(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
This simulated 3-D flyby animation using TRMM precipitation radar data on April 9 shows rain falling at a rate of over 99 mm/3.9 inches per hour (red) within Ita's feeder...
Click here for more information.
Tropical Cyclone Ita has been intensifying as it tracks from Papua New Guinea toward Queensland, Australia, and NASA's TRMM satellite noticed the development of an eye feature.
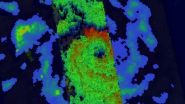
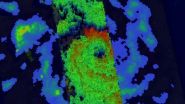
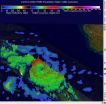
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew above intensifying Tropical Cyclone Ita in the Coral Sea near the southeastern tip of Papua New Guinea on April 9, 2014 at 0536 UTC/1:36 a.m. EDT. Tropical cyclone had developed a large but well defined eye and had sustained winds estimated at 65 knots/75 mph. Rainfall derived from TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data was used to create a rainfall analysis.
TRMM PR data unveiled rain falling at a rate of over 99 mm/3.9 inches per hour within Ita's feeder bands over the coast of southeastern Papua New Guinea. TRMM PR found that tall thunderstorms in Ita's eye wall were reaching heights of over 16 km/9.9 miles and were returning radar reflectivity values of over 57dBZ to the satellite.
On April 9 at 0900 UTC/5 a.m. EDT, Tropical Cyclone Ita's maximum sustained winds had increased to 80 knots/92 mph/148.2 kph. Ita is a Category one hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Scale. According to the scale, a Category 1 hurricane can cause the following: well-constructed frame homes could have damage to roof, shingles, vinyl siding and gutters. Large branches of trees will snap and shallowly rooted trees may be toppled. Extensive damage to power lines and poles likely will result in power outages that could last a few to several days.
Ita was still over 400 miles from Cairns, Australia at 0900 UTC/5 a.m. EDT. It was centered near 11.5 south and 150.2 east and moving to the west at 9 knots/10.3 mph/16.6 kph. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) noted that Ita is generating 25-foot/7.6 -meter high waves in the Coral Sea.
On April 9, animated multispectral satellite imagery showed Ita has tightly curved bands of thunderstorms wrapping into a consolidating low level circulation center. TRMM microwave imagery revealed a well-formed eye around that consolidating center.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) is forecasting Ita to strengthen over the next two days with maximum sustained winds peaking near 105 knots before weakening from interaction with the land. Ita is expected to move southwest through the Coral Sea and reach the eastern Cape York Peninsula, Queensland by Friday, April 11. The Australian Bureau of Meteorology (ABM) noted that Ita is expected to cross the far north Queensland coast between Lockhart River and Cape Flattery late Friday.
ABM has posted a Cyclone Watch for coastal areas from Cape Grenville to Cairns, extending up to 124 miles/200 kilometers inland to areas including Kalinga, Laura, and Palmerville. For updates, visit the ABM website: http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/index.shtml.
From April 11 through the 14, JTWC expects an approaching shortwave trough (elongated area of low pressure) to begin pushing Ita away from the coast. Current JWTC forecasts take Ita's center near Cairns and slowly turn Ita in a southeasterly direction causing the storm parallel the Queensland coast to Brisbane.
INFORMATION:
NASA's TRMM satellite sees Tropical Cyclone Ita intensifying
2014-04-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Skulls of red and giant pandas provide insight into coexistence
2014-04-09
New research on the skulls of red pandas and giant pandas provides further explanation as to why the two species—which are not closely related but dine on the same food, bamboo, in the same geographic area—are able to coexist. Using high-resolution imaging and biting simulations, scientists at the American Museum of Natural History and the University of Málaga in Spain found that the skulls of the two panda species not only are distantly related but also have structural differences related to the way the animals chew. These substantial differences reflect distinct bamboo ...
Oyster aquaculture could significantly improve Potomac River estuary water quality
2014-04-09
Oyster aquaculture in the Potomac River estuary could result in significant improvements to water quality, according to a new NOAA and U.S. Geological Survey study published in the journal Aquatic Geochemistry.
All of the nitrogen currently polluting the Potomac River estuary could be removed if 40 percent of its river bed were used for shellfish cultivation, according to the joint study. The researchers determined that a combination of aquaculture and restored oyster reefs may provide even larger overall ecosystem benefits. Oysters, who feed by filtering, can clean an ...
