(Press-News.org) A new research discovery published in the April 2014 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology may open the door to new therapies that help treat immune disorders or curb runaway inflammation. Specifically, scientists have discovered a molecule that can induce cell death (apoptosis) in a key type of immune cell (dendritic cells). With this understanding, it may be possible to develop new therapies that essentially shut down dendritic cell activity, and thereby reducing an immune reaction.
"We hope that our findings provide better understanding of immune regulation, which might give new insights into identifying new targets for immunotherapies,'" said Young Chul Sung, Ph.D., a researcher involved in the work from the Division of Integrative Bioscience and Biotechnology at the Pohang University of Science and Technology in Pohang, Korea.
To make this discovery, scientists used two groups of mice. One group was bred to lack the molecule believed to induce dendritic cell apoptosis and the second were normal (wild-type). Dendritic cells, obtained from the spleens of both groups of mice, were activated in vivo and in vitro, and apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry. Significantly lower apoptosis was found in the mice lacking the molecule necessary to induce apoptosis, when compared to their counterparts
"Dendritic cells are the essential inducers of immune responses and sense the need to activate many other immune cascades, but sometimes these cells get it wrong," said John Wherry, Ph.D., Deputy Editor of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology. "Understanding how one might selectively induce cell death in dendritic cells may reveal novel opportunities to eliminate these key orchestrators of immune responses in pathogenic settings such as autoimmunity or inflammatory diseases."
INFORMATION:
The Journal of Leukocyte Biology publishes peer-reviewed manuscripts on original investigations focusing on the cellular and molecular biology of leukocytes and on the origins, the developmental biology, biochemistry and functions of granulocytes, lymphocytes, mononuclear phagocytes and other cells involved in host defense and inflammation. The Journal of Leukocyte Biology is published by the Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Details: Seong Jeong Park, Hong Namkoong, Junsang Doh, Jong-Cheol Choi, Bo-Gie Yang, Yunji Park, and Young Chul Sung. Negative role of inducible PD-1 on survival of activated dendritic cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. April 2014 95:621-629; doi:10.1189/jlb.0813443 ; http://www.jleukbio.org/content/95/4/621.abstract
Newly discovered molecule may offer hope for immune disorders and runaway inflammation
New research published in the Journal of Leukocyte Biology identifies new molecule that can be manipulated to induce apoptosis in dendritic cells
2014-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
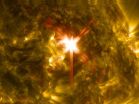
NASA releases images of X-class solar flare
2014-03-31
The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 1:48 p.m. EDT March 29, 2014, and NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured images of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event impacted Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, the U.S. government's ...
Stats show growth of breast lifts outpacing implants 2 to 1
2014-03-31
VIDEO:
New statistics from the American Society of Plastic Surgeons show that since 2000, breast lift procedures have grown by 70 percent, twice the rate of breast implants. According to the...
Click here for more information.
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill., March 31, 2014 – New statistics released today by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) show that breast lift procedures are growing at twice the rate of breast implant surgeries. Since 2000, breast lifts have grown by ...
Comparison of drug-releasing stents show similar safety outcomes after 2 years
2014-03-31
A comparison of the safety of biodegradable polymer biolimus-eluting stents vs durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents finds similar outcomes for measures including death and heart attack after two years, according to a JAMA study released online to coincide with presentation at the 2014 American College of Cardiology Scientific Sessions.
Recent studies have raised concerns about the safety of biodegradable polymer drug-eluting stents (BP-DES) compared with durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents (DP-EES). The NOBORI Biolimus-Eluting vs XIENCE/PROMUS Everolimus-Eluting ...
Six new Dracula ants from Madagascar: Minor workers become queens in Mystrium
2014-03-31
Six new species of Dracula ants from the Malagasy region have been discovered by scientists at the California Academy of Sciences. The discoveries, by postdoctoral fellow Masashi Yoshimura from Japan and curator of entomology Brian L. Fisher, represent a completely new twist in the typically rigid caste system of ants, where anatomy is typically destiny. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
"The genus Mystrium is the most mysterious group within the bizarre Dracula ants," said Yoshimura.
Mystrium species have unique features such as long, spatulate ...
Study further illuminates heart-healthy benefits of Mediterranean diet
2014-03-31
(WASHINGTON, March 31, 2014) – New research further illuminates the heart-healthy benefits of the Mediterranean diet, tying the eating plan to lower levels of platelets and white blood cells, two markers of inflammation. Inflammation has an association with greater risk of heart attack and stroke. Study, results are published online today in Blood, the Journal of the American Society of Hematology (ASH).
The Mediterranean diet, characterized by generous servings of foods such as greens, whole grains, fish, and olive oil, has long been hailed as a heart-healthy eating ...
Scientists discover a number of novel genetic defects which cause oesophageal cancer
2014-03-31
A team of scientists from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore and National University Cancer Institute Singapore (NCIS), and their collaborators from the Cedars-Sinai Medical Centre, UCLA School of Medicine, demonstrated that a number of novel genetic defects are able to induce oesophageal cancer.
The research group, led by Professor H. Phillip Koeffler, Senior Principal Investigator at CSI Singapore and Deputy Director of NCIS, has conducted a successful comprehensive genomic study of oesophageal squamous ...
What will climate policy mean for coal?
2014-03-31
Limiting climate change to 2°C means shutting down coal power plants - an unpopular proposition for coal power companies. But a new study shows that delaying climate policies could prove even worse for power plant owners.
Coal power plants are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, and new plants are planned around the world, particularly in India and China. These new power plants are built to run for 30-50 years, paying off only after years of operation. But stringent climate policies could make the cost of emission so high that coal power generation is no longer ...
Online self-injury information often inaccurate, study finds
2014-03-31
People seeking help or information online about cutting and other forms of self-injury are likely finding falsehoods and myths, according to new research from the University of Guelph.
Only about 10 per cent of websites providing information about non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) are endorsed by health or academic institutions, according to a study published recently in JAMA Pediatrics, a journal of the American Medical Association.
It's a troubling finding, says lead author Stephen Lewis, a Guelph psychology professor. "This is a salient public health issue," he said.
People ...
Tamiflu-resistant influenza: Parsing the genome for the culprits
2014-03-31
Tamiflu is one of the few available treatments for those who come down with the flu. But the virus quickly develops resistance; multiplying at a rate of several generations a day, these tiny pathogens rapidly accumulate genetic mutations. Because of this, they have a good chance of developing counterattacks to the antiviral. How can these infinitesimal variations be identified within the immensity of the virus' genetic code? EPFL researchers have created a computer tool that can shed light on the flu virus' formidable adaptability. They were able to find mutations that ...
Using different scents to attract or repel insects
2014-03-31
Flowering plants attract pollinating insects with scent from their flowers and bright colours. If they have become infested with herbivores like caterpillars, they attract beneficial insects like parasitic wasps with the help of scent signals from their leaves. The wasps then lay their eggs in the caterpillars and kill the parasites. Floral and foliar scents can, however, mutually reduce their attractiveness. That's why flowering plants face a dilemma: should they use their resources to attract pollinating insects and, by extension, for reproduction or should they invest ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
[Press-News.org] Newly discovered molecule may offer hope for immune disorders and runaway inflammationNew research published in the Journal of Leukocyte Biology identifies new molecule that can be manipulated to induce apoptosis in dendritic cells