(Press-News.org) The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has released the final report on its technical investigation into the impacts of the May 22, 2011, tornado that struck Joplin, Mo. The final report is strengthened by clarifications and supplemental text suggested by organizations and individuals from across the nation in response to the request for comments on the draft Joplin report, released Nov. 21, 2013.
The revisions did not alter the investigation team's major findings or its 16 recommendations, highlighted by NIST's call for nationally accepted standards for building design and construction, public shelters and emergency communications that can significantly reduce deaths and the steep economic costs of property damage caused by tornadoes.
NIST will now work with the appropriate code development organizations to use the study's recommendations to improve model building codes and lay the foundation for nationally accepted standards. NIST also will work with organizations representing state and local governments—including building officials—to encourage them to consider implementing its recommendations. These include calls to develop and adopt:
Nationally accepted performance-based standards for the tornado-resistant design of buildings and infrastructure to ensure the resiliency of communities to tornado hazards;
Standards for designing and constructing essential buildings—such as hospitals and emergency operations centers—and infrastructure to remain operational in the event of a tornado;
Design methods that will ensure all building components and systems meet the proposed performance objectives;
Uniform national guidelines that enable communities to create safe and effective public sheltering strategies; and
Nationally accepted codes and standards, as well as uniform guidance for clear, consistent and accurate emergency communications.
The report also includes a number of recommendations for future research and development of technologies and strategies to advance tornado wind measurements, strengthen emergency communications, increase warning time, create more accurate tornado hazard maps and improve public response during tornado events.
The NIST Joplin tornado study was the first to scientifically study a tornado in terms of four key aspects: storm characteristics, building performance, human behavior and emergency communication—and then assess the impact of each on preventing injury or death. It also is the first to recommend that standards and model codes be developed and adopted for designing buildings to better resist tornadoes.
The tornado in Joplin was rated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service (NWS) as category EF 5, the most powerful on the Enhanced Fujita scale. The massive storm impacted an area 35 kilometers (22 miles) long, destroyed some 8,000 structures in its path and killed 161 people. This makes it the single deadliest tornado in the United States in the 64 years that official records have been kept.
INFORMATION:
The complete text of the final report, Technical Investigation of the May 22, 2011, Tornado in Joplin, Missouri is available at http://www.nist.gov/manuscript-publication-search.cfm?pub_id=915628.
Additional information about the tornado event and the NIST investigation, may be accessed at http://www.nist.gov/el/disasterstudies/weather/joplin_tornado_2011.cfm.
NIST issues final Joplin tornado report, begins effort to improve standards and codes
2014-03-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Whether they reduce fat or not, obesity programs lower kids' blood pressure
2014-03-28
BUFFALO, N.Y. – One of the serious health consequences of obesity is elevated blood pressure (BP), a particular problem in children because research has found that high BP in children usually follows them into adulthood, carrying with it a wide range of possible negative consequences.
Even modest elevations in the BP of adolescents, according to recent research, can pose cardiovascular problems later in life.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies of the effect of child obesity intervention programs on blood pressure has found that whether such programs ...
Stigmas, once evolutionarily sound, are now bad health strategies
2014-03-28
Stigmatization may have once served to protect early humans from infectious diseases, but that strategy may do more harm than good for modern humans, according to Penn State researchers.
"The things that made stigmas a more functional strategy thousands of years ago rarely exist," said Rachel Smith, associate professor of communication arts and sciences and human development and family studies. "Now, it won't promote positive health behavior and, in many cases, it could actually make the situation worse."
Stigmatizing and ostracizing members stricken with infectious ...
Fabricating nanostructures with silk could make clean rooms green rooms
2014-03-28
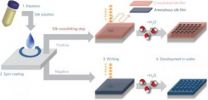
MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, MASS. -- Tufts University engineers have demonstrated that it is possible to generate nanostructures from silk in an environmentally friendly process that uses water as a developing agent and standard fabrication techniques. This approach provides a green alternative to the toxic materials commonly used in nanofabrication while delivering fabrication quality comparable to conventional synthetic polymers. Nanofabrication is at the heart of manufacture of semi-conductors and other electronic and photonic devices.
