(Press-News.org) PRINCETON, N.J.—Affluent individuals and business corporations already have vastly more influence on federal government policy than average citizens, according to recently released research by Princeton University and Northwestern University. This research suggests that the Supreme Court's continuing attack on campaign finance laws is further increasing the political clout of business firms and the wealthy.
Martin Gilens, professor of politics at Princeton, and Benjamin I. Page, Gordon Scott Fulcher Professor of Decision Making, of Northwestern University used a unique data set comprised of 1,779 policy issues over a thirty-year period to estimate how much influence affluent citizens, organized interest groups and ordinary citizens each have on policy outcomes – while taking into account (statistically "controlling for") the influence of the other actors. Affluent citizens, those at the 90th income percentile, turn out to have the most influence. Organized interest groups also have a great deal of impact, but the preferences of average citizens have no discernable, independent effect on policy making at all.
"This does not mean that the average American always loses out," said Gilens, "because the affluent and ordinary citizens frequently want the same thing. But when they disagree – and they do disagree on many important matters – the affluent generally get their way. If democracy means that all citizens should have a say in shaping government policy, our findings cast doubt upon just how democratic U.S. policy making actually is."
Gilens and Page note that ever since the time of James Madison, observers of American politics have hoped that organized interest groups might represent the diverse wants and interests of the citizenry as a whole so that democracy might work well even if individual citizens among the general public exert little or no direct influence.
"This study dashes hopes for this democratic kind of interest-group influence,' said Gilens. "We found that corporations and business-oriented interest groups, which often seek policies that the public opposes, have much more impact on policy making than mass-based groups. Moreover, even mass-based groups (taken together) do not actually line up very well with the policies that ordinary citizens want."
"The Supreme Court's recent decisions, which have removed most legal limits on big financial contributions to politics, are likely to increase the political clout of wealthy individuals and leave average citizens with even less influence than they have now," said Page. "I find this very troubling. The Court's view that political donations constitute 'speech' protected by the First Amendment opens the door to money-driven politics and a distortion of democracy."
INFORMATION:
Gilens is author of the prize-winning book Affluence and Influence, which is now being issued in paperback by Princeton University Press. He can be contacted at mgilens@princeton.edu.
Page is author or coauthor of a number of books and articles on American politics. He is currently studying the philanthropic activities and the political views and actions of the wealthiest Americans. He can be contacted at b-page@northwestern.edu.
Gilens' and Page's research findings are forthcoming in Perspectives on Politics and are available at Testing Theories of American Politics: Elites, Interest Groups, and Average Citizens or http://scholar.princeton.edu/mgilens/pages/research.
Gutting of campaign finance laws enhances influence of corporations and wealthy Americans
2014-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pseudo-mathematics and financial charlatanism
2014-04-10
Providence, RI---Your financial advisor calls you up to suggest a new
investment scheme. Drawing on 20 years of data, he has set his
computer to work on this question: If you had invested according to
this scheme in the past, which portfolio would have been the best?
His computer assembled thousands of such simulated portfolios and
calculated for each one an industry-standard measure of return on
risk. Out of this gargantuan calculation, your advisor has chosen the
optimal portfolio. After briefly reminding you of the oft-repeated
slogan that "past performance ...
Name of new weakly electric fish species reflects hope for peace in Central Africa
2014-04-10
Two new species of weakly electric fishes from the Congo River basin are described in the open access journal ZooKeys. One of them, known from only a single specimen, is named "Petrocephalus boboto." "Boboto" is the word for peace in the Lingala language, the lingua franca of the Congo River, reflecting the authors' hope for peace in troubled Central Africa.
On a 2010 field trip to the Congo River of Democratic Republic of the Congo, in the riverside village of Yangambi-Lokélé, French ichthyologist Sébastien Lavoué of the Taiwan Institute of Oceanography and American ...
