(Press-News.org) A breakthrough in the design of signal amplifiers for mobile phone masts could deliver a massive 200MW cut in the load on UK power stations, reducing CO2 emissions by around 0.5 million tonnes a year.
Funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), the Universities of Bristol and Cardiff have designed an amplifier that works at 50 per cent efficiency compared with the 30 per cent now typically achieved.
Currently, a 40W transmitter in a phone mast's base station* requires just over 130W of power to amplify signals and send them wirelessly to people's mobiles. The new design, however, enables the transmitter to work effectively while using just 80W of power.
If 10,000 base stations in the UK were fitted with the new amplifier, it is estimated that the total saving would amount to half the output of a mid-size, 400MW power station. There are currently around 50,000 phone mast base stations in the UK,** so the potential energy and carbon-saving benefits could be even greater.
The team's development of a less power-hungry amplifier has focused on devising sophisticated new computing algorithms for incorporation into its inbuilt electronic management system, as well as on making a number of adjustments to the amplifier hardware.
Dr Kevin Morris, project leader and Reader in Radio Frequency Engineering, Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering at the University of Bristol, said: "This new amplifier design represents a step change in energy efficiency that could make a really valuable contribution to meeting the UK's carbon reduction targets."
The team have also succeeded in simplifying the whole amplifier design process, which is of vital importance to encouraging widespread take-up of the project's findings.
"Traditionally, designing signal amplifiers for base stations has been a long, complex process involving a trial-and-error approach and producing one-off solutions," Dr Morris explained. "This has fuelled a reluctance to develop new amplifier designs. To get over that barrier, we've made it a priority to ensure our design is easily replicable."
The team are now working with a major electronics company to take some of the project's key findings towards commercialisation. Follow-up funding has also been secured through an Impact Acceleration Grant awarded by EPSRC.
Results from the project were presented at CeBIT 2014, a major trade fair for the digital industry held in Hanover, Germany.
INFORMATION:
Notes to Editors:
An image is available to download from the link below. The image is for single-use only and should not be archived.
https://fluff.bris.ac.uk/fluff/u3/injf/1dwGrhYhP2ZQ8_wo7mIMcgK2N/
Caption: A signal amplifier
Credit Image courtesy of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Bristol, copyright © 2014
The project 'Holistic Design of Power Amplifiers for Future Wireless Systems' lasted 5.5 years and received total EPSRC funding of around £1.8 million.
* Base stations for mobile phone masts incorporate transmitters that are installed in a cabinet and connected to the antenna.
** Number of base stations in the UK (2011 estimate): http://www.mobilemastinfo.com/base-stations-and-masts/
For more information on CeBIT 2014, see http://www.cebit.de
For more information, contact:
Dr Kevin Morris, University of Bristol, Tel: 0117 954 5268, email: kevin.morris@bristol.ac.uk
For media enquiries contact:
Joanne Fryer, Press Officer, University of Bristol, Tel: (0117) 331 7276, mobile: 07747 768805, email joanne.fryer@bristol.ac.uk
OR
The EPSRC Press Office, Tel: 01793 444 404, e-mail: pressoffice@epsrc.ac.uk
Notes to Editors:
Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC)
The Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) is the UK's main agency for funding research in engineering and the physical sciences. EPSRC invests around £800 million a year in research and postgraduate training, to help the nation handle the next generation of technological change. The areas covered range from information technology to structural engineering, and mathematics to materials science. This research forms the basis for future economic development in the UK and improvements for everyone's health, lifestyle and culture. EPSRC works alongside other Research Councils with responsibility for other areas of research. The Research Councils work collectively on issues of common concern via Research Councils UK. http://www.epsrc.ac.uk
New design for mobile phone masts could cut carbon emissions
2014-04-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Speed-reading apps may impair reading comprehension by limiting ability to backtrack
2014-04-22
To address the fact that many of us are on the go and pressed for time, app developers have devised speed-reading software that eliminates the time we supposedly waste by moving our eyes as we read. But don't throw away your books, papers, and e-readers just yet — research suggests that the eye movements we make during reading actually play a critical role in our ability to understand what we've just read.
The research is published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Our findings show that eye movements are a crucial part ...
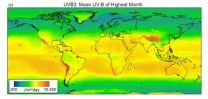
UV-radiation data to help ecological research
2014-04-22
Many research projects study the effects of temperature and precipitation on the global distribution of plant and animal species. However, an important component of climate research, the UV-B radiation, is often neglected. The landscape ecologists from UFZ in collaboration with their colleagues from the Universities in Olomouc (Czechia), Halle and Lüneburg have processed UV-B data from the U.S. NASA space agency in such a way that they can be used to study the influence of UV-B radiation on organisms.
