(Press-News.org) (SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — For the first time, scientists have succeeded in coaxing laboratory cultures of human stem cells to develop into the specialized, unique cells needed to repair a patient's defective or diseased bladder.
The breakthrough, developed at the UC Davis Institute for Regenerative Cures and published today in the scientific journal Stem Cells Translational Medicine, is significant because it provides a pathway to regenerate replacement bladder tissue for patients whose bladders are too small or do not function properly, such as children with spina bifida and adults with spinal cord injuries or bladder cancer.
"Our goal is to use human stem cells to regenerate tissue in the lab that can be transplanted into patients to augment or replace their malfunctioning bladders," said Eric Kurzrock, professor and chief of the division of pediatric urologic surgery at UC Davis Children's Hospital and lead scientist of the study, which is titled "Induction of Human Embryonic and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Urothelium."
To develop the bladder cells, Kurzrock and his UC Davis colleagues investigated two categories of human stem cells. In their key experiments, they used induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), which were derived from lab cultures of human skin cells and umbilical blood cells that had been genetically reprogrammed to convert to an embryonic stem cell-like state.
If additional research demonstrates that grafts of bladder tissue grown from human stem cells will be safe and effective for patient care, Kurzrock said that the source of the grafts would be iPS cells derived from a patient's own skin or umbilical cord blood cells. This type of tissue would be optimal, he said, because it lowers the risk of immunological rejection that typifies most transplants.
In their investigation, Kurzrock and his colleagues developed a protocol to prod the pluripotent cells into becoming bladder cells. Their procedure was efficient and, most importantly, the cells proliferated over a long period of time — a critical element in any tissue engineering application.
"What's exciting about this discovery is that it also opens up an array of opportunities using pluripotent cells," said Jan Nolta, professor and director of the UC Davis Stem Cell program and a co-author on the new study. "When we can reliably direct and differentiate pluripotent stem cells, we have more options to develop new and effective regenerative medicine therapies. The protocols we used to create bladder tissue also provide insight into other types of tissue regeneration."
UC Davis researchers first used human embryonic stem cells obtained from the National Institutes of Health's repository of human stem cells. Embryonic stem cells can become any cell type in the body (i.e., they are pluripotent), and the team successfully coaxed these embryonic stem cells into bladder cells. They then used the same protocol to coax iPS cells made from skin and umbilical cord blood into bladder cells, called urothelium, that line the inside of the bladder. The cells expressed a very unique protein and marker of bladder cells called uroplakin, which makes the bladder impermeable to toxins in the urine.
The UC Davis researchers adjusted the culture system in which the stem cells were developing to encourage the cells to proliferate, differentiate and express the bladder protein without depending upon signals from other human cells, said Kurzrock. In future research, Kurzrock and his colleagues plan to modify the laboratory cultures so that they will not need animal and human products, which will allow use of the cells in patients.
Kurzrock's primary focus as a physician is with children suffering from spina bifida and other pediatric congenital disorders. Currently, when he surgically reconstructs a child's defective bladder, he must use a segment of their own intestine. Because the function of intestine, which absorbs food, is almost the opposite of bladder, bladder reconstruction with intestinal tissue may lead to serious complications, including urinary stone formation, electrolyte abnormalities and cancer. Developing a stem cell alternative not only will be less invasive, but should prove to be more effective, too, he said.
Another benefit of the UC Davis study is the insight it may provide about the pathways of bladder cancer, which is diagnosed in more than 70,000 Americans each year, according to the National Cancer Institute. "Our study may provide important data for basic research in determining the deviations from normal biological processes that trigger malignancies in developing bladder cells," said Nolta. More than 90 percent of patients who need replacement bladder tissue are adults with bladder cancer. Kurzrock said "cells from these patients' bladders cannot be used to generate tissue grafts because the implanted tissue could carry a high risk of becoming cancerous. On the other hand, using bladder cells derived from patients' skin may alleviate that risk. Our next experiments will seek to prove that these cells are safer."
INFORMATION:
The UC Davis research was supported by a grant from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (the state stem cell agency). Shriner's Hospitals for Children has also provided Dr. Kurzrock with grant funds to explore pediatric bladder tissue regeneration.
In addition to Kurzrock and Nolta, co-authors of the paper are Stephanie L. Osborn, Ravikumar Thangappan, Ayala Luria, and Justin H. Lee.
UC Davis is playing a leading role in regenerative medicine, with nearly 150 scientists working on a variety of stem cell-related research projects at campus locations in both Davis and Sacramento. The UC Davis Institute for Regenerative Cures, a facility supported by the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), opened in 2010 on the Sacramento campus. This $62 million facility is the university's hub for stem cell science. It includes Northern California's largest academic Good Manufacturing Practice laboratory, with state-of-the-art equipment and manufacturing rooms for cellular and gene therapies. UC Davis also has a Translational Human Embryonic Stem Cell Shared Research Facility in Davis and a collaborative partnership with the Institute for Pediatric Regenerative Medicine at Shriners Hospital for Children Northern California. All of the programs and facilities complement the university's Clinical and Translational Science Center, and focus on turning stem cells into cures. For more information, visit http://www.ucdmc.ucdavis.edu/stemcellresearch.
