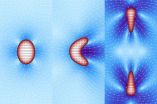
(Press-News.org) Counterfeiters, beware! Scientists are reporting the development of a new type of inexpensive barcode that, when added to documents or currency, could foil attempts at making forgeries. Although the tags are easy for researchers to make, they still require ingredients you can't exactly find at the local hardware store. Their report appears in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Xiaogang Liu and colleagues explain that scientists have used fluorescent and DNA-based barcodes, or tags of known composition and sequence, in attempts to develop tests for cancer and other diseases. But their high cost and faint signal have hampered their application in security inks. One estimate states that about $220 million in counterfeit bills are currently in circulation just in the U.S., and there's no way to tell how many other "official" documents are fake. Liu's team set out to thwart counterfeiters and overcome these obstacles by using microscopic "lanthanide-doped upconversion materials." Lanthanides are a set of elements that are in a wide variety of products, including ceramics, glass and portable x-ray devices.
The team made a set of multicolor barcodes with different combinations of red, green or blue fluorescent dots on either end of a tiny lanthanide-containing microrod using an inexpensive process. They then used these microrods to produce a transparent security ink. In this format, the barcodes are easily readable with a conventional microscope fitted with a near-infrared laser, but are invisible to the naked eye. They say the materials also could find application in imaging cells from the body.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from the National University of Singapore, the Ministry of Education, the Singapore-MIT Alliance, and the Agency for Science, Technology and Research.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter Facebook END
New type of barcode could make counterfeiters' lives more difficult
2014-04-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A greener source of polyester -- cork trees
2014-04-16
On the scale of earth-friendly materials, you'd be hard pressed to find two that are farther apart than polyester (not at all) and cork (very). In an unexpected twist, however, scientists are figuring out how to extract a natural, waterproof, antibacterial version of the first material from the latter. Their new technique, which could have applications in medical devices, appears in the ACS journal Biomacromolecules.
Cristina Silva Pereira and colleagues explain that polyesters are ubiquitous in modern life, and not just as a practical fabric for clothing. Their durability ...
Local homicide rate increases cause more elementary students to fail school
2014-04-16
WASHINGTON, DC, April 16, 2014 — A new study finds that an increase in a municipality's homicide rate causes more elementary school students in that community to fail a grade than would do so if the rate remained stable.
"This finding is a source of concern because exposure to environmental violence is highly prevalent in contemporary societies and is unequally distributed along socioeconomic lines," said study co-author Florencia Torche, an associate professor of sociology at New York University. "To the extent that children living in poverty are more likely to experience ...
Making radiation-proof materials for electronics, power plants
2014-04-16
The 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster made the dangers of radiation all too real. To avoid similar tragedies in the future, scientists are working to develop new radiation-proof materials for nuclear power plants, as well as for less obvious applications such as medical devices and airplanes. An article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the American Chemical Society's weekly news magazine, explores the latest developments.
Jyllian Kemsley, a senior editor at C&EN, points out that radiation can cause a range of problems from temperature misreadings in electronic devices ...
U of T study finds toddlers 'surprisingly sophisticated' at understanding unfamiliar accents
2014-04-16
TORONTO, ON -- A new University of Toronto study has found that by two years of age, children are remarkably good at comprehending speakers who talk with accents the toddlers have never heard before.
Even more striking, say researchers, children as young as 15 months who have difficulty comprehending accents they've never heard before can quickly learn to understand accented speech after hearing the speaker for a short time.
"Fifteen-month-olds typically say relatively few words, yet they can learn to understand someone with a completely unfamiliar accent," says Elizabeth ...
Survey: Percent of uninsured Texans has declined since September 2013
2014-04-16
HOUSTON – (April 16, 2014) – The percentage of uninsured adults ages 18 to 64 in Texas declined from 24.8 to 23.5 between September 2013 and March 2014, according to a report released today by Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy and the Episcopal Health Foundation. The decrease in uninsured appears to be attributable to an increase in employer-sponsored health insurance.
The report also found that during this period approximately 746,000 Texans purchased health insurance through the Affordable Care Act's Health Insurance Marketplace, of which 178,000 ...
HIV+ women respond well to HPV vaccine
2014-04-16
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — HIV-positive women respond well to a vaccine against the human papillomavirus (HPV), even when their immune system is struggling, according to newly published results of an international clinical trial. The study's findings counter doubts about whether the vaccine would be helpful, said the Brown University medical professor who led the study. Instead, the data support the World Health Organization's recommendation to vaccinate women with HIV.
HPV causes cervical and other cancers. The commonly used HPV vaccine Gardasil had not been ...
First metritis vaccine protects dairy cows
2014-04-16
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell scientists have created the first vaccines that can prevent metritis, one of the most common cattle diseases. The infection not only harms animals and farmers' profits, but also drives more systemic antibiotic use on dairy farms than any other disease.
The new vaccines prevent metritis infection of the uterus from taking hold and reduce symptoms when it does, a prospect that could save the United States billions of dollars a year and help curb the growing epidemic of antibiotic resistance. The research was published in the journal PLOS One.
Metritis ...
At the origin of cell division
2014-04-16
Droplets of filamentous material enclosed in a lipid membrane: these are the models of a "simplified" cell used by the SISSA physicists Luca Giomi and Antonio DeSimone, who simulated the spontaneous emergence of cell motility and division - that is, features of living material - in inanimate "objects". The research is one of the cover stories of the April 10th online issue of the journal Physical Review Letters.
Giomi and DeSimone's artificial cells are in fact computer models that mimic some of the physical properties of the materials making up the inner content and ...
EU must take urgent action on invasive species
2014-04-16
The EU must take urgent action to halt the spread of invasive species that are threatening native plants and animals across Europe, according to a scientist from Queen's University Belfast.
The threats posed by these species cost an estimated €12 billion each year across Europe. Professor Jaimie Dick, from the Institute for Global Food Security at Queen's School of Biological Sciences, is calling on the EU to commit long-term investment in a European-wide strategy to manage the problem.
Invasive species are considered to be among the major threats to native biodiversity ...
Expect changes in appetite, taste of food after weight loss surgery
2014-04-16
Changes in appetite, taste and smell are par for the course for people who have undergone Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery during which one's stomach is made smaller and small intestines shortened. These sensory changes are not all negative, and could lead to more weight loss among patients, says Lisa Graham, lead author of a study by researchers from Leicester Royal Infirmary in the UK. Their findings, published in Springer's journal Obesity Surgery showed that after gastric bypass surgery, patients frequently report sensory changes.
Graham and her colleagues say their ...