(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH—The robust defenses that yeast cells have evolved to protect themselves from environmental threats hold lessons that can be used to design computer networks and analyze how secure they are, say computer scientists at Carnegie Mellon University.
Environmental "noise" is a key evolutionary pressure that shapes the interconnections within cells, as well as those of neural networks and bacterial/ecological networks, they observe in a paper to be published online April 30 by the Journal of the Royal Society Interface. The researchers factored this into an established model for the evolution of molecular connections, resulting in an algorithm that gives rise to a rich range of architectures found in biological, computer and other types of networks.
Saket Navlakha, a post-doctoral researcher in CMU's Machine Learning Department, said this approach is particularly helpful in understanding how networks respond to cascading failures, whether it be an overloaded power grid or a computer network being overwhelmed by fake identities in a so-called sybil attack.
The generative model the CMU team developed can be used to tailor networks to the environments in which they are expected to operate. These strike a balance between highly connected networks that are efficient and fast but are prone to infections and cascading failures, such as the Internet and its large service providers, and more sparsely connected elements that are less efficient, requiring more time to relay information, but can better tolerate failures and attacks, such as peer to peer networks. That's a balance that evolution already has achieved in yeast. A yeast cell has about 6,000 genes, of which 20 percent are considered essential — that is, if the gene is removed, the cell dies. But Ziv Bar-Joseph, an associate professor in the Machine Learning Department and the Lane Center for Computational Biology, said that view of what is essential and what isn't reflects how scientists study genes — by noting their effects on an organism when a gene is removed — not necessarily the gene's importance.
"The cell did not evolve to protect itself against the deletion of these 'essential' genes," Bar-Joseph said, noting that's an event that doesn't often occur in nature.
Rather, the fragility of genes, proteins and other cell components may reflect exposure to their environment. Those that lie near the cell surface, for instance, can expect to encounter lots of environmental stress, so the cell has evolved to tolerate the loss of some of them. Those involved in DNA duplication, on the other hand, normally don't experience that kind of exposure to noise and so don't have the same robust interconnections. That's why the cell dies if one of those genes is removed, Bar-Joseph noted.
Just as biologists study genes by knocking them out, one by one, computer scientists often evaluate network security by removing a server and seeing how the network responds. But Navlakha said that's not always realistic; many attacks or failures of computer and electrical networks can involve the loss of multiple, neighboring nodes.
To better understand the significance of how various networks are interconnected, the Carnegie Mellon researchers, including Christos Faloutsos, professor of computer science, and Xin He, a Lane Fellow in computational biology, modified the well-known duplication-divergence model used to explain the evolution of molecular networks. The concept is that gene duplication can result in two equivalent proteins that, over time, diverge to develop specialized subtasks, while also maintaining common connections.
By adjusting the duplication-divergence model to account for the pressure of environmental noise, the researchers developed a method that can be used to generate or evaluate the interconnection, or topology, of networks that work in a variety of environments. A military network, for instance, might not worry about malevolent viruses and noise because access is restricted, while a wireless sensor network deployed over a wide area might need to tolerate continual losses of random nodes.
At the same time, the evolutionary role of external noise might well prove to be an insight that will enhance the understanding of biological networks, Bar-Joseph added.
INFORMATION:
The work was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the James S. McDonnell Foundation.
The Lane Center and the Machine Learning Department are part of Carnegie Mellon's top-ranked School of Computer Science, which is celebrating its 25th year. Follow the school on Twitter @SCSatCMU.
About Carnegie Mellon University: Carnegie Mellon is a private, internationally ranked research university with programs in areas ranging from science, technology and business, to public policy, the humanities and the arts. More than 12,000 students in the university's seven schools and colleges benefit from a small student-to-faculty ratio and an education characterized by its focus on creating and implementing solutions for real problems, interdisciplinary collaboration and innovation. A global university, Carnegie Mellon has campuses in Pittsburgh, Pa., California's Silicon Valley and Qatar, and programs in Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe and Mexico.
Molecular networks provide insights for computer security, Carnegie Mellon finds
Viruses and other external threats drive evolution of robust architectures
2014-04-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bigger is not always better, but it helps, says new research on beetles
2014-04-30
Researchers at the University of Exeter have found that the probability of a burying beetle winning fights, for the small animal carcasses it needs, depends on a combination of early life experiences and the competition it faces as an adult.
These beetles use small dead animals, such as mice and songbirds, to provide food for their young and competition for a carcass can be fierce.
Previous work has found that success in such contests depends on how good your early adult life environment was, not just how big you are. However, in many animals food availability can ...