The paper describing this work, "All ...
Safety and immunogenicity of 2 doses of the HPV-16/18 AS04 adjuvanted vaccine Cervarix
2014-03-28
A recent study in the journal Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, showed that two doses of the HPV-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine Cervarix (GlaxoSmithKline) are non-inferior to three-doses in the current schedule.
Since high coverage and compliance rates can be difficult to achieve with the current three-dose HPV vaccineregimen, several studies have looked at the possibility of reducing the number of doses. Proof-of-principle that a two-dose schedule can provide sufficient protection against cervical cancer came initially from a study performed in Costa Rica in 2011. ...
Repeated hUCB injections may improve prognosis of children with deadly inherited disorder
2014-03-28
Putnam Valley, NY. (Mar. 28 2014) – New insight has been gained into treating an inherited disorder that creates serious neurological and behavioral disabilities in children and usually leads to death in the teen years.
In a recent study into the effects of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells (hUCB MNCs) when they are injected to counter the symptoms and progression of Sanfilippo syndrome type III B (MPS III B), researchers found that repeated injections into laboratory mice modeled with the disorder had clear benefits for the mice receiving multiple injections ...
Rainbow-catching waveguide could revolutionize energy technologies
2014-03-28
BUFFALO, N.Y. – More efficient photovoltaic cells. Improved radar and stealth technology. A new way to recycle waste heat generated by machines into energy.
All may be possible due to breakthrough photonics research at the University at Buffalo.
The work, published March 28 in the journal Scientific Reports, explores the use of a nanoscale microchip component called a "multilayered waveguide taper array" that improves the chip's ability to trap and absorb light.
Unlike current chips, the waveguide tapers (the thimble-shaped structures above) slow and ultimately absorb ...
Gene may predict if further cancer treatments are needed
2014-03-28
DALLAS – March 28, 2014 – UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers are developing a new predictive tool that could help patients with breast cancer and certain lung cancers decide whether follow-up treatments are likely to help.
Dr. Jerry Shay, Vice Chairman and Professor of Cell Biology at UT Southwestern, led a three-year study on the effects of irradiation in a lung cancer-susceptible mouse model. When his team looked at gene expression changes in the mice, then applied them to humans with early stage cancer, the results revealed a breakdown of which patients have ...
Erectile dysfunction can be reversed without medication
2014-03-28
Men suffering from sexual dysfunction can be successful at reversing their problem, by focusing on lifestyle factors and not just relying on medication, according to research at the University of Adelaide.
In a new paper published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine, researchers highlight the incidence of erectile dysfunction and lack of sexual desire among Australian men aged 35-80 years.
Over a five-year period, 31% of the 810 men involved in the study developed some form of erectile dysfunction.
"Sexual relations are not only an important part of people's wellbeing. ...
NUS researchers developed world's first fluorescent sensor to detect date rape drug
2014-03-28
A team of researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) has developed the world's first fluorescent sensor to identify the presence of a drug known as GHB that is commonly used to spike beverages. When the sensor is mixed with a sample of a beverage containing GHB, the mixture changes colour in less than 30 seconds, making detection of the drug fast and easy.
This simple mix-and-see discovery, led by Professor Chang Young-Tae of the Department of Chemistry at the NUS Faculty of Science, is a novel scientific breakthrough that contributes towards prevention ...
More male fish 'feminized' by pollution on the Basque coast
2014-03-28
The UPV/EHU's Cell Biology in Environmental Toxicology group has conducted research using thick-lipped grey mullet and has analysed specimens in six zones: Arriluze and Gernika in 2007 and 2008, and since then, Santurtzi, Plentzia, Ondarroa, Deba and Pasaia. The acquisition of feminine features by male fish has been detected, to a greater or lesser extent, in all the estuaries, not only in the characteristics of the gonads of the specimens analysed but also in various molecular markers. According to Miren P. Cajaraville, director of the research group, the results show ...