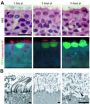
(Press-News.org) MAYWOOD, Ill. – People who are injured while binge drinking are much slower to heal from wounds suffered in car accidents, shootings, fires, etc.
Now a new study is providing insights into why alcohol has such a negative effect on wound healing. Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine researchers report that binge alcohol exposure significantly reduced levels of key components of the immune system involved in healing.
The study by senior author Katherine A. Radek, PhD, and colleagues from Loyola's Alcohol Research Program and the Infectious Disease and Immunology Research Institute is published online ahead of print in the journal Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research.
In the United States, alcohol dependence and/or abuse affects 20 percent to 40 percent of hospitalized patients. Alcohol increases the risk of infections in the hospital, including surgical site infections. Patients with surgical-site infections are hospitalized for twice as long, have a higher rate of re-admission and are twice as likely to die as patients who did not binge drink.
The study showed, for the first time, that binge alcohol exposure reduces the amount of white blood cells called macrophages that chew up bacteria and debris. This defect, in part, makes the wound more likely to be infected by bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus.
The study also found that binge alcohol exposure impaired the production of a protein that recruits macrophages to the wound site. (This protein is called macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha, or MIP-1α.) Binge alcohol also reduced levels of another key component of the immune system known as CRAMP (cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide). CRAMP is a type of small protein present in the outermost layer of the skin, the epidermis. These small proteins, called antimicrobial peptides, kill bacteria and recruit macrophages and other immune system cells to the wound site.
"Together these effects likely contribute to delayed wound closure and enhanced infection severity observed in intoxicated patients," researchers concluded.
The study involved an in vivo model and a typical pattern of binge drinking: three days of alcohol exposure, followed by four days without alcohol, followed by three more days of binge alcohol exposure. The binge alcohol exposures were equivalent to roughly twice the legal limit for driving.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism and the Marian and Ralph C. Falk Medical Research Trust.
The work was conducted in the Burn and Shock Trauma Research Institute by Brenda J. Curtis (a post-doctoral fellow), Sara Hlavin (MS student) and Aleah L. Brubaker (MD/PhD student) along with Elizabeth J. Kovacs, PhD.
Why binge drinkers are slower to heal from their wounds
2014-04-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Global health funding reaches new high as funding priorities shift
2014-04-08
Washington, D.C.—Global health funding hit an all-time high of $31.3 billion in 2013, five times greater than in 1990. Yet with 3.9% growth from 2012 to 2013, the year-over-year increase falls short of the rapid rates seen over the previous decade, according to new research by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington being published online in a web first edition on April 8 by Health Affairs.
As funding from many bilateral donors and development banks has declined, growth in funding from the GAVI Alliance, the Global Fund ...
UNC researchers find genetic trigger for RSV-induced infant hospitalizations
2014-04-08
April 8, 2014 CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Researchers at UNC School of Medicine have pinpointed a viral protein that plays a major role in making respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) the most common cause of hospitalization in children under one year of age.
The discovery, published April 8 in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, is the first step toward identifying better diagnostics and potential treatments for an infection that strikes nearly all children before they reach the age of three and causing severe disease in 3 percent of infected children. RSV infection leads to ...
The double whammy of multiple sex partners and drinking in HIV/STI prevention
2014-04-08
PHILADELPHIA (April 8, 2014) – The cartoon character Homer J. Simpson once said "Alcohol: The source of, and solution to, all of life's problems."
The sage of the ubiquitous and fictional town of Springfield may have hit the nail on the head when it comes to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) counseling and prevention. The more you drink and/or the more sex partners you have, the less likely you are to engage in HIV-prevention programs.
This rather grim assessment came about from the study, "Barriers to accessing HIV-prevention ...
Language structure… you're born with it
2014-04-08
Humans are unique in their ability to acquire language. But how? A new study published in the Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences shows that we are in fact born with the basic fundamental knowledge of language, thus shedding light on the age-old linguistic "nature vs. nurture" debate.
THE STUDY
While languages differ from each other in many ways, certain aspects appear to be shared across languages. These aspects might stem from linguistic principles that are active in all human brains. A natural question then arises: are infants born with knowledge of how ...
Advanced warning systems increase safety at intersections, study shows
2014-04-08
Most drivers have experienced a traffic signal that turns yellow just as they approach an intersection, which makes it difficult for them to decide whether to stop or proceed through it. The wrong choice in this situation, known as the "dilemma zone," may lead to crashes, especially at high-speed intersections.
A major factor making driving difficult is hazards that are sudden and hard to predict. Roadside and in-vehicle display warning systems may help drivers handle these hazards by predicting their occurrence and providing advanced warning to the driver, according ...
Lipid levels during prenatal brain development impact autism: York U study
2014-04-08
In a groundbreaking York University study, researchers have found that abnormal levels of lipid molecules in the brain can affect the interaction between two key neural pathways in early prenatal brain development, which can trigger autism. And, environmental causes such as exposure to chemicals in some cosmetics and common over-the-counter medication can affect the levels of these lipids, according to the researchers.
"We have found that the abnormal level of a lipid molecule called Prostaglandin E2 in the brain can affect the function of Wnt proteins. It is important ...
Kinesin-5 structure opens cancer drug targets
2014-04-08
VIDEO:
Kinesin-5 plays a crucial role in cell division by allow microfilaments to slide past each other. The kinesin-5 structure shows a central rod connecting two motor units that walk along...
Click here for more information.
The structure of a key part of the machinery that allows cells to divide has been identified by researchers at the University of California, Davis -- opening new possibilities for throwing a wrench in the machine and blocking runaway cell division in cancer.
"The ...
Phase II trial of efatutazone shows challenge of matching treatment to population
2014-04-08
Work at the University of Colorado Cancer Center led to phase II trial of efatutazone with erlotinib in patients with refractory non-small cell lung cancer. Results are reported today at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2014. While efatutazone did not improve the efficacy of erlotinib in this trial, researchers hope lessons from the trial will allow them to make better future use of the drug or other drugs in its class.
"In oncology and especially in lung cancer, everything is personalized. We're exploring different molecular markers ...
Glucosamine promotes longevity by mimicking a low-carb diet
2014-04-08
Glucosamine has been freely available in drugstores for many decades. It is widely used to treat arthritis and to prevent joint degeneration. Moreover, glucosamine is known to delay cancer growth. In addition, glucosamine reduces metabolism of nutritive sugars, as was already shown some 50 years ago.
In 2007, Michael Ristow showed that too much nutritive sugar shortens the lifespan of roundworms, a widely studied model organism in ageing research. Conversely, impairing carbohydrate metabolism in these worms was capable of extending lifespan [reference 1]. Unfortunately, ...
Future computers that are 'normally off'
2014-04-08
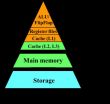
WASHINGTON D.C., April 8, 2014 -- If a research team in Japan gets its wish, "normally off" computers may one day soon be replacing present computers in a move that would both eliminate volatile memory, which requires power to maintain stored data, and reduce the gigantic energy losses associated with it.
Most parts of present computers are made with volatile devices such as transistors and dynamic random access memory (DRAM), which loses information when powered off. So computers are designed on the premise that power is "normally on."
Back in 2000, the concept of ...