(Press-News.org) Microbes can be highly efficient, versatile and sophisticated manufacturing tools, and have the potential to form the basis of a vibrant economic sector. In order to take full advantage of the opportunity microbial-based industry can offer, though, educators need to rethink how future microbiologists are trained, according to a report by the American Academy of Microbiology.
"Industrial microbiology is experiencing a Renaissance; microorganisms make products ranging from the tightly regulated pharmaceuticals industry to large-scale production of commodity chemicals and biofuels. Educating and training the next generation of employees for these rapidly expanding industries is critically important to their survival," says Joy Doran-Peterson of the University of Georgia who chaired the steering committee that produced the report.
For thousands of years humans have harnessed the power of microbes to make products such as bread, cheese, beer and wine. In the early 20th century scientists discovered how to use mold to produce antibiotics. It has only been in the past few decades, with the advent of DNA-based technologies, that our understanding of the vast diversity of microbial capabilities has exploded.
"If there is a chemical you want to break down, there is probably a microbe that can do it. If there is a compound you wish to synthesize, a microbe can probably help," says the report, entitled Microbe-Powered Jobs: How Microbiologists Can Help Build the Bioeconomy. The report provides a litany of examples of potential biological products including bioenergy, biofuels, environmentally friendly industrial chemicals, and bioenzymes (the production of which already fuels a nearly $4 billion market).
To take full advantage of the potential the bioeconomy offers, academia needs to re-think and take a broader approach to teaching microbiology at the undergraduate level. According to the report, the future growth of a microbial-based industry sector depends on two crucial elements: expansion of the fundamental understanding of microbiology and translation of that understanding into viable products.
Current microbiology education primarily trains scientists with an eye toward academic research, which is what is needed to continue the expansion of knowledge. Most undergraduates that take microbiology, though, have an eye on a medical career, so many undergraduate microbiology curricula focus on the biomedical aspects of microbiology, according to the report.
"One can imagine that instead of the current situation where pre-medicine is virtually the only undergraduate program with a microbiology component, there could be a series of majors with microbiology at their cores," says the report.
One specific major, which the report outlines, could be an industrial microbiology track, with a focus towards translation. Not only would it emphasize microbiology, but it would also include quantitative skills important for success in industry. This type of curriculum could also be made available to engineering students in the form of a bioengineering track.
In addition to the traditional degree programs, the report also recommends other formats be used to teach specialized skills or offer intensive introductions to new fields of study.
The report is based on the deliberations of experts who were gathered by the Academy to discuss the potential contributions of a microbe-powered industry and the human elements needed for this emerging sector to thrive. The contents reflect the discussions of the colloquium and are not intended to reflect official positions of the American Academy of Microbiology or the American Society for Microbiology.
INFORMATION:
The American Academy of Microbiology is the honorific leadership group of the American Society for Microbiology. The mission of the Academy is to recognize scientific excellence, as well as foster knowledge and understanding in the microbiological sciences. A full list of Academy colloquia reports can be found at http://academy.asm.org/index.php/browse-all-reports. For more information about the American Society for Microbiology, visit http://www.asm.org.
Rethink education to fuel bioeconomy, says report
2014-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UC research illuminates 'touchy' subject
2014-04-15
By solving a long standing scientific mystery, the common saying "you just hit a nerve" might need to be updated to "you just hit a Merkel cell," jokes Jianguo Gu, PhD, a pain researcher at the University of Cincinnati (UC).
That's because Gu and his research colleagues have proved that Merkel cells— which contact many sensory nerve endings in the skin—are the initial sites for sensing touch.
"Scientists have spent over a century trying to understand the function of this specialized skin cell and now we are the first to know … we've proved the Merkel cell to be a primary ...
Predicting bioavailable cadmium levels in soils
2014-04-15
New Zealand's pastoral landscapes are some of the loveliest in the world, but they also contain a hidden threat. Many of the country's pasture soils have become enriched in cadmium. Grasses take up this toxic heavy metal, which is then eaten by the cattle and sheep that graze them. The problem is not unique to New Zealand; cadmium-enriched soils being reported worldwide.
The concern is that if cadmium concentrations rise to unsafe levels in meat and dairy products, human health and New Zealand's agricultural economy could be jeopardized. That so far hasn't happened.
