(Press-News.org) The metallic particles in the smoke emitted by fireworks pose a health risk, particularly to people who suffer from asthma. This is the conclusion of a study led by researchers from the Institute of Environmental Assessment and Water Research (IDAEA-CSIC), published this week in the Journal of Hazardous Materials.
"The toxicological research has shown that many of the metallic particles in the smoke from fireworks are bio-reactive and can affect human health", Teresa Moreno, a researcher from the IDAEA (CSIC) and lead author of a study that has been published this week in the Journal of Hazardous Materials, tells SINC.
The different colours and effects produced in these displays are achieved by adding metals to the gunpowder. When a pyrotechnic display takes place it releases a lot of smoke, liberating minute metallic particles (of a few microns in size, or even less), which are small enough to be inhaled deeply into the lungs.
"This poses a risk to health, and the effects are probably more acute in people with a background of asthma or cardiovascular problems", Moreno explains. "The effects in healthy people are still unknown, but common sense tells us it cannot be good to inhale the high levels of metallic particles in this smoke, even if this only happens a few times a year".
The study focused on the San Juan fiestas (the night of 23 June through to 24 June, 2008) in the Spanish city of Girona. The researchers analysed the levels of more than 30 chemical elements and compounds in May and June in order to confirm that the levels of lead, copper, strontium, potassium and magnesium skyrocketed after the fireworks were launched.
The team found the results were similar in other towns too. During the Mascletà (18 March), for example, in the Las Fallas fiestas in Valencia, levels of these elements rose once again, as well as others such as aluminium, titanium, barium and antimony, and also concentrations of nitric oxide (NO) and sulphur dioxide (SO2).
Other studies have confirmed that the smoke from fireworks increases the presence of metallic particles in the skies over L'Alcora and Borriana (Castellón), Barcelona and even London (United Kingdom) during the Guy Fawkes' Night celebrations.
"People who live in cities already inhale significant amounts of contaminant particles stemming from traffic emissions, chimneys and cigarettes, and the dense smoke caused by fireworks only worsens this situation", points out Moreno.
Possible solutions
The researcher compares the problem with that of tobacco. "The less you expose yourself to the smoke, the fewer negative effects it will have on your health, and so the best solution is to avoid inhaling it".
According to the scientists, in the absence of a ban on fireworks, spectators should stay well back in a place not affected by the smoke and pay attention to the wind direction. They also recommend that fireworks displays should be sited in a place that ensures the plume of smoke will blow away from densely populated areas.
An added problem is the chemical mixtures in the different kinds of fireworks, since some contain extremely toxic metals such as lead. "There should be strict controls on fireworks imports so that those with the potentially most dangerous chemical composition can be avoided", concludes Moreno.
INFORMATION:
References:
Teresa Moreno, Xavier Querol, Andrés Alastuey, Fulvio Amato, Jorge Pey, Marco Pandolfi, Nino Kuenzli, Laura Bouso, Marcela Rivera y Wes Gibbons. "Effect of fireworks events on urban background trace metal aerosol concentrations: Is the cocktail worth the show?" Journal of Hazardous Materials 183 (1-3): 945-949, 15 de noviembre de 2010. Doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.082.
Smoke from fireworks is harmful to health
2010-11-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Structure of a protein related to heart and nervous system health revealed
2010-11-17
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- University of Michigan researchers have solved the structure of a protein that is integral to processes responsible for maintaining a healthy heart and nervous system.
The protein structure in question is cystathionine beta-synthase, known as CBS. CBS uses vitamin B6 to make hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a gaseous signaling molecule that helps maintain a healthy heart and nervous system. H2S also induces a state of suspended animation or hibernation in animals by decreasing body temperature and lowering metabolic rate.
The work to decode the structure ...
New dry powder antibiotic targets tuberculosis, reduces treatment time
2010-11-17
Arlington, Va. — New research being presented at the 2010 International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) Pharmaceutical Sciences World Congress (PSWC) in association with the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS) Annual Meeting and Exposition will feature an inhalable dry powder antibiotic that when used alone or with current treatments may significantly reduce treatment for tuberculosis (TB) and multi-drug resistant TB.