Planaria deploy an ancient gene expression program in the course of organ regeneration
2014-04-10
KANSAS CITY, MO - As multicellular creatures go, planaria worms are hardly glamorous. To say they appear rudimentary is more like it. These tiny aquatic flatworms that troll ponds and standing water resemble brown tubes equipped with just the basics: a pair of beady light-sensing "eyespots" on their head and a feeding tube called the pharynx (which doubles as the excretory tract) that protrudes from a belly sac to suck up food. It's hard to feel kinship with them.
But admiration is another thing, because many planaria species regenerate in wondrous ways—namely, when ...
Scarless wound healing -- applying lessons learned from fetal stem cells
2014-04-10
New Rochelle, NY, April 10, 2014—In early fetal development, skin wounds undergo regeneration and healing without scar formation. This mechanism of wound healing later disappears, but by studying the fetal stem cells capable of this scarless wound healing, researchers may be able to apply these mechanisms to develop cell-based approaches able to minimize scarring in adult wounds, as described in a Critical Review article published in Advances in Wound Care, a monthly publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers and an Official Journal of the Wound Healing Society. ...
Therapeutic options and bladder-preserving strategies in bladder cancer
2014-04-10
New Rochelle, NY, April 10, 2014—Men are three to four times more likely to get bladder cancer than women. The possible causes for this greater risk among men, the importance of early and accurate diagnosis, and the scope of available and emerging surgical, chemotherapeutic, and immunotherapeutic approaches for treating bladder cancer in men are the focus of a comprehensive Review article in Journal of Men's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Men's Health website.
Coauthors R. ...
Camels emit less methane than cows or sheep
2014-04-10
Ruminant cows and sheep account for a major proportion of the methane produced around the world. Currently around 20 percent of global methane emissions stem from ruminants. In the atmosphere methane contributes to the greenhouse effect – that's why researchers are looking for ways of reducing methane production by ruminants. Comparatively little is known about the methane production of other animal species – but one thing seems to be clear: Ruminants produce more of the gas per amount of converted feed than other herbivores.
The only other animal group that regularly ...
Neurofinance study confirms that financial decisions are made on an emotional basis
2014-04-10
The willingness of decision makers to take risks increases when they play games of chance with money won earlier. Risk taking also rises when they have the opportunity to compensate for earlier losses by breaking even. This outcome was demonstrated by Dr. Kaisa Hytönen, a Finnish Aalto University researcher in neurofinance, together with her international colleagues.
There are frequently various linkages between financial decisions: the circumstances accompanying the decision are rarely completely independent of each other. Both profits and losses, for example, on the ...
HIV battle must focus on hard-hit streets, paper argues
2014-04-10
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — In U.S. cities, it's not just what you do, but also your address that can determine whether you will get HIV and whether you will survive. A new paper in the American Journal of Public Health illustrates the effects of that geographic disparity – which tracks closely with race and poverty – and calls for an increase in geographically targeted prevention and treatment efforts.
"People of color are disproportionately impacted, and their risk of infection is a function not just of behavior but of where they live and the testing and treatment ...
Obsessive-compulsive disorder may reflect a propensity for bad habits
2014-04-10
Philadelphia, PA, April 10, 2014 – Two new studies published this week in Biological Psychiatry shed light on the propensity for habit formation in obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). These studies suggest that a tendency to develop habits, i.e., the compulsive component of the disorder, may be a core feature of the disorder rather than a consequence of irrational beliefs. In other words, instead of washing one's hands because of the belief that they are contaminated, some people may develop concerns about hand contamination as a consequence of a recurring urge to wash ...
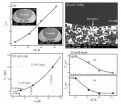
Solute redistribution profiles during rapid solidification of undercooled ternary Co-Cu-Pb alloy
2014-04-10
Researchers at the Department of Applied Physics, Northwestern Polytechnical University, in Xi'an, China, are engaged in revealing the mysteries of solidification process and the development of new materials using self-designed experimental instrument which can simulate the space environment such as containerless state. Solidification mechanism is of great importance to better understand the relationship between solidification process and microstructure evolution, so that we can follow them to design and prepare new materials which can meet the application requirements.
Dr. ...