(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA (March 31, 2014) – Keeping young people in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) prevention programs is a major goal in reducing the incidence of HIV, and multi-session interventions are often more effective than single-sessions. But according to a new study from the Annenberg School for Communication, the way these programs are designed and implemented may turn off the very people they are trying to help.
The study, "Motivational barriers to retention of at-risk young adults in HIV-prevention interventions: perceived pressure and efficacy," is published in AIDS Care: Psychological and Socio-medical Aspects of AIDS/HIV. Authors include Jiaying Liu, Christopher Jones, Kristina Wilson, Marta R. Durantini, and Dolores Albarracín, all with the Annenberg School for Communication; and William Livingood, Florida Department of Health, Duval County, Jacksonville, Fla.
The newly-published study is part of a larger research project on retention in HIV-prevention counseling conducted with community members at risk for HIV in northern Florida. Duval County remains fourth in sexually transmitted infection (STI) rates among Florida's 67 counties. Presently, Duval is faced with a 25 percent increase in reported HIV/AIDS cases, escalating STI/HIV co-infections, increasing STI infections in pregnant women, increasing repeat STI infections, and continued levels of unacceptable STI rates. The alarming rates of infection are complicated high rates of poverty and racial segregation issues in Duval County.
Understanding barriers to retention is necessary to reduce morbidity and improve health outcomes for Duval residents. The study investigated three potential motivational barriers that might affect the likelihood of retention among a vulnerable population with high levels of risk behavior: perceived pressure, perceived efficacy and fear.
According to the study, when young adults (18-35 years old) feel pressured or coerced by HIV-prevention counselors to change their lifestyle and behaviors, they often become defensive and are less likely to return to recommended follow-up counseling sessions. This is especially the case with younger (18-22 years old) intervention recipients. Moreover, intervention program retention rates are also lower when participants view the initial intervention as ineffective or irrelevant to their life.
"Our findings suggest that practitioners make efforts to ensure younger clients in particular do not feel coerced, because such threats to autonomy can backfire," wrote the authors. "Practitioners should also make efforts to explicitly communicate the efficacy of the intervention and to foster a sense of self-relevance [perhaps by] delivering tailored information about HIV risk in a personalized manner."
The study also looked at the effect of HIV-related fear on retention rates and found no significant association. However, it did find an association between retention rates and both gender and age: Male clients and older clients were more likely to return for follow-up sessions than female clients and younger clients.
"It is important that practitioners understand the psychological factors that can turn clients away from interventions, and for whom these factors are especially likely to matter," concluded the authors. "In this way, effective tailoring of interventions can be grounded in the collective experiences of successes and failures in retaining members of at-risk populations."
INFORMATION: END
Psychological factors turn young adults away from HIV intervention counseling
Pressure from counselors and perceived ineffectiveness & irrelevance of intervention keep young adults from returning to follow-up sessions
2014-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research shows link between states' personalities and their politics
2014-03-31
One state's citizens are collectively more agreeable and another's are more conscientious. Could that influence how each state is governed?
A recently published study suggests it could.
Jeffery Mondak and Damarys Canache, political science professors at the University of Illinois, analyzed personality data from more than 600,000 Americans, identified by state, who had responded to an online survey for another research study. They then matched that data with state-level measures of political culture, as identified by other, unrelated research.
The results were striking. ...
Warming climate may spread drying to a third of earth, says study
2014-03-31
Increasing heat is expected to extend dry conditions to far more farmland and cities by the end of the century than changes in rainfall alone, says a new study. Much of the concern about future drought under global warming has focused on rainfall projections, but higher evaporation rates may also play an important role as warmer temperatures wring more moisture from the soil, even in some places where rainfall is forecasted to increase, say the researchers.
The study is one of the first to use the latest climate simulations to model the effects of both changing rainfall ...
Black police officers good for entertainment only -- at least that's what movies tell us
2014-03-31
The presence of African-American police officers has been shown to increase the perceived legitimacy of police departments; however, their depiction in film may play a role in delegitimizing African-American officers in real life, both in the eyes of the general public and the African-American community.
