(Press-News.org) Alexandria, Va., USA – Today during the 43rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition of the American Association for Dental Research, held in conjunction with the 38th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research, Mathilde C. Peters, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, USA, will present research titled "Resin Infiltration Effects in a Caries-Active Environment – 2 Year Results."
The objective of this study was to compare carious lesion changes after resin infiltration of approximal non-cavitated lesions in a high caries risk population after two years. Resin infiltration (I=Icon, DMG-Germany) was compared to mock infiltration (C=Control) in a split-mouth RCT. Lesion progression was monitored at two levels (lesion depth rating (E2/D1/D2) and lesion depth changes within ratings) in caries-active subjects (mean DMFT=7.4+2.0, age=14-36yrs), receiving standard-of-care preventive measures including F-supplementation.
After two years, 15 tooth pairs (68% recall) in 10 patients were available for analysis. Lesion depth rating and depth increase (within ratings) were visually determined from digital radiographs by two independent examiners (intra-/inter-evaluator agreement: k>0.70). Depth increase was confirmed by digital subtraction radiography (SDR). Ratings were statistically analyzed by logistic regression. Discrete time survival analysis (logistic regression and GEE modeling) was used to examine effects of treatment on probability of lesion increase over time, controlling for baseline severity.
The researchers found that infiltration successfully stabilized early non-cavitated lesions in a small population with high caries-activity. Continuing follow-up may further confirm its efficacy.
This pilot study identified important promising trends between the plaque and salivary metabolomes from caries-active and caries-free children, despite a relatively low number of subjects.
INFORMATION:
This study was supported in part by DMG Germany and University of Michigan.
This is a summary of abstract #161, "Resin Infiltration Effects in a Caries-Active Environment – 2 Year Results," which will be presented on Thursday, March 20, 2014: 10:45 a.m. – 12:15 p.m. in Exhibit Hall AB of the Charlotte Convention Center.
About the American Association for Dental Research
The American Association for Dental Research (AADR), headquartered in Alexandria, Va., is a nonprofit organization with more than 3,600 members in the United States. Its mission is: (1) to advance research and increase knowledge for the improvement of oral health; (2) to support and represent the oral health research community; and (3) to facilitate the communication and application of research findings. AADR is the largest Division of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR). To learn more about the AADR, visit http://www.aadr.org.
Resin infiltration effects in a caries-active environment -- 2 year results
2014-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Thermal conductance can be controlled like waves using nanostructures
2014-03-20
Thermal conduction is a familiar everyday phenomenon. In a hot sauna, for instance, you can sit comfortably on a wooden bench that has a temperature of 100C (212F), but if you touch a metallic nail with the same temperature, you will hurt yourself. The difference of these two experiences is due to the fact that some materials, such as metals, conduct heat well, whereas some other materials, such as wood, do not. It is therefore commonly thought that thermal conductance is simply a materials parameter. Now, researchers at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland, led by Professor ...
Oldest fossil evidence of modern African venomous snakes found in Tanzania
2014-03-20
ATHENS, Ohio (March 19, 2014)—Ohio University scientists have found the oldest definitive fossil evidence of modern, venomous snakes in Africa, according to a new study published March 19 in the journal PLOS ONE.
The newly discovered fossils demonstrate that elapid snakes—such as cobras, kraits and sea snakes—were present in Africa as early as 25 million years ago, said lead author Jacob McCartney, a postdoctoral researcher in the Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine. He's part of a team that has been examining the Rukwa Rift Basin of Tanzania over ...
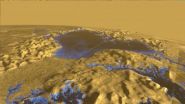
Surface of Titan Sea is mirror smooth, Stanford scientists find
2014-03-20
New radar measurements of an enormous sea on Titan offer insights into the weather patterns and landscape composition of the Saturnian moon. The measurements, made in 2013 by NASA's Cassini spacecraft, reveal that the surface of Ligeia Mare, Titan's second largest sea, possesses a mirror-like smoothness, possibly due to a lack of winds.
