(Press-News.org) HOUSTON – (March 27, 2014) – National efforts in the last decade to clear the air of dangerous particulate matter have been so successful that most urban areas have already attained the next benchmark, according to new research by Rice University.
Atmospheric researchers at Rice studied the state implementation plans (SIPs) from 23 regions mandated by the Environmental Protection Agency to reduce particulate matter (PM) smaller than 2.5 microns (PM 2.5) to less than 15 micrograms per cubic meter by 2009.
The Rice analysis appears this week in the Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association.
All but one of the regions studied reported they had met the goal by deadline. States with regions that met the deadline included Connecticut, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, Missouri, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee and West Virginia, as well as the District of Columbia. The final region, Alabama, reported attainment in 2010.
PM 2.5 concentrations in the nonattainment regions that filed SIPs to attain the standard by 2009 declined by an average 2.6 micrograms per cubic meter – significantly greater improvement than in regions that had attained the standard from its inception. The study showed PM reductions in the SIP regions were broadly spread, rather than pinpointed at the most polluted monitors.
"One of the things we were most interested in looking at was to see if states were cherry-picking their measures to meet the standard by reducing pollution at their worst monitors, compared with how much they were doing to bring down levels all across the region so that people were breathing cleaner air," said Daniel Cohan, an associate professor of civil and environmental engineering at Rice.
"It was encouraging to find that across the country, we have seen overall particulate-matter levels come down. We found very slight extra improvement at monitors that were targeted the most, but regions that had to develop plans achieved pretty solid controls that didn't just pinpoint the worst monitors. And the large populations of these regions benefited."
Cohan and Rice alumna Ran Chen also documented that air pollution continued to decline even after the 2009 standards were met. The majority of the SIP regions had already attained the mandated 2014 goal of 12 micrograms per cubic meter by 2012.
"We've been on a good trajectory," Cohan said. "This demonstrates that the combination of state and federal controls has been substantially improving air quality in the U.S."
Recent stories about the ongoing crisis in Beijing, where PM has reached hazardous levels, and in rapidly industrializing countries such as India set the U.S. efforts in sharp relief, Cohan said. The World Health Organization announced this month that about 7 million people die each year as a result of air pollution exposure.
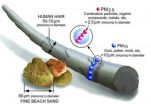
Particulate matter consists of microscopic particles spewed into the air by vehicles and industry, as well as particles that form from pollutant gases. "Particulate matter is not a chemical, like ozone; it's a category, and it's a real challenge to figure out the origin of those particles," Cohan said. "Are they sulfates or carbons or nitrates? Each of these needs vastly different control approaches to make a difference."
PM also includes natural emissions from plants, volcanoes, forest fires and desert dust and can be blown across states or even continents.
The health community, Cohan said, has long expressed concerns about particulate matter in the atmosphere and determined in the 1990s that PM 2.5 particles can penetrate deeply into the lungs and cause heart attacks, decrease lung function and even cause premature death. The EPA found healthy people could experience symptoms from exposure to elevated levels of particulate matter and set mandates for regions deemed in 1997 to be in "nonattainment" to file cleanup plans and follow through by 2009.
The study was the first to take a comprehensive, retrospective look at the overall effectiveness of SIPs for PM. A previous study by Cohan and alumnus Andrew Pegues conducted similar analysis of progress by states in achieving ozone standards.
INFORMATION:
The National Science Foundation and the NASA Air Quality Applied Sciences Team funded the research.
Read the abstract at http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10962247.2014.905509#.UzQw71zbQ7Q
This news release can be found online at http://news.rice.edu/2014/03/27/us-clean-air-efforts-stay-on-target/
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
Related Materials:
Cohan Research Group: https://cohan.rice.edu
EPA Particulate Matter page: http://epa.gov/air/particlepollution/
Image for download:
http://news.rice.edu/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/0331_PM-GRAPHIC-1-web.jpg
The Environmental Protection Agency regulates inhalable particles that can lodge in lung tissue and affect human health. (Credit: EPA)
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,920 undergraduates and 2,567 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6.3-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go here.
David Ruth
713-348-6327
david@rice.edu
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
mikewilliams@rice.edu
US clean-air efforts stay on target
Rice University analysis of state efforts show dramatic gains in reducing airborne particulate matter
2014-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mechanical forces driving breast cancer lead to key molecular discovery
2014-03-27
The stiffening of breast tissue in breast-cancer development points to a new way to distinguish a type of breast cancer with a poor prognosis from a related, but often less deadly type, UC San Francisco researchers have found in a new study.
The findings, published online March 16, 2014 in Nature Medicine, may lead eventually to new treatment focused not only on molecular targets within cancerous cells, but also on mechanical properties of surrounding tissue, the researchers said.