In their recently released study, Sam Houston State University associate professor of criminal justice Howard Henderson and Indiana State University assistant professor of criminology and criminal justice Franklin T. Wilson found that African-American city police officers ...
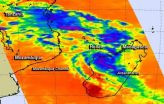
Tropical Cyclone Hellen makes landfall in Madagascar
2014-03-31
Tropical Cyclone Hellen made landfall in west central Madagascar as NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead capturing temperature data on its towering thunderstorms.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Madagascar on March 31 at 10:47 UTC/6:47 a.m. EDT and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard captured infrared data on Hellen. AIRS data showed powerful thunderstorms circling the center of circulation with cloud top temperatures in excess of -63F/-52C indicating they were high into the troposphere. Thunderstorms reaching those heights also have the ...
Urban gardeners may be unaware of how best to manage contaminants in soil
2014-03-31
Consuming foods grown in urban gardens may offer a variety of health benefits, but a lack of knowledge about the soil used for planting, could pose a health threat for both consumers and gardeners. In a new study from the Johns Hopkins Center for a Livable Future (CLF), researchers identified a range of factors and challenges related to the perceived risk of soil contamination among urban community gardeners and found a need for clear and concise information on how best to prevent and manage soil contamination. The results are featured online in PLOS ONE .
"While the ...
New functions for 'junk' DNA?
2014-03-31
DNA is the molecule that encodes the genetic instructions enabling a cell to produce the thousands of proteins it typically needs. The linear sequence of the A, T, C, and G bases in what is called coding DNA determines the particular protein that a short segment of DNA, known as a gene, will encode. But in many organisms, there is much more DNA in a cell than is needed to code for all the necessary proteins. This non-coding DNA was often referred to as "junk" DNA because it seemed unnecessary. But in retrospect, we did not yet understand the function of these seemingly ...
Hybrid vehicles more fuel efficient in India, China than in US
2014-03-31
What makes cities in India and China so frustrating to drive in—heavy traffic, aggressive driving style, few freeways—makes them ideal for saving fuel with hybrid vehicles, according to new research by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab). In a pair of studies using real-world driving conditions, they found that hybrid cars are significantly more fuel-efficient in India and China than they are in the United States.
These findings could have an important impact in countries that are on the brink of experiencing ...
Behind the scenes of the IPCC report, with Stanford scientists
2014-03-31
In the summer of 2009, Stanford Professor Chris Field embarked on a task of urgent global importance.
Field had been tapped to assemble hundreds of climate scientists to dig through 12,000 scientific papers concerning the current impacts of climate change and its causes.
The team, Working Group II, would ultimately produce a 2,000-page report as part of a massive, three-part U.N. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fifth Assessment Report, which details a consensus view on the current state and fate of the world's climate.
The job would take nearly five ...
USC Viterbi researchers developing cheap, better-performing lithium-ion batteries
2014-03-31
Researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering have improved the performance and capacity of lithium batteries by developing better-performing, cheaper materials for use in anodes and cathodes (negative and positive electrodes, respectively).
Lithium-ion batteries are a popular type of rechargeable battery commonly found in portable electronics and electric or hybrid cars. Traditionally, lithium-ion batteries contain a graphite anode, but silicon has recently emerged as a promising anode substitute because it is the second most abundant element on earth and has ...
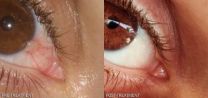
New non-surgical treatment for common, vexing eye condition
2014-03-31
Baltimore, MD, 31 March 2014. – A new report reveals a potential breakthrough in the treatment of a common eye ailment known as pterygium (Surfer's eye) that impacts the vision, eye health, and cosmetic appearance of countless sufferers.
The newly published report shows that eye drops containing the anti-anginal drug dipyridamole (Persantin®, Cardoxin®) led to almost total disappearance of an inflamed pterygium in a 35 year old otherwise healthy woman.
Dipyridamole is a drug in use over the past 55 years to treat other disorders, but now found to have this remarkable ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
[Press-News.org] Psychological factors turn young adults away from HIV intervention counselingPressure from counselors and perceived ineffectiveness & irrelevance of intervention keep young adults from returning to follow-up sessions