(Press-News.org) It was disastrous when Europeans first arrived in what would become Brazil -- 95 percent of its population, the majority of its tribes, and essentially all of its urban and agricultural infrastructure vanished. The experiences of Brazil's indigenous societies mirror those of other indigenous peoples following "first contact."
A new study of Brazil's indigenous societies led by Santa Fe Institute researcher Marcus Hamilton paints a grim picture of their experiences, but also offers a glimmer of hope to those seeking ways to preserve indigenous societies.
Even among the indigenous societies contacted in just the last 50 years, says Hamilton, "all of them went through a collapse, and for the majority of them it was disastrous," with disease and violence responsible in most cases, and with lasting detrimental effects. "That's going on today -- right now."
Brazil is "a tragic natural experiment," Hamilton says: several hundred native tribes contacted by outsiders remain, according to Instituto Socioambiental, a non-governmental organization that reports census data on 238 of those societies going back a half-century or more. That volume of data makes possible a detailed analysis of the health and prospects of the surviving contacted -- and uncontacted -- societies, an analysis that wouldn't be possible any where else in the world.
Using a method called population viability analysis, the researchers found that contact by outsiders is typically catastrophic, yet survivable. While first contacts in Brazil led to population declines of 43 percent on average, that decline bottomed out an average of eight or nine years after contact, following which population numbers grew as much as four percent a year -- about as much as possible. Projecting those results into the future suggests that contacted and as-yet uncontacted populations could recover from a low of just 100 individuals.
Hamilton and co-authors Robert Walker and Dylan Kesler of the University of Missouri describe their analysis in a paper published this week in Scientific Reports.
While their analysis paints a hopeful picture, Hamilton notes that deforestation, the breakdown of interactions between tribes, and assimilation with the outside world pose ongoing threats to indigenous societies.
"Demographically they're healthy," Hamilton says, but as for their long-term survival, "it's very up in the air."
INFORMATION: END
Indigenous societies' 'first contact' typically brings collapse, but rebounds are possible
2014-04-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA's Aqua satellite flies over newborn Tropical Depression 05W
2014-04-03
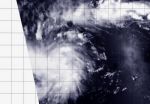
The fifth tropical depression of the northwestern Pacific Ocean tropical cyclone season formed far from land as NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and captured a visible image of the storm on April 4.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over newborn Tropical Depression 05W on April 3 at 03:10 UTC/April 2 at 11:10 p.m. EDT. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument captured a visible picture of the storm, revealing good circulation and strong convection and thunderstorms around the center of circulation.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center or JTWC ...
Sanford-Burnham presents cancer research at AACR
2014-04-03
LA JOLLA, Calif., April 3, 2014 — Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute will present a wide range of new research data at the annual American Association for Cancer Research Meeting in San Diego starting Saturday, April 5, at the San Diego Convention Center. The presentations will cover a variety of topics including breast, melanoma, and prostate cancer, as well as novel methods of delivering drugs to tumors.
If you are interested in interviewing a Sanford-Burnham researcher, please contact Susan Gammon at sgammon@sanfordburnham.org.
Highlights of Sanford-Burnham's ...
A new approach to detecting changes in GM foods
2014-04-03
Does genetic manipulation causes unintended changes in food quality and composition? Are genetically modified (GM) foods less nutritious than their non-GM counterparts, or different in unknown ways?
Despite extensive cultivation and testing of GM foods, those questions still linger in the minds of many consumers. A new study in the March issue of The Plant Genome demonstrates a potentially more powerful approach to answering them.
In research led by Owen Hoekenga, a Cornell University adjunct assistant professor, scientists extracted roughly 1,000 biochemicals, or "metabolites," ...
Quantum cryptography for mobile phones
2014-04-03
Secure mobile communications underpin our society and through mobile phones, tablets and laptops we have become online consumers. The security of mobile transactions is obscure to most people but is absolutely essential if we are to stay protected from malicious online attacks, fraud and theft.
Currently available quantum cryptography technology is bulky, expensive and limited to fixed physical locations – often server rooms in a bank. The team at Bristol has shown how it is possible to reduce these bulky and expensive resources so that a client requires only the ...
Fermi data tantalize with new clues to dark matter
2014-04-03
VIDEO:
This animation zooms into an image of the Milky Way, shown in visible light, and superimposes a gamma-ray map of the galactic center from NASA's Fermi. Raw data transitions to...
Click here for more information.
A new study of gamma-ray light from the center of our galaxy makes the strongest case to date that some of this emission may arise from dark matter, an unknown substance making up most of the material universe. Using publicly available data from NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray ...
Which couples who meet on social networking sites are most likely to marry?
2014-04-03
New Rochelle, NY, April 3, 2014—Nearly 7% of Americans married between 2005-2012 met on social networking sites. How those couples compare to couples who met through other types of online meetings or the "old-fashioned" way in terms of age, race, frequency of Internet use, and other factors is explored in an article in Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking website.
In "First Comes Social Networking, Then Comes ...
Sage grouse losing habitat to fire as endangered species decision looms
2014-04-03
As fires sweep more frequently across the American Great Basin, the US Bureau of Land Management (BLM) has been tasked with reseeding the burned landscapes to stabilize soils. BLM's interventions have not helped to restore habitat for the greater sage grouse (Centrocercus urophasianus) reported scientists from the US Geological Survey (USGS) and US Forest Service in the Ecological Society of America's journal Ecosphere last week, but outlier project sites with good grouse habitat may yield clues to successful management scenarios.
Their report arrives in the shadow of ...
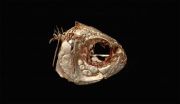
Examination of a cave-dwelling fish finds a possible genetic link to human disorders
2014-04-03
Researchers have identified a genetic association with facial asymmetry in an ancient cavefish, a natural trait that may solve mysteries surrounding facial asymmetries in humans – conditions such as cleft palate or hemifacial microsomia. This exciting discovery by Joshua Gross, a University of Cincinnati assistant professor for the Department of Biological Sciences; and doctoral students Amanda Krutzler and Brian Carlson, is published in the research journal, Genetics.
The researchers are studying the craniofacial features of the eyeless, cave-dwelling fish, Astyanax ...
Synergy of high protein intake and exercise in youth enhances bone structure and strength
2014-04-03
A study presented during the World Congress on Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases in Seville shows that high levels of protein intake (HProt) enhance the positive impact of high physical activity (HPA) on bone structure and strength in healthy pre-pubertal boys.
Researchers from the University of Geneva in Switzerland and Eindhoven University in the Netherlands tracked 176 healthy pre-pubertal boys (average age 7.4 years) to mid-adolescence (average age 15.2 years). Compared to moderate protein intake, HProt in combination with HPA was associated ...
Adults' tonsillectomy complications are higher than previously thought
2014-04-03
Twenty percent of adults who have tonsillectomies will have a complication, which is significantly higher than previously shown, according to a team of researchers. The team also found that these complications substantially increase health care expenditures.
"Since 1973, John Wenneberg and his colleagues at Dartmouth have been examining variation in the rates of tonsillectomy performed across regions, trying to explain why such wide variation is observed," said Dennis Scanlon, professor of health policy and administration, Penn State. "In other words, why are some patients ...