The basic input data were provided by a NASA satellite that regularly, ...
A family of compact schemes with minimized dispersion and controllable dissipation was developed
2014-04-22
Spectral properties optimization is an important issue for developing schemes to resolve flow fields that are characterized by a wide range of length scales such as turbulent flows and aero acoustic phenomena. The work finished by Dr SUN Zhensheng and his ground provided a novel approach to optimize the dissipation and dispersion properties of a family of tri-diagonal compact schemes. The corresponding paper entitled "A high-resolution, hybrid compact-WENO scheme with minimized dispersion and controllable dissipation" was published in Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2014 Vol. ...
'Tween' television programming promotes some stereotypical conceptions of gender roles
2014-04-22
COLUMBIA, Mo. – The term "tween" denotes a child who is between the ages of 8 and 12 and is used to describe a preadolescent who is "in between" being a child and a teen. This demographic watches more television than any other age group and is considered to be a very lucrative market. Tween television programming consists of two genres: "teen scene" (geared toward girls) and "action-adventure" (geared toward boys). Researchers at the University of Missouri found that these programs could lead tweens to limit their views of their potential roles in society just as they begin ...
How often are unauthorized immigrant workers trafficked and abused?
2014-04-22
Los Angeles, CA (April 22, 2014) Labor trafficking – or recruiting a person for labor through force, fraud, or coercion for involuntary servitude, debt bondage, or even slavery – has been a difficult problem to track among undocumented migrant workers. With unique access to a "hidden population" from one of America's largest Spanish-speaking immigrant destinations, a recent study finds that more than 30% of undocumented migrant laborers in this area are victims of labor trafficking and 55% are victims of other labor abuses.
In this study, published in the May issue of ...
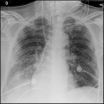
New tool helps doctors better predict, prevent deadly respiratory failure
2014-04-22
A new prediction tool can help doctors better identify patients who are at highest risk for respiratory failure after surgery and therefore prevent the often deadly condition, suggest data from a large multi-center study published in the May issue of Anesthesiology.
Affecting nearly 200,000 Americans a year, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a sudden failure of the lungs caused by a number of issues ranging from smoke inhalation to pneumonia or blood infection. High-risk patients can develop ARDS after surgery. ARDS is difficult to treat once it develops and ...
Minnesota projects offer hope and practical help to communities facing more extreme storms
2014-04-22
Recent projects in two Minnesota cities demonstrate how communities can protect themselves from worsening storms. These projects continue a ten year program in New England and the Midwest providing practical and affordable plans tailored to local conditions.
"Our goal is to help communities begin the steps to protect themselves," said program co-leader Latham Stack, of Syntectic International, Portland, OR. "It's important because storms have already worsened. We help communities move beyond feeling paralyzed from the lack of local information and the sense that the problem ...
False-positive mammogram anxiety has limited impact on women's well-being
2014-04-22
(Lebanon, NH, 4/22/14). Dartmouth researchers have found that the anxiety experienced with a false-positive mammogram is temporary and does not negatively impact a woman's overall well-being. Their findings are reported in "Consequences of False-Positive Screening Mammograms," which was published online in the April 21, 2014 JAMA Internal Medicine
Anywhere from 40 to 60 percent of women who undergo routine screening mammography during a ten-year period will experience a false-positive mammogram. Such mammograms require additional testing, sometimes involving a biopsy, ...
Cannabis chemistry: How scientists test pot for potency and safety (video)
2014-04-22
WASHINGTON, April 22, 2014 — Marijuana is in the headlines as more and more states legalize it for medicinal use or decriminalize it entirely. In the American Chemical Society's (ACS') newest Reactions video, we explain the chemistry behind marijuana's high, and investigate what scientists are doing to ensure that legalized weed won't send users on a bad trip. The video is available at http://youtu.be/4ukdUDCE56c
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:
The American ...
Researchers identify a mechanism linking bariatric surgery to health benefits
2014-04-22
Bariatric surgery has positive effects not only on weight loss but also on diabetes and heart disease. Researchers at the Sahlgrenska Academy and University of Cincinnati have shown that the health benefits are not caused by a reduction in the stomach size but by increased levels of bile acids in the blood. These findings, reported in Nature, indicate that bile acids could be a new target for treating obesity and diabetes.
Previous research from the Sahlgrenska Academy has demonstrated that obesity surgery is the only effective treatment for obesity and obesity-related ...