Passive smokers at increased risk of hearing loss
Secondhand smoke exposure and the risk of hearing loss
2010-11-16
(Press-News.org) Non-smokers who regularly breathe in others' tobacco smoke are at increased risk of some degree of hearing loss, reveals research published online in Tobacco Control.
Previous research indicates that former and current smokers are more likely to lose some of their full range of hearing, but it's not been known whether passive smokers are also prone to this.
The authors drew on 1999-2004 data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), a yearly household survey combined with a physical examination of a representative sample of the US population.
In all, a total of 3307 adults aged between 20 and 69 were included in the final analysis. They had all had their hearing tested, and were classified as passive smokers according to levels of a constituent of tobacco smoke (cotinine) in their blood.
They were also able to provide information on their medical history, levels of noise exposure, and whether they had ever smoked or lived/worked with a smoker.
The degree of hearing loss in each ear was assessed by testing the ability to hear pure tones over a range of frequencies from 500 Hz (low) to 8000 Hz (high).
Men, those who were older, and those with diabetes were significantly more likely to have high frequency hearing loss. And this was true of those who were former smokers and those who had never smoked.
But even after taking account of these factors, both former and passive smoking were associated with impaired hearing.
Former smokers were significantly more likely to have impaired hearing. The prevalence of low to mid frequency hearing loss among this group was 14%. And almost half (over 46%) had high frequency hearing loss (more than 25 decibels).
Although the risk was not as strong among those who had never smoked, almost one in 10 (8.6%) had low to mid frequency hearing loss and one in four (26.6%) had high frequency hearing loss.
And the stronger findings among former smokers suggest that continued passive smoking in this group, even at low levels, could continue the progression of high frequency hearing loss that began when they were active smokers, say the authors.
"Further research is required to determine whether [passive smoking] potentiates the effect of noise exposure and ageing on hearing," they conclude. "If this finding is independently confirmed, then hearing loss can be added to the growing list of health consequences associated with exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke."
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-11-16
US scientists are significantly more likely to publish fake research than scientists from elsewhere, finds a trawl of officially withdrawn (retracted) studies, published online in the Journal of Medical Ethics.
Fraudsters are also more likely to be "repeat offenders," the study shows.
The study author searched the PubMed database for every scientific research paper that had been withdrawn—and therefore officially expunged from the public record—between 2000 and 2010.
A total of 788 papers had been retracted during this period. Around three quarters of these papers ...
2010-11-16
According to recent research the color, shape, taste and even name of a tablet or pill can have an effect on how patients feel about their medication. Choose an appropriate combination and the placebo effect gives the pill a boost, improves outcomes and might even reduce side effects. Now, researchers at the University of Bombay, New Mumbai, India, have surveyed users of over-the-counter (OTC) medication to find out just how much the color of a tablet influences patient choice.
Writing in the International Journal of Biotechnology, R.K. Srivastava and colleagues report ...
2010-11-16
Evidence from Disneyland suggests that human creativity may have evolved not in response to sexual selection as some scientists believe but as a way to help parents bond with their children and to pass on traditions and cultural knowledge, a new study published in the inaugural issue of the International Journal of Tourism Anthropology suggests.
Evolutionary psychologist Geoffrey Miller of the University of New Mexico has suggested that human creativity, storytelling, humor, wit, music, fantasy, and morality, all evolved as forms of courtship behavior. He used evidence ...
2010-11-16
HOUSTON -- (Nov. 15, 2010) -- Rice University scientists have found a way to predict rapidly whether a new strain of the influenza virus should be included in the annual seasonal flu vaccine. While it sometimes takes new flu strains up to three years to become dominant worldwide, the new method can predict whether they will become dominant as little as two weeks after the sequence first appears in the GenBank database, the National Institutes of Health's collection of all publicly available DNA sequences.
"We studied a new strain of the virus that evolved in British Columbia ...
2010-11-16
(Boston) - Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have found that both physical and sexual abuse history were positively associated with a higher incidence of uterine fibroids later in life. These findings currently appear on-line in the journal Epidemiology.
Uterine leiomyomas, also known as fibroids or myomas, are benign, hormone-dependent tumors that are clinically symptomatic in 20 percent of reproductive age women. Fibroids contribute to a third of hysterectomies in the US, increase risk of infertility, spontaneous abortion and pelvic ...
2010-11-16
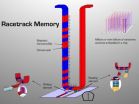
Annoyed by how long it took his computer to boot up, Kläui began to think about an alternative. Hard disks are cheap and can store enormous quantities of data, but they are slow; every time a computer boots up, 2-3 minutes are lost while information is transferred from the hard disk into RAM (random access memory). The global cost in terms of lost productivity and energy consumption runs into the hundreds of millions of dollars a day.
Like the tried and true VHS videocassette, the proposed solution involves data recorded on magnetic tape. But the similarity ends there; ...
2010-11-16
A new study on gaming and health in adolescents, conducted by researchers at Yale School of Medicine, found some significant gender differences linked to gaming as well as important health risks associated with problematic gaming. Published today in the journal Pediatrics, the study is among the first and largest to examine possible health links to gaming and problematic gaming in a community sample of adolescents.
Rani Desai, associate professor of psychiatry and epidemiology and public health at Yale, and colleagues anonymously surveyed 4,028 adolescents about their ...
2010-11-16
Arlington, Va. — A new inhalable dry powder treatment for lung cancer shows a significant increase in survival rates and is far less invasive than current treatment options, which frequently include radiation and surgery. This research is being presented at the 2010 International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) Pharmaceutical Sciences World Congress (PSWC) in association with the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS) Annual Meeting and Exposition in New Orleans, La., Nov. 14-18.
Lung cancer is the second most common type of cancer in the U.S., accounting ...
2010-11-16
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a sensor that allows engineers to assess the scour potential of soils at various depths and on-site for the first time – a technology that will help evaluate the safety of civil infrastructure before and after storm events. Scour, or erosion of soil around structures due to water flow, is responsible for a wide range of critical infrastructure failures – from unstable bridges to the levees that gave way in the wake of Hurricane Katrina.
"The 'in situ scour evaluation probe' (ISEP) is the first technology ...
2010-11-16
Philadelphia, PA, 15 November 2010 - A family history of Alzheimer's disease significantly increases the risk for developing this disorder, but a new study in Biological Psychiatry suggests that which of your parents has the disease is very important.
Alzheimer's is the most common form of dementia in late-life, affecting over 5 million elderly in the United States alone. In order to develop preventative treatments, it is necessary to identify those individuals who are at highest risk for developing Alzheimer's.
Although individuals with a parental history of Alzheimer's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Passive smokers at increased risk of hearing loss
Secondhand smoke exposure and the risk of hearing loss