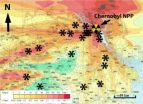
Radiation damage at the root of Chernobyl's ecosystems
2014-03-19
Radiological damage to microbes near the site of the Chernobyl disaster has slowed the decomposition of fallen leaves and other plant matter in the area, according to a study just published in the journal Oecologia. The resulting buildup of dry, loose detritus is a wildfire hazard that poses the threat of spreading radioactivity from the Chernobyl area.
Tim Mousseau, a professor of biology and co-director of the Chernobyl and Fukushima Research Initiatives at the University of South Carolina, has done extensive research in the contaminated area surrounding the Chernobyl ...
Research reveals true value of cover crops to farmers, environment
2014-03-19
Planting cover crops in rotation between cash crops -- widely agreed to be ecologically beneficial -- is even more valuable than previously thought, according to a team of agronomists, entomologists, agroecologists, horticulturists and biogeochemists from Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
"As society places increasing demands on agricultural land beyond food production to include ecosystem services, we needed a new way to evaluate 'success' in agriculture," said Jason Kaye, professor of biogeochemistry. "This research presents a framework for considering ...
Researchers identify potential new therapeutic target for controlling high blood sugar
2014-03-19
DALLAS – March 19, 2014 – A UT Southwestern Medical Center study has identified a new potential therapeutic target for controlling high blood sugar, a finding that could help the estimated 25 million Americans with type 2 diabetes.
Researchers showed that lipid molecules called phosphatidic acids enhance glucose production in the liver. These findings suggest that inhibiting or reducing production of phosphatidic acids may do the opposite.
“This study establishes a role for phosphatidic acids in enhancing glucose production by the liver and identifies enzymes involved ...
NASA sees ex-Tropical Cyclone Gillian affect Indonesia
2014-03-19
The remnants of former Tropical Cyclone Gillian moved out of the Southern Pacific Ocean and into the Indian Ocean only to trigger warnings and watches for part of Indonesia on March 19. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the stubborn storm and took a visible image of the re-organizing tropical low pressure area.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Gillian's remnants on March 19 at 05:30 UTC/1:30 a.m. EDT and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument took a visible picture of the storm. The image showed that the storm appeared to be well-defined, ...
Satellite sees newborn So. Pacific Tropical Storm Mike
2014-03-19
NOAA's GOES-West satellite caught the birth of Tropical Storm Mike in the Southern Pacific Ocean on March 19. Mike's formation has generated warnings for the Southern Cook Islands.
NOAA's GOES-West or GOES-15 satellite captured an infrared image of newborn Tropical Storm Mike in the Southwestern Pacific Ocean on March 19 at 1200 UTC/8 a.m. EDT. Mike appeared to be a compact, rounded tropical storm with bands of thunderstorms wrapping into it. NOAA's GOES-West satellite sits in a fixed orbit in space capturing visible and infrared imagery of all weather over the western ...
The scientific legacy of colonialism in Africa
2014-03-19
Colonial legacy has a significant impact on scientific productivity across the continent of Africa, according to a study by researchers at the University of Lomé, in Togo. Writing in the International Journal of Education Economics and Development, the team suggests that Africa performs relatively poorly compared with other regions of the world. Moreover, their analysis of data for the period 1994 to 2009 shows that African nations with a British colonial legacy are much more productive than countries with French or other history. This, the team adds, correlates with superior ...
French Alps Property Market Witnesses a Surge in Interest From International Buyers
2014-03-19
Demand for property in the Alps is on the increase with a growing number of foreigners looking to invest in resorts such as Chamonix, according to new figures.
Property agents in Chamonix, a resort in France's Savoie region and one of the key Alpine winter destinations, are reporting soaring property demand, much of which is being driven by the international buyers. The real estate agents also revealed an increase in property prices of more than eight per cent during 2013. This surge in interest can be attributed to the infrastructure upgrades in Chamonix and also to ...
Catching the early spread of breast cancer
2014-03-19
DALLAS, March 19, 2014 — When cancer spreads from one part of the body to another, it becomes even more deadly. It moves with stealth and can go undetected for months or years. But a new technology that uses "nano-flares" has the potential to catch these lurking, mobilized tumor cells early on. Today, scientists presented the latest advances in nano-flare technology as it applies to the detection of metastatic breast cancer cells.
The report was one of more than 10,000 at the 247th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS). The meeting is taking ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
The ISSCR honors stem cell COREdinates and CorEUstem with the 2026 ISSCR Public Service Award
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
[Press-News.org] Study describes first maps of neural activity in behaving zebrafishChampalimaud Foundation neuroscientists publish in the scientific journal Neuron