The intergalactic medium unveiled: Caltech's Cosmic Web Imager
2014-04-30
Caltech astronomers have taken unprecedented images of the intergalactic medium (IGM)—the diffuse gas that connects galaxies throughout the universe—with the Cosmic Web Imager, an instrument designed and built at Caltech. Until now, the structure of the IGM has mostly been a matter for theoretical speculation. However, with observations from the Cosmic Web Imager, deployed on the Hale 200-inch telescope at Palomar Observatory, astronomers are obtaining our first three-dimensional pictures of the IGM. The Cosmic Web Imager will make possible a new understanding of galactic ...
Stem cells aid heart regeneration in salamanders
2014-04-29
SAN DIEGO (April 29, 2014) – Imagine filling a hole in your heart by regrowing the tissue. While that possibility is still being explored in people, it is a reality in salamanders. A recent discovery that newt hearts can regenerate may pave the way to new therapies in people who need to have damaged tissue replaced with healthy tissue.
Heart disease is the leading cause of deaths in the United States. Preventative measures like healthful diets and lifestyles help ward off heart problems, but if heart damage does occur, sophisticated treatments and surgical procedures ...
Study confirms increased prevalence of GI symptoms among children with autism
2014-04-29
A new study conducted by researchers at Marcus Autism Center, Children's Healthcare of Atlanta and Emory University School of Medicine indicates that children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are more than four times more likely to experience general gastrointestinal (GI) complaints compared with peers, are more than three times as prone to experience constipation and diarrhea than peers, and complain twice as much about abdominal pain compared to peers.
The results were reported in the April 28, 2014, online early edition of the journal Pediatrics.
While parents ...
NASA satellite sees colder temperatures at tops of severe weather thunderstorms
2014-04-29
The weather system that dropped tornadoes in seven central and southern U.S. states on April 27-28, moved east and generated more tornadoes on April 29. NASA's Aqua satellite gathered temperature data on the thunderstorm cloud tops in the system and found them to be higher in the atmosphere and colder. The tornado outbreak over the evening and overnight hours of April 28-29 is thought to have generated more tornadoes in northern Mississippi and Alabama.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the eastern U.S. early in the morning on April 29 at 07:41 UTC/3:41 a.m. EDT and gathered ...
Search for extraterrestrial life more difficult than thought
2014-04-29
A new study from the University of Toronto Scarborough suggests the search for life on planets outside our solar system may be more difficult than previously thought.
The study, authored by a team of international researchers led by UTSC Assistant Professor Hanno Rein from the Department of Physical and Environmental Science, finds the method used to detect biosignatures on such planets, known as exoplanets, can produce a false positive result.
The presence of multiple chemicals such as methane and oxygen in an exoplanet's atmosphere is considered an example of a ...
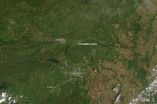
NASA satellite spots tornado track near Conway, Ark.
2014-04-29
A violent tornado touched down in Arkansas on April 27, 2014, killing as many as 15 people. The top image, acquired on April 28 by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA's Aqua satellite, shows what appears to be a tornado track north of Little Rock, Arkansas. The lower image, from April 25, shows the same area before the storm. The tracks are pale brown trails where trees and plants have been uprooted, leaving disturbed ground.
The difference in clarity between the two images is likely due to the centering of the scene beneath the satellite. ...
Preliminary results show improvement in MS symptoms
2014-04-29
Combining the estrogen hormone estriol with Copaxone, a drug indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), may improve symptoms in patients with the disorder, according to preliminary results from a clinical study of 158 patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). The findings were presented today by Rhonda Voskuhl, M.D., from the University of California, Los Angeles, at the American Academy of Neurology Annual Meeting in Philadelphia. The study was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and ...
Octillions of microbes in the seas: Ocean microbes show incredible genetic diversity
2014-04-29
The smallest, most abundant marine microbe, Prochlorococcus, is a photosynthetic bacterial species essential to the marine ecosystem.
It's estimated that billions of the single-celled creatures live in the oceans, forming the center of the marine food web.
They occupy a range of ecological niches based on temperature, light, water chemistry and interactions with other species.
But the diversity within this single species remains a puzzle.
To probe this question, scientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) recently performed a cell-by-cell genomic ...
Consuming high-protein breakfasts helps women maintain glucose control, MU study finds
2014-04-29
COLUMBIA, Mo. – In healthy individuals, the amount of glucose, or sugar, in the blood increases after eating. When glucose increases, levels of insulin increase to carry the glucose to the rest of the body. Previous research has shown that extreme increases in glucose and insulin in the blood can lead to poor glucose control and increase an individual's risk of developing diabetes over time. Now, a University of Missouri researcher has found that when women consumed high-protein breakfasts, they maintained better glucose and insulin control than they did with lower-protein ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
[Press-News.org] Molecular networks provide insights for computer security, Carnegie Mellon findsViruses and other external threats drive evolution of robust architectures