There are an estimated 9.4 million new cases of TB worldwide, according to the most recent statistics from the World Health Organization. ...
Dressing indicates infections
2010-11-17
Whether a small cut with a fruit knife, a surgical wound or a major injury caused by a fall – the body's defense and repair system leaps into action and tries to close the wound as quickly as possible. Small injuries usually heal within a few days, but a gaping wound will take longer to heal, and an infection can take hold even after several days. Dressings protect the site of the injury but to check the wound they have to be removed. This can be painful for the patient and moreover it risks giving germs the chance to enter and cause infection. Scientists at the Fraunhofer ...
Back off, Rudolph: Protecting this year's Christmas tree crop
2010-11-17
Hair clippings, cayenne pepper and raw eggs – these are just a few of the odd ingredients recommended to keep those pesky deer away from your backyard garden. But what about farmers who have hundreds of acres of Christmas trees to protect? North Carolina State University extension specialists have now found an effective, inexpensive alternative to available commercial products to keep the deer at bay.
The NC State researchers, led by Jeff Owen, a Christmas-tree production specialist, are exploring the use of inexpensive, inedible food byproducts – such as dried blood ...
Imaging tool may aid nanoelectronics by screening tiny tubes
2010-11-17
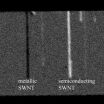
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers have demonstrated a new imaging tool for rapidly screening structures called single-wall carbon nanotubes, possibly hastening their use in creating a new class of computers and electronics that are faster and consume less power than today's.
The semiconducting nanostructures might be used to revolutionize electronics by replacing conventional silicon components and circuits. However, one obstacle in their application is that metallic versions form unavoidably during the manufacturing process, contaminating the semiconducting nanotubes.
Now ...
Engineers test effects of fire on steel structures
2010-11-17
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers at Purdue University are studying the effects of fire on steel structures, such as buildings and bridges, using a one-of-a-kind heating system and a specialized laboratory for testing large beams and other components.
Building fires may reach temperatures of 1,000 degrees Celsius, or more than 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit, said Amit Varma, a Purdue associate professor of civil engineering who is leading the work.g1
"At that temperature, exposed steel would take about 25 minutes to lose about 60 percent of its strength and stiffness," he ...
Organ network uses Carnegie Mellon algorithm to match live kidney donors with recipients
2010-11-17
PITTSBURGH—A computer algorithm developed at Carnegie Mellon University matched living kidney donors with medically compatible transplant candidates late last month as the national Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN), operated by the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS), began a national pilot program to increase the number of kidney paired-donation (KPD) transplants.
The initial run of the computer matching process included just 43 kidney transplant candidates and 45 potential living donors, but a national KPD pool eventually could include as many ...
International discussions on FRAX smooth the way for implementation in clinical practice
2010-11-17
Three days of critical international discussion and debate, led by a panel of experts from the International Society of Clinical Densitometry (ISCD) and the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF), have served to clarify a number of important questions pertaining to the interpretation and use of FRAX® in clinical practice.
The WHO Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX®), with models for some 26 countries, is an important new online tool that is being used by a steadily increasing number of physicians around the world. FRAX® is country-specific and calculates a patient's ...
Heart surgeries can trigger strokes, seizures and other neurological complications
2010-11-17
Strokes, seizures and other neurological complications related to heart surgery account for "considerable morbidity and mortality," Loyola University Health System neurologists report in the November issue of the journal Hospital Practice.
Other complications include delirium, central nervous system infections, pituitary gland problems, spinal cord or peripheral nerve injuries, residual effects of anesthesia and medication toxicity.
Complications can involve any part of the central and peripheral nervous systems. "Neurologic complications are always a risk with cardiac ...
Depression linked to HIV risk among South African young people, study shows
2010-11-17
University of Alberta research has discovered a strong link between depression and risky sexual behaviours such as improper condom use, transactional sex and relationship violence among young people in South Africa.
The research shows that depression is common among young South Africans, and could be making a significant contribution towards the HIV epidemic.
As well, the researchers believe that depression could be contributing to risky sexual behaviours around the world, and that preventing or treating it may reduce the global burden of sexually transmitted diseases, ...