But, ...
Remnants of Tropical Depression Peipah still raining on Philippines
2014-04-15
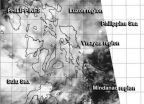
Several regions in the south and central Philippines have flood advisories as the remnants of now dissipated Tropical Depression Peipah continue to linger over the country. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite got a look at the remnant clouds from its orbit in space on April 15.
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a look at Peipah's remnant clouds on April 15 at 5:44 a.m. EDT. VIIRS collects visible and infrared imagery and global observations of land, atmosphere, cryosphere and oceans. The VIIRS ...
Study examines Vitamin D deficiency and cognition relationship
2014-04-15
WINSTON-SALEM – April 15, 2014 – Vitamin D deficiency and cognitive impairment are common in older adults, but there isn't a lot of conclusive research into whether there's a relationship between the two.
A new study from Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center published online ahead of print this month in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society enhances the existing literature on the subject.
"This study provides increasing evidence that suggests there is an association between low vitamin D levels and cognitive decline over time," said lead author Valerie Wilson, ...
NASA's TRMM Satellite adds up Tropical Cyclone Ita's Australian soaking
2014-04-15
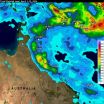
After coming ashore on April 11, Tropical Cyclone Ita dropped heavy rainfall over the weekend that caused flooding in many areas of northeastern Australia's state of Queensland. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM gathered data on rainfall that was used to create a rainfall map at NASA.
TRMM is a satellite managed by both NASA and JAXA, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Hal Pierce created a TRMM-based near-real time Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA). The TMPA precipitation ...
The key to easy asthma diagnosis is in the blood
2014-04-15
MADISON, Wis. — Using just a single drop of blood, a team of University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers has developed a faster, cheaper and more accurate tool for diagnosing even mild cases of asthma.
This handheld technology — which takes advantage of a previously unknown correlation between asthmatic patients and the most abundant type of white blood cells in the body — means doctors could diagnose asthma even if their patients are not experiencing symptoms during their visit to the clinic.
The team described its findings in the journal Proceedings of the National ...
Girls' mental health suffers when romances unfold differently than they imagined
2014-04-15
WASHINGTON, DC, April 15, 2014 — A new study reveals that for adolescent girls, having a romantic relationship play out differently than they imagined it would has negative implications for their mental health.
"I found that girls' risk of severe depression, thoughts of suicide, and suicide attempt increase the more their relationships diverge from what they imagined," said the study's author Brian Soller, an assistant professor of sociology and a senior fellow of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Center for Health Policy at the University of New Mexico.
"Conversely, ...
Genetic pre-disposition toward exercise and mental development may be linked
2014-04-15
COLUMBIA, Mo. – University of Missouri researchers have previously shown that a genetic pre-disposition to be more or less motivated to exercise exists. In a new study, Frank Booth, a professor in the MU College of Veterinary Medicine, has found a potential link between the genetic pre-disposition for high levels of exercise motivation and the speed at which mental maturation occurs.
For his study, Booth selectively bred rats that exhibited traits of either extreme activity or extreme laziness. Booth then put the rats in cages with running wheels and measured how much ...
How mothers help children explore right and wrong
2014-04-15
Montreal, April 15, 2014 — There's no question that mothers want their children to grow up to be good people — but less is known about how they actually help their offspring sort out different types of moral issues.
According to a new study published in Developmental Psychology and led by Holly Recchia, assistant professor in Concordia's Department of Education and the Centre for Research in Human Development, many mums talk to their kids in ways that help them understand moral missteps.
The study — co-written by Cecilia Wainryb, Stacia Bourne and Monisha Pasupathi ...
Biologists develop nanosensors to visualize movements and distribution of plant hormone
2014-04-15
Biologists at UC San Diego have succeeded in visualizing the movement within plants of a key hormone responsible for growth and resistance to drought. The achievement will allow researchers to conduct further studies to determine how the hormone helps plants respond to drought and other environmental stresses driven by the continuing increase in the atmosphere's carbon dioxide, or CO2, concentration.
A paper describing their achievement appears in the April 15 issue of the scientific journal eLife and is accessible at: http://elife.elifesciences.org/lookup/doi/10.7554/elife.01739 ...