(Press-News.org) Once a hospital reaches a certain occupancy level, the quality of care it provides deteriorates, increasing the risk of mortality of critically ill patients. What is worrying is that this safety 'tipping point' is reached at occupancy levels that are below 100%. The findings are reported by a team of researchers led by Ludwig Kuntz, Professor of Health Management at the University of Cologne. Their paper (Stress on the Ward: Evidence of Safety Tipping Points in Hospitals) is to appear shortly in the international journal Management Science.
For the purposes of their study, the academics looked at occupancy levels and death rates in 83 German hospitals; they discovered that mortality began to increase at an occupancy level of 92.5%, which they thus define as the safety tipping point. For patients, this means that as soon as occupancy levels exceed this tipping point, there is a greater probability of their dying in hospital. Of the patient collective they investigated, 17.4% had been in a department in which the occupancy level exceeded the safety tipping point on at least one day while they were there. The researchers claim that one in seven deaths among these patients could have been avoided if they had not been exposed to such high occupancy levels.
The paper's authors attribute the effect to the fact that the number of personnel hospitals assign to their wards is only sufficient to cope with average levels of occupancy. If the occupancy tipping point is consistently exceeded, the result is a persistent safety problem and failure to appropriately adjust the number of personnel may lead to a significantly increased threat to the survival of hospitalised patients.
It is of even greater concern if the safety tipping point is only occasionally exceeded and this potentially dangerous situation is never recognised. There is then the risk that a hospital could be perceived as safe although, in fact, it isn't. In their publication, the team provides advice on strategies that can be used to ensure that the safety tipping point is not exceeded.
INFORMATION:
For more information, please contact:
Prof. Dr. Ludwig Kuntz
University of Cologne
Department of Business Administration and Health Care Management
Email: kuntz(at)wiso.uni-koeln.de
Tel.: 0221 470-5416
Excessive hospital occupancy levels result in avoidable mortality
Cologne-based researchers identify a safety 'tipping point' at which hospitals fail
2014-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Anesthetic technique important to prevent damage to brain
2014-03-31
Researchers at the University of Adelaide have discovered that a commonly used anesthetic technique to reduce the blood pressure of patients undergoing surgery could increase the risk of starving the brain of oxygen.
Reducing blood pressure is important in a wide range of surgeries – such as sinus, shoulder, back and brain operations – and is especially useful for improving visibility for surgeons, by helping to remove excess blood from the site being operated on.
There are many different techniques used to lower patients' blood pressure for surgery – one of them is ...
Minneapolis Cardiology Fellow named an ACCF Young Investigators Awards finalist
2014-03-31
MINNEAPOLIS, MN – March 31, 2014 – Minneapolis Heart Institute Chief Cardiology Fellow Ankur Kalra, MD has been named as a finalist for the 2014 ACCF Young Investigators Awards. Kalra's research, funded by the Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation (MHIF), supports the ongoing quest to better identify, with noninvasive tools, which heart attack survivors are at greatest risk for sudden cardiac death, and therefore may benefit from ICD (implantable cardioverter defibrillator) therapy. Kalra will present his research at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) meeting in ...
Can gratitude reduce costly impatience?
2014-03-31
The human mind tends to devalue future rewards compared to immediate ones – a phenomenon that often leads to favoring immediate gratification over long-term wellbeing. As a consequence, patience has long been recognized to be a virtue. And indeed, the inability to resist temptation underlies a host of problems ranging from credit card debt and inadequate savings to unhealthy eating and drug addiction.
The prevailing view for reducing costly impatience has emphasized the use of willpower. Emotions were to be tamped down in order to avoid irrational impulses for immediate ...
Periodic puns: Chemistry jokes just in time for April Fools' Day (video)
2014-03-31
WASHINGTON, March 31, 2014 — It's almost April Fools' Day, and the American Chemical Society's (ACS') Reactions video series is celebrating with an episode featuring our favorite chemistry jokes. Which two elements look cute together? Why is father water concerned about his "iced out" son? What do you get when you combine sulfur, tungsten and silver? Get all the punchlines in the latest Reactions episode, available at: http://youtu.be/C5RZRkhk0OM.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions.
INFORMATION:
The American Chemical ...
New Penn-designed gel allows for targeted therapy after heart attack
2014-03-31
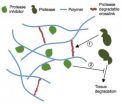
Combatting the tissue degrading enzymes that cause lasting damage following a heart attack is tricky. Each patient responds to a heart attack differently and damage can vary from one part of the heart muscle to another, but existing treatments can't be fine-tuned to deal with this variation.
University of Pennsylvania researchers have developed a way to address this problem via a material that can be applied directly to the damaged heart tissue. The potentially dangerous enzymes break down this gel-like material, releasing enzyme inhibitors contained within. This responsive, ...
New Zealand physicists split and collide ultracold atom clouds
2014-03-31
VIDEO:
Physicists from New Zealands' University of Otago have pushed the frontiers of quantum technology by developing a steerable 'optical tweezers' unit that uses intense laser beams to precisely split minute...
Click here for more information.
Physicists at New Zealand's University of Otago have pushed the frontiers of quantum technology by developing a steerable 'optical tweezers' unit that uses intense laser beams to precisely split minute clouds of ultracold atoms and to ...
Childhood virus may increase type 1 diabetes risk
2014-03-31
The study, published today in PLOS Pathogens, explored the ways the rotavirus infection contributes to autoimmune disease in mice, and researchers believe the breakthrough could be relevant to human infection with rotavirus.
The research found that it may be the "bystander effect" that causes the rotavirus infection to accelerate the onset of type 1 diabetes.
The "bystander effect" suggests that the virus provokes a strong activation of the immune system, which then spills over, allowing the immune system to attack not only the viral intruder but some of the body's ...
Role of type-2 astrocytes on the repair of spinal cord injury
2014-03-31
Increasing expression of bone morphogenetic proteins at the lesion site of the central nervous system possibly induces oligodendrocyte precursor cells to differentiate into type-2 astrocytes. While the restriction of oligodendrocyte differentiation could affect remyelination, it remains poorly understood how type-2 astrocytes regulate regeneration and functional recovery. Thus, examining the effects of type-2 astrocytes on neuronal growth is helpful in understanding the possible influential factors of oligodendrocyte precursor cells on axonal regeneration and remyelination, ...
Resting-state functional connectivity as an auxillary diagnosis of depression
2014-03-31
According to a paper published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 2, 2014), both depressive patients and healthy controls presented typical small-world attributes, and compared with healthy controls, characteristic path length was significantly shorter in depressive patients, suggesting development toward randomization. Patients with depression showed apparently abnormal node attributes at key areas in cortical-striatal-pallidal-thalamic circuits. In addition, right hippocampus and right thalamus were closely linked with the severity of depression. An artificial ...
How does acupuncture at Baihui and Dazhui reduce brain cell apoptosis in heroin readdicts?
2014-03-31
Acupuncture has therapeutic effects on cerebral ischemia, dementia, epilepsy and other brain diseases, and also functions to repair the nervous system. Dazhui (GV14) and Baihui (GV20) are the preferred acupoints for treatment. However, whether acupuncture can treat addiction and prevent readdiction through changes to brain cell ultrastructure remains unknown. A research team from Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China pointed out that cell apoptosis was observed in the hippocampus and frontal lobe of heroin readdicted rats by electron microscopy, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
[Press-News.org] Excessive hospital occupancy levels result in avoidable mortalityCologne-based researchers identify a safety 'tipping point' at which hospitals fail