(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
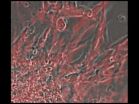
This shows heart tissue grown in a dish from mouse cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs). The CPCs, and the tissue they built, were engineered to produce a red protein.
Click here for more information.
A type of cell that builds mouse hearts can renew itself, Johns Hopkins researchers report. They say the discovery, which likely applies to such cells in humans as well, may pave the way to using them to repair hearts damaged by disease — or even grow new heart tissue for transplantation.
In a study to be published in an upcoming issue of the journal eLife, the scientists also found that during heart formation, these so-called cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs) multiply without becoming heart cells in a cellular environment known as the second pharyngeal arch. This insight into the biology of CPCs may contribute to better understanding of how to prevent and treat congenital heart defects, they say.
"Our finding that CPCs are self-renewing — that they can keep dividing to form new CPCs — means they might eventually be maintained in a dish and used to make specific types of heart cells," says Chulan Kwon, Ph.D., an assistant professor of cardiology and member of the Institute for Cell Engineering at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. "Growing such cells in a dish would be an enormous step toward better treatment for heart disease."
Kwon's research group's first step was figuring out the role of two genes, Numb and Numbl, in CPCs, which others' studies had shown are needed for guiding stem and progenitor cells to their fully mature, specialized functions. Numb and Numbl are highly conserved, meaning that they're nearly identical in mice, humans and other animals, a sign that they're likely very important. To find out whether these genes are required for heart formation, the group disabled Numb and Numbl in early CPCs in developing mouse embryos. "The embryos failed to develop normal hearts and died at an early stage of development, showing us that Numb and Numbl are needed for CPCs to build the heart," Kwon says.
The researchers next set out to find where CPCs live in the developing embryo. Using embryonic stem cells from mouse embryos, they again disabled Numb and Numbl while also engineering the cells to produce a glowing red protein, which would give away the CPCs' location. But because the engineered stem cells alone wouldn't grow into a viable embryo, the team injected them into normal mouse blastocysts — a structure formed in the early stage of mammalian development that forms both the embryo and placenta. "The normal cells in these blastocysts compensated for those that lacked Numb and Numbl, allowing the resulting embryos to survive," Kwon says.
When the team checked the hearts of the embryos, they found the glowing red cells in the second pharyngeal arch, which is known for forming parts of the neck and face. Kwon says theirs is the first study to identify it as home to CPCs. His team took cells surrounding CPCs from this arch and grew them with CPCs in a dish. They found that the CPCs self-renewed without developing into specialized heart cells. This is an important step, he says, toward using CPCs to treat heart disease.
The next step, he says, is to coax the lab-grown CPCs to form new heart tissue that could be used to regenerate disease-damaged heart tissue. "Eventually, we might even be able to deliver cells to damaged hearts to repair heart disease," Kwon says.
INFORMATION:
Link to the article: http://elifesciences.org/content/early/2014/04/23/eLife.02164
Other authors on the paper were Lincoln Shenje, Peter Andersen, Hideki Uosaki, Laviel Fernandez, Peter Rainer, Gunsik Cho, Dong-ik Lee and David Kass of The Johns Hopkins University; Weimin Zhong of Yale University; and Richard Harvey of the Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute.
Mouse study points to potentially powerful tool for treating damaged hearts
May also lead to new insights into congenital heart defects
2014-04-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Suomi NPP satellite sees clouds filling Tropical Storm Tapah's eye
2014-04-30
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP passed over Tapah and captured a visible image of the storm that gave a hint of weakening as clouds began to fill its eye. On April 30 at 0900 UTC/5 a.m. EDT, Tropical Storm Tapah continued to weaken as wind shear began to increase and the storm moved toward cooler waters in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Tapah on April 30 and the VIIRS instrument aboard captured a visible image of the storm as it weakened from a typhoon to a tropical storm. The imagery showed that Tapah's eye was becoming ...
New experimental vaccine produces immune response against MERS virus
2014-04-30
The University of Maryland School of Medicine (UM SOM) and Novavax, Inc. (NASDAQ: NVAX) today announced that an investigational vaccine candidate developed by Novavax against the recently emerged Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) blocked infection in laboratory studies. UM SOM and Novavax also reported that a vaccine candidate against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) developed by Novavax on a similar platform also inhibited virus infection. Researchers reported these findings in an article published in the April 13, 2014 issue ...
Whey beneficially affects diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk factors in obese adults
2014-04-30
New evidence shores up findings that whey protein, which is found in milk and cheese, could have health benefits for people who are obese and do not yet have diabetes. The study, which appears in ACS' Journal of Proteome Research, examined how different protein sources affect metabolism.
Lars O. Dragsted, Kjeld Hermansen and colleagues point out that obesity continues to be a major public health problem worldwide. In the U.S. alone, about 35 percent of adults and about 17 percent of children are obese, a condition that can lead to a number of health issues, including ...
SDSC resources, expertise used in genomic analysis of 115 year-old woman
2014-04-30
A team of researchers investigating the genome of a healthy supercentenarian since 2011 has found many somatic mutations – permanent changes in cells other than reproductive ones – that arose during the woman's lifetime. Led by Erik Sistermans and Henne Holstege from the VU University Medical Center in Amsterdam, the team recently published its findings in the journal Genome Research as reported by GenomeWeb.
While previous studies have examined mutations that arise in certain disease conditions such as leukemia, Sistermans said that it was not well known how many mutations ...
N-glycan remodeling on glucagon receptor is an effector of nutrient-sensing by HBP
2014-04-30
TORONTO -- A possible therapeutic target for control of blood glucose in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity has been identified by Dr. Anita Johswich and her colleagues. Their findings were published in Journal of Biological Chemistry, online April 17, 2014.
An imbalance in the competing action of insulin and glucagon is widely viewed as a critical factor in onset of type 2 diabetes, a relentlessly increasing health problem. A delicate balance between two hormones controls blood glucose levels day and night. After a meal, blood glucose rises, which stimulates ...
A protein key to the next green revolution sits for its portrait
2014-04-30
If you pull up a soybean or bean plant and shake off the dirt, you might see odd swellings or bumps, like rheumatic finger joints, on its roots. Inside the cool, soil-covered bumps are bacteria that are making nitrogen with the help of an enzyme, something chemical factories can do only with the help of a catalyst and at high temperature and pressure.
The bacteria, typically members of the genus Rhizobia, break the strong triple bond between the nitrogen molecules in the air and repackage the nitrogen atoms in chemical compounds the plant can use. In return, the plant ...
'Charismatic' organisms still dominating genomics research
2014-04-30
Decades after the genomics revolution, half of known eukaryote lineages still remain unstudied at the genomic level--with the field displaying a research bias against 'less popular', but potentially genetically rich, single