Stem cell findings may offer answers for some bladder defects and disease
2014-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Keck Medicine of USC research may point to better predictor of prostate cancer survival
2014-03-21
New research by USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center scientists demonstrates that measuring circulating tumor cells (CTCs) – the cells that spread cancer through the body – may be a better predictor of patient survival than the prostate specific antigen (PSA).
The research was published March 10, 2014 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology by a team led by Amir Goldkorn, M.D., assistant professor of medicine at USC Norris, part of Keck Medicine of USC. Goldkorn's team discovered that elevated CTC counts after chemotherapy indicated as much as a five-fold higher risk of ...
Cold snare polypectomy effective for removal of small colorectal polyps in patients on anticoagulants
2014-03-21
DOWNERS GROVE, Ill. – March 21, 2014 – In recognition of National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month, GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy has published a special issue for March on colorectal cancer. The issue includes a new study that compares cold snare polypectomy with conventional polypectomy for the removal of small colorectal polyps in anticoagulated patients. The study showed that delayed bleeding requiring hemostasis (stoppage of bleeding) occurred significantly less often after cold snare polypectomy than during conventional polypectomy despite continuation of anticoagulants. ...
Genetic signature reveals new way to classify gum disease
2014-03-21
NEW YORK, NY (March 21, 2014) — Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) have devised a new system for classifying periodontal disease based on the genetic signature of affected tissue, rather than on clinical signs and symptoms. The new classification system, the first of its kind, may allow for earlier detection and more individualized treatment of severe periodontitis, before loss of teeth and supportive bone occurs. The findings were published recently in the online edition of the Journal of Dental Research.
Currently, periodontal disease is classified ...
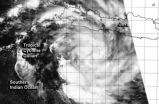
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Gillian reborn near Java
2014-03-21
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the reborn tropical cyclone known as Gillian on March 21 and captured a visible image of the storm, located just south of the island of Java.
Java is highly populated island of Indonesia that includes the capital city of Jakarta. Java is divided into four provinces, East, West and Central Java and Banten. There are also two special regions of Java called Jakarta and Yogyakarta.
The MODIS instrument that flies aboard Aqua captured a visible image of Gillian on March 21 at 06:55 UTC/2:55 a.m. EDT. The image showed bands of thunderstorms ...
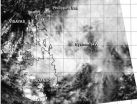
NASA's Aqua satellite sees Tropical System 94W affecting Philippines
2014-03-21
The tropical low pressure area centered just east of the southern Philippines appeared more organized on visible imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite on March 21. System 94W appears to be developing and the Philippine authorities have already issued warnings on the system locally designated as "Caloy."
The MODIS instrument (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of System 94W coming together east of the southern Philippines on March 21 at 5:25 UTC/1:25 a.m. EDT. The image revealed a circulation with ...
Deep ocean current may slow due to climate change, Penn research finds
2014-03-21
Far beneath the surface of the ocean, deep currents act as conveyer belts, channeling heat, oxygen, carbon and nutrients around the globe.
A new study by the University of Pennsylvania's Irina Marinov and Raffaele Bernardello and colleagues from McGill University has found that recent climate change may be acting to slow down one of these conveyer belts, with potentially serious consequences for the future of the planet's climate.
"Our observations are showing us that there is less formation of these deep waters near Antarctica," Marinov said. "This is worrisome because, ...
Pushing and pulling: Using strain to tune a new quantum material
2014-03-21
Research into a recently discovered class of materials shows they have the necessary characteristics to develop ultra-energy efficient electronics. Topological insulators (TI) are three-dimensional materials that conduct electricity on their surfaces, while the interior insulates.
Their surfaces are particularly unique because the motion of the electrons is "protected" by symmetry, meaning electrons will keep moving without scattering even when they encounter defects and contamination.
In fact, electrons on the surface of TIs move so robustly scientists are trying ...
Computers spot false faces better than people
2014-03-21
TORONTO, ON — A joint study by researchers at the University of California San Diego and the University of Toronto has found that a computer system spots real or faked expressions of pain more accurately than people can. The work, titled "Automatic Decoding of Deceptive Pain Expressions," is published in the latest issue of Current Biology.
"The computer system managed to detect distinctive dynamic features of facial expressions that people missed," said Marian Bartlett, research professor at UC San Diego's Institute for Neural Computation and lead author of the study. ...
Characteristics of lung cancers arising in germline EGFR T790M mutation carriers
2014-03-21
DENVER –Two studies are providing new insight into germline epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation in familial non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The findings suggest the need for tailored approaches for early detection and treatment, as well as for genetic testing to identify carriers.
"These studies now solidify the fact that routine clinical management of lung cancer now has to include the awareness of this inherited cancer syndrome," wrote David P. Carbone, MD, PhD, President-Elect of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer ...
Ground-improvement methods might protect against earthquakes
2014-03-21
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Researchers from the University of Texas at Austin's Cockrell School of Engineering are developing ground-improvement methods to help increase the resilience of homes and low-rise structures built on top of soils prone to liquefaction during strong earthquakes.
Findings will help improve the safety of structures in Christchurch and the Canterbury region in New Zealand, which were devastated in 2010 and 2011 by a series of powerful earthquakes. Parts of Christchurch were severely affected by liquefaction, in which water-saturated soil temporarily ...