(Press-News.org) Growing agave and other carefully chosen plants amid photovoltaic panels could allow solar farms not only to collect sunlight for electricity but also to produce crops for biofuels, according to new computer models by Stanford scientists.
This co-location approach could prove especially useful in sunny, arid regions such as the southwestern United States where water is scarce, said Sujith Ravi, who is conducting postdoctoral research with professors David Lobell and Chris Field, both on faculty in environmental Earth system science and senior fellows at the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment. "Co-located solar-biofuel systems could be a novel strategy for generating two forms of energy from uncultivable lands: electricity from solar infrastructure and easily transportable liquid fuel from biofuel cultivation," said Ravi, the lead author of a new study published in a recent issue of the journal Environmental Science & Technology that details the idea.
Photovoltaic (PV) solar farms run on sunlight, but water is required to remove dust and dirt from the panels to ensure they operate at maximum efficiency. Water is also used to dampen the ground to prevent the buildup and spread of dust. Crops planted beneath the solar panels would capture the runoff water used for cleaning the PV panels, thus helping to optimize the land. The plants' roots would also help anchor the soil and their foliage would help reduce the ability of wind to kick up dust.
Computer simulations of a hypothetical co-location solar farm in Southern California's San Bernardino County by Ravi and colleagues suggest that these two factors together could lead to a reduction in the overall amount of water that solar farms need to operate. "It could be a win-win situation," Ravi said. "Water is already limited in many areas and could be a major constraint in the future. This approach could allow us to produce energy and agriculture with the same water."
But which crops to use? Many solar farms operate in sunny but arid regions that are inhospitable to most food crops. But there is one valuable plant that thrives at high temperatures and in poor soil: agave. Native to North and South America, the prickly plant can be used to produce liquid ethanol, a biofuel that can be mixed with gasoline or used to power ethanol vehicles. "Unlike corn or other grains, most of the agave plant can be converted to ethanol," Ravi said.
The team plans to test the co-location approach around the world to determine the ideal plants to use and to gather realistic estimates for crop yield and economic incentives.
"Sujith's work is a great example of how thinking beyond a single challenge like water or food or energy sometimes leads to creative solutions," said Lobell, who is a coauthor on the new study. "Of course, creative solutions don't always work in the real world, but this one at least seems worthy of much more exploration."
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by the TomKat Center for Sustainable Energy at Stanford.
Ker Than is associate director of communications for the School of Earth Sciences.
Stanford scientists model a win-win situation: Growing crops on photovoltaic farms
2014-04-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Medication therapy management works for some but not all home health patients
2014-04-09
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Low-risk Medicare patients entering home health care who received medication therapy management by phone were three times less likely to be hospitalized within the next two months, while those at greater risk saw no benefit, according to a study led by Purdue University.
The study helped determine which patients benefit most from medication therapy management by phone and a way to identify them through a standardized risk score, said Alan Zillich, associate professor of pharmacy practice at Purdue, who led the research.
"Hopefully, this study ...
UC-led research finds chips with olestra cause body toxins to dip
2014-04-09
According to a clinical trial led by University of Cincinnati researchers, a snack food ingredient called olestra has been found to speed up the removal of toxins in the body.
Results are reported in the April edition of the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.
The trial demonstrated that olestra—a zero-calorie fat substitute found in low-calorie snack foods such as Pringles—could reduce the levels of serum polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in people who had been exposed to PCBs.
High levels of PCBs in the body are associated with an increase in hypertension and diabetes. ...
Gusev Crater once held a lake after all, says ASU Mars scientist
2014-04-09
TEMPE, Ariz. - If desert mirages occur on Mars, "Lake Gusev" belongs among them. This come-and-go body of ancient water has come and gone more than once, at least in the eyes of Mars scientists.
Now, however, it's finally shifting into sharper focus, thanks to a new analysis of old data by a team led by Steve Ruff, associate research professor at Arizona State University's Mars Space Flight Facility in the School of Earth and Space Exploration. The team's report was just published in the April 2014 issue of the journal Geology.
The story begins in early 2004, when NASA ...
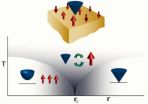
One kind of supersymmetry shown to emerge naturally
2014-04-09
UC Santa Barbara physicist Tarun Grover has provided definitive mathematical evidence for supersymmetry in a condensed matter system. Sought after in the realm of subatomic particles by physicists for several decades, supersymmetry describes a unique relationship between particles.
"As yet, no one has found supersymmetry in our universe, including at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)," said the associate specialist at UCSB's Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics (KITP). He is referring to the underground laboratory in Switzerland where the famous Higgs boson was identified ...
Violence intervention program effective in Vanderbilt pilot study
2014-04-09
Violent behavior and beliefs among middle school students can be reduced through the implementation of a targeted violence intervention program, according to a Vanderbilt study released in the Journal of Injury and Violence Research.
Manny Sethi, M.D., assistant professor of Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehabilitation, and his Vanderbilt co-authors evaluated 27 programs nationwide as part of a search for an appropriate school-based violence prevention program.
Their findings led to a single, evidence-based conflict resolution program that was evaluated in a pilot study of ...
Stanford scientists discover a novel way to make ethanol without corn or other plants
2014-04-09
Stanford University scientists have found a new, highly efficient way to produce liquid ethanol from carbon monoxide gas. This promising discovery could provide an eco-friendly alternative to conventional ethanol production from corn and other crops, say the scientists. Their results are published in the April 9 advanced online edition of the journal Nature.
"We have discovered the first metal catalyst that can produce appreciable amounts of ethanol from carbon monoxide at room temperature and pressure – a notoriously difficult electrochemical reaction," said Matthew ...
Novel approach to accelerate metabolism could lead to new obesity treatment
2014-04-09
BOSTON – By manipulating a biochemical process that underlies cells' energy-burning abilities, investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) have made a novel discovery that could lead to a new therapy to combat obesity and diabetes.
Published in the April 10 issue of the journal Nature, the new findings show that reducing the amount of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) protein in fat and liver dramatically reduces the development of obesity and diabetes in mice.
'With this discovery, we now have a means of metabolic manipulation that could ...
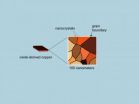
A bad penny: Cancer's thirst for copper can be targeted
2014-04-09
DURHAM, N.C. – Drugs used to block copper absorption for a rare genetic condition may find an additional use as a treatment for certain types of cancer, researchers at Duke Medicine report.
The researchers found that cancers with a mutation in the BRAF gene require copper to promote tumor growth. These tumors include melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer that kills an estimated 10,000 people in the United States a year, according to the National Cancer Institute.
"BRAF-positive cancers like melanoma almost hunger for copper," said Christopher M. Counter, ...
UC San Diego researchers develop bacterial 'FM radio'
2014-04-09
Programming living cells offers the prospect of harnessing sophisticated biological machinery for transformative applications in energy, agriculture, water remediation and medicine. Inspired by engineering, researchers in the emerging field of synthetic biology have designed a tool box of small genetic components that act as intracellular switches, logic gates, counters and oscillators.
But scientists have found it difficult to wire the components together to form larger circuits that can function as "genetic programs." One of the biggest obstacles? Dealing with a small ...
New 'switch' could power quantum computing
2014-04-09
Using a laser to place individual rubidium atoms near the surface of a lattice of light, scientists at MIT and Harvard University have developed a new method for connecting particles — one that could help in the development of powerful quantum computing systems.
The new technique, described in a paper published today in the journal Nature, allows researchers to couple a lone atom of rubidium, a metal, with a single photon, or light particle. This allows both the atom and photon to switch the quantum state of the other particle, providing a mechanism through which quantum-level ...