(Press-News.org) CINCINNATI—Researchers at the University of Cincinnati (UC) have found a potential genetic target for heart disease, which could lead to therapies to prevent the development of the nation's No. 1 killer in its initial stages.
These findings will be presented for the first time at the American Heart Association's (AHA) Scientific Sessions in Chicago Nov. 17.
The study, led by WenFeng Cai, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow under the direction of Litsa Kranias, PhD, AHA distinguished scientist and Hanna Chair in Cardiology in the department of pharmacology and cell biophysics, shows that a micro-RNA, known as miR765, which regulates gene expressions, can down-regulate the expression of protein phosphatase 1 inhibitor-1 (I-1) and reduce the contractility of cells that make up cardiac muscle.
"Previous studies have shown that the reduction in I-1 expression may play a role in the pathogenesis of heart disease," Cai says. "However, the underlying molecular mechanism contributing to this down-regulation is unknown.
"We wanted to see if miR765 would serve as a candidate to regulate this protein expression and affect the contractility of the cardiac muscle cells."
Using a gene transfer agent—or virus—researchers moved either miR-765 or a control agent into ventricular cells of animal models.
Data showed that the expression of I-1 messenger RNA was decreased by 20 percent in the miR765 cells of these models when compared with the control models.
"Under resting conditions, the contractile parameters were decreased in miR765-treated animal models," Cai says. "Although beta adrenergic agonist, used to speed up the pumping action of the heart, had a positive effect, the contractile function remained suppressed in the miR765 group."
Cai adds that analysis showed both phosphorylations of phospholamban and ryanodine receptor, the proteins that regulate calcium uptake and calcium release, were significantly reduced in the miR765 group both in the presence and in the absence of beta adrenergic agonist.
"These findings show that miR765 can down-regulate the expression and reduce contractility of heart cells by decreasing or deactivating a number of proteins that help the heart function at full capacity," Cai says. "This leads us to believe that miR765 may play a role in the development of heart failure.
"Hopefully, these findings will lead to future studies, helping researchers and clinicians develop a therapeutic target to stop heart disease where it first starts: in the genes."
INFORMATION:
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Researchers discover potential genetic target for heart disease
2010-11-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers fight America's 'other drug problem'
2010-11-18
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Medications do not have a chance to fight health problems if they are taken improperly or not taken at all. Non-adherence to medications costs thousands of lives and billions of dollars each year in the United States alone, according to the New England Healthcare Institute. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have developed an intervention strategy that is three times more effective than previously studied techniques at improving adherence in patients.
Cynthia Russell, associate professor in the MU Sinclair School of Nursing, found that patients ...
Toronto Western Hospital study demonstrates improved wait times for patients suffering back pain
2010-11-18
Results of a Toronto Western Hospital study show that patients suffering back pain get quicker diagnosis and treatment when a Nurse Practitioner conducts the first examination. Traditionally, patients face long and anxiety-ridden wait times - up to 52 weeks – before an initial examination by a spine surgeon. Results from the year long TWH study showed wait times for patients examined by a Nurse Practitioner were significantly shorter, ranging from 10 to 21 weeks.
"Waiting times for specialty consultations in public healthcare systems worldwide are lengthy and impose undue ...
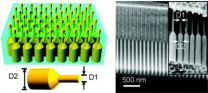
A new twist for nanopillar light collectors
2010-11-18
Sunlight represents the cleanest, greenest and far and away most abundant of all energy sources, and yet its potential remains woefully under-utilized. High costs have been a major deterrant to the large-scale applications of silicon-based solar cells. Nanopillars - densely packed nanoscale arrays of optically active semiconductors - have shown potential for providing a next generation of relatively cheap and scalable solar cells, but have been hampered by efficiency issues. The nanopillar story, however, has taken a new twist and the future for these materials now looks ...
Battling a bat killer
2010-11-18
Scientists are looking for answers — including commercial bathroom disinfectants and over-the-counter fungicides used to fight athlete's foot — to help in the battle against a strange fungus that threatens bat populations in the United States. That's the topic of an article in the current issue of Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), ACS' weekly newsmagazine.
C&EN Senior Correspondent Stephen K. Ritter notes that despite their poor public image, bats are beneficial. They pollinate plants, spread seeds, and eat vast numbers of insects that otherwise could destroy food ...
Low-allergenic wines could stifle sniffles and sneezes in millions of wine drinkers
2010-11-18
Scientists have identified a mysterious culprit that threatens headaches, stuffy noses, skin rash and other allergy symptoms when more than 500 million people worldwide drink wine. The discovery could help winemakers in developing the first low allergenic vintages — reds and whites with less potential to trigger allergy symptoms, they say. The new study appears in ACS' monthly Journal of Proteome Research.
Giuseppe Palmisano and colleagues note growing concern about the potential of certain ingredients in red and white to cause allergy-like symptoms that range from stuffed ...
Differences in brain development between males and females may hold clues to mental health disorders
2010-11-18
Many mental health disorders, such as autism and schizophrenia, produce changes in social behavior or interactions. The frequency and/or severity of these disorders is substantially greater in boys than girls, but the biological basis for this difference between the two sexes is unknown.
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine have discovered differences in the development of the amygdala region of the brain – which is critical to the expression of emotional and social behaviors – in animal models that may help to explain why some mental health disorders ...
Advance toward controlling fungus that caused Irish potato famine
2010-11-18
Scientists are reporting a key advance toward development of a way to combat the terrible plant diseases that caused the Irish potato famine and still inflict billions of dollars of damage to crops each year around the world. Their study appears in ACS' bi-weekly journal Organic Letters.
Teck-Peng Loh and colleagues point out that the Phytophthora fungi cause extensive damage to food crops such as potatoes and soybeans as well as to ornamental plants like azaleas and rhododendrons. One species of the fungus caused the Irish potato famine in the mid 1840s. That disaster ...
Study: Employers, workers may benefit from employee reference pool
2010-11-18
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — With employers increasingly reluctant to supply references for former employees in order to avoid legal liability, the creation of a centralized reference pool for workers may make labor markets in the U.S. more efficient, a University of Illinois expert in labor and employment law says.
Law professor Matthew W. Finkin says that not only do employees face challenges when securing references from past employers, but employers also expose themselves to lawsuits when they provide a reference.
"Employees benefit from references, but there's nothing in ...
Multiple sclerosis drug serves as model for potential drugs to treat botulism poisoning
2010-11-18
Scientists are reporting that variants of a drug already approved for treating multiple sclerosis show promise as a long sought treatment for victims of bioterrorist attack with botulinum neurotoxin — which is 10,000 times deadlier than cyanide and the most poisonous substance known to man. The potential drugs also could be useful in treating other forms of botulism poisoning as well as Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, and myasthenia gravis, they say in an article in ACS Chemical Biology, a monthly journal.
Kim D. Janda and colleagues explain that the lack of ...
Being faced with gender stereotypes makes women less likely to take financial risks
2010-11-18
Last year Nicholas Kristof declared in his New York Times column what banks need to fix their problems: Not just a bailout, but also "women, women, and women." Women are generally thought to be less willing to take risks than men, so he speculated that the banks could balance out risky men by employing more women. Stereotypes like this about women actually influence how women make financial decisions, making them more wary of risk, according to a new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Anecdotally, many people ...