"If you could look out on this sea, it would be really still. It would just be a totally glassy surface," said Howard Zebker, professor of geophysics and of electrical engineering at Stanford who is the lead author of a new study detailing ...
Parents should try to find middle ground to keep teens safe online
2014-03-20
Parents might take a lesson from Goldilocks and find a balanced approach to guide their teens in making moral, safe online decisions, according to Penn State researchers.
In a study on parenting strategies and online adolescent safety, the researchers found evidence that suggests that parents should try to establish a middle ground between keeping their teens completely away from the internet not monitoring their online activities at all.
"It's a Goldilocks problem," said Pamela Wisniewski, a postdoctoral scholar in information sciences and technology. "Overly restrictive ...
Low levels of oxgen, nitric oxide worsen sickle cell disease
2014-03-20
Low levels of both oxygen and the powerful blood vessel dilator nitric oxide appear to have an unfortunate synergy for patients with sickle cell disease, researchers report.
Their studies indicate that the two conditions common in sickle cell disease, dramatically increase red blood cells' adhesion to the lining of blood vessels walls and the debilitating pain crises that can result.
The good news is that restoring normal levels of nitric oxide can substantially reduce red blood cell adhesion, said Dr. Tohru Ikuta, a molecular hematologist at the Medical College of ...
School hearing tests do not detect noise exposure hearing loss
2014-03-20
School hearing tests cannot effectively detect adolescent high-frequency hearing loss, which is typically caused by loud noise exposure, according to researchers at Penn State College of Medicine.
The Pennsylvania Department of Health mandates school-administered hearing screens for children in kindergarten to third, seventh and 11th grades. The school screenings primarily focus on low-frequency hearing loss. This is logical for young children, who are more likely to develop low-frequency hearing loss due to fluid in the ear after a bad cold or an ear infection. Adolescents, ...
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria among children in the United States on the rise
2014-03-20
(Chicago)--Infections caused by a specific type of antibiotic-resistant bacteria are on the rise in U.S. children, according to new study published in the Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. While still rare, the bacteria are increasingly found in children of all ages, especially those 1-5 years old, raising concerns about dwindling treatment options.
"Some infections in children that have typically been treated with oral antibiotics in the past may now require hospitalization, treatment with intravenous drugs, or both, as there may not be an oral treatment ...
Obesity and diabetes have adverse effects on cancer outcomes
2014-03-20
Both obesity and diabetes have adverse effects on outcomes in breast cancer patients who receive chemotherapy as primary treatment before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy), according to research to be presented at the 9th European Breast Cancer Conference (EBCC-9) tomorrow (Friday). Although a high body mass index (BMI) is known to have a negative impact on cancer development and prognosis, until now there has been uncertainty as to whether having a high BMI had an equal effect on patients with different types of breast tumours.
Dr Caterina Fontanella, MD, a trainee in ...
Deaths from breast cancer fall in Europe
2014-03-20
Improvements in treatment, as well as enhanced access to care, underlie the sustained decreases in breast cancer mortality seen in 30 European countries [1] from 1989 to 2010. But there are notable variations between different countries that cannot be explained simply by the resources devoted to cancer care, and these differences need to be studied further, according to research to be presented to the 9th European Breast Cancer Conference (EBCC-9) tomorrow (Friday).
Professor Philippe Autier, from the International Prevention Research Institute, Lyon, France, told a press ...
In the genome of loblolly pine lies hope for better resistance to a damaging disease
2014-03-20
"The project was a huge undertaking because at 22 gigabases, the loblolly pine genome is about eight times larger than the human genome," said C. Dana Nelson, SRS Southern Institute for Forest Genetics (SIFG) project leader and research geneticist. "The group chose loblolly pine both because of its economic importance, and the knowledge gained from 60 years of breeding the species and managing millions of trees in genetic trials."
As part of the project, researchers identified a candidate for a gene involved in resistance to fusiform rust, a disease that infects southern ...