In a mouse model of breast cancer, scientists led by Valerie Weaver, PhD, professor of ...
Notre Dame scientists develop largest developmental proteomic data set for any animal
2014-03-27
Now that the human genome is sequenced, University of Notre Dame researchers are focusing on the study of the proteome, which is the protein content of an organism, tissue or cell. Bioanalytical chemist Norman Dovichi and molecular biologist Paul Huber have successfully tracked the changing patterns of protein expression during early development of Xenopus laevis, or African clawed frog, embryos. They have developed the largest data set on developmental proteomics for any organism, and have included the single-cell zygote.
Their research has uncovered an unexpected amount ...
The circadian clock is like an orchestra with many conductors
2014-03-27
ANN ARBOR—You've switched to the night shift and your weight skyrockets, or you wake at 7 a.m. on weekdays but sleep until noon on weekends—a social jet lag that can fog your Saturday and Sunday.
Life runs on rhythms driven by circadian clocks, and disruption of these cycles is associated with serious physical and emotional problems, says Orie Shafer, a University of Michigan assistant professor of molecular, cellular and developmental biology.
Now, new findings from Shafer and U-M doctoral student Zepeng Yao challenge the prevailing wisdom about how our body clocks ...
Scientists synthesize first functional 'designer' chromosome in yeast
2014-03-27
An international team of scientists led by Jef Boeke, PhD, director of NYU Langone Medical Center's Institute for Systems Genetics, has synthesized the first functional chromosome in yeast, an important step in the emerging field of synthetic biology, designing microorganisms to produce novel medicines, raw materials for food, and biofuels.
Over the last five years, scientists have built bacterial chromosomes and viral DNA, but this is the first report of an entire eukaryotic chromosome, the threadlike structure that carries genes in the nucleus of all plant and animal ...
New way to filter light
2014-03-27
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Light waves can be defined by three fundamental characteristics: their color (or wavelength), polarization, and direction. While it has long been possible to selectively filter light according to its color or polarization, selectivity based on the direction of propagation has remained elusive.
But now, for the first time, MIT researchers have produced a system that allows light of any color to pass through only if it is coming from one specific angle; the technique reflects all light coming from other directions. This new approach could ultimately lead ...
Quality early childhood programs help prevent chronic diseases in later life
2014-03-27
Disadvantaged children who attend high-quality early childhood development programs including healthcare and nutrition have significantly improved health as adults, reports a new study.
The study was led by researchers from UCL (University College London), the University of Chicago and the University of North Carolina. These findings build upon existing evidence that high-quality early childhood programs produce better economic and social outcomes for disadvantaged children.
Based on more than three decades of studying children involved in the Abecedarian program ...
Study shows promise of preserving fertility in boys with cancer
2014-03-27
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – March 27, 2014 – Scientists have moved a step closer to being able to preserve fertility in young boys who undergo chemotherapy and radiation treatments for cancer. The new research, published in Fertility and Sterility, the journal of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, addresses the safety of an option scientists are developing for boys who aren't sexually mature and cannot bank sperm.
Scientists aim to freeze a sample of the boys' testicular tissue so that when they reach adulthood, spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs) found in the ...
Research from CHORI scientists demonstrates first genome methylation in fruit fly
2014-03-27
March 27, 2013, Oakland, CA – A group of scientists from Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute and UC Berkeley report the first mapping of genome methylation in the fruit-fly Drosophila melanogaster in their paper "Genome methylation in D. melanogaster is found at specific short motifs and is independent of DNMT2 activity," published this month in Genome Research.
This paper represents a major advance in the study of DNA methylation in insects. No previous study has succeeded in pinpointing the location of DNA methylation in the fly genome. The common opinion ...
Natural history dying of neglect
2014-03-27
Natural history provides essential knowledge for human wellbeing, yet its research, use and instruction in academia, government agencies and non-government organizations is declining drastically.
Simon Fraser University ecologist Anne Salomon is among 17 authors of a new paper that claims this decline in the developed world could seriously undermine the world's progress in research, conservation and management.
The paper, Natural History's Place in Science and Society, evaluates the state of natural history research and use today. The journal BioScience has just published ...
Antidepressants during pregnancy linked to preterm birth
2014-03-27
BOSTON -- Antidepressant medications taken by pregnant women are associated with increased rates of preterm birth. This finding reinforces the notion that antidepressants should not be used by pregnant women in the absence of a clear need that cannot be met through alternative approaches, say researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital, Vanderbilt University, MetroWest Medical Center, and Tufts Medical Center.
"Preterm birth is a major clinical problem throughout the world and rates have been increasing over the past two decades. At the same time, rates of antidepressant ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] US clean-air efforts stay on targetRice University analysis of state efforts show dramatic gains in reducing airborne particulate matter