Genome sequencing of MRSA infection predicts disease severity
2014-04-09
April 9, 2014 –The spread of the antibiotic-resistant pathogen MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) remains a concerning public health problem, especially among doctors trying to determine appropriate treatment options for infected patients. Bacterial pathogens, such as MRSA, cause disease in part due to toxicity, or the bacterium's ability to damage a host's tissue. In a study published online today in Genome Research, researchers used the genome sequence of MRSA to predict which isolates were highly toxic, thus potentially personalizing the treatment of ...
Farming for improved ecosystem services seen as economically feasible
2014-04-09
By changing row-crop management practices in economically and environmentally stable ways, US farms could contribute to improved water quality, biological diversity, pest suppression, and soil fertility while helping to stabilize the climate, according to an article in the May issue of BioScience. The article, based on research conducted over 25 years at the Kellogg Biological Station in southwest Michigan, further reports that Midwest farmers, especially those with large farms, appear willing to change their farming practices to provide these ecosystem services in exchange ...
DNA data could help doctors treat MRSA shows new study
2014-04-09
A team of scientists led by the University of Bath has developed a new technique to predict the toxicity of an MRSA infection from its DNA sequence. With the MRSA superbug an increasing problem in hospitals and communities, this new technique could soon help clinicians better decide the best course of treatment for infections.
Bacterial pathogens, such as MRSA, cause disease in part due to their toxicity, or the bacterium's ability to damage a host's tissue. In a study published online today in Genome Research, researchers used the genome sequence of MRSA to predict toxicity ...
Stressful environments genetically affect African-American boys
2014-04-09
PRINCETON, N.J.—Stressful upbringings can leave imprints on the genes of children as young as age 9, according to a study led by Princeton University and Pennsylvania State University researchers. Such chronic stress during youth leads to physiological weathering similar to aging.
A study of 40 9-year-old black boys, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, shows that those who grow up in disadvantaged environments have shorter telomeres — DNA sequences that generally shrink with age — than their advantaged peers. The researchers also report ...
Bone marrow stem cells show promise in stroke treatment, UCI team finds
2014-04-09
Irvine, Calif., April 9, 2014 — Stem cells culled from bone marrow may prove beneficial in stroke recovery, scientists at UC Irvine's Sue & Bill Gross Stem Cell Research Center have learned.
In an analysis of published research, neurologist Dr. Steven Cramer and biomedical engineer Weian Zhao identified 46 studies that examined the use of mesenchymal stromal cells – a type of multipotent adult stem cells mostly processed from bone marrow – in animal models of stroke. They found MSCs to be significantly better than control therapy in 44 of the studies.
Importantly, the ...
See what a child will look like using automated age-progression software
2014-04-09
It's a guessing game parents like to ponder: What will my child look like when she grows up? A computer could now answer the question in less than a minute.
University of Washington researchers have developed software that automatically generates images of a young child's face as it ages through a lifetime. The technique is the first fully automated approach for aging babies to adults that works with variable lighting, expressions and poses.
"Aging photos of very young children from a single photo is considered the most difficult of all scenarios, so we wanted to focus ...
Sunken logs create new worlds for seafloor animals
2014-04-09
MOSS LANDING, CA — When it comes to food, most of the deep sea is a desert. Many seafloor animals feed on marine snow—the organic remnants of algae and animals that live in the sunlit surface waters, far above. However, marine snow only falls as a light dusting and doesn't have much nutritional value. Thus, any other sources of food that reach the deep sea provide a temporary feast. Even bits of dead wood, waterlogged enough to sink, can support thriving communities of specialized animals. A new paper by biologists at the National Evolutionary Synthesis Center and the Monterey ...
Scientists reconstruct ancient impact that dwarfs dinosaur-extinction blast
2014-04-09
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- Picture this: A massive asteroid almost as wide as Rhode Island and about three to five times larger than the rock thought to have wiped out the dinosaurs slams into Earth. The collision punches a crater into the planet's crust that's nearly 500 kilometers (about 300 miles) across: greater than the distance from Washington, D.C. to New York City, and up to two and a half times larger in diameter than the hole formed by the dinosaur-killing asteroid. Seismic waves bigger than any recorded earthquakes shake the planet for about half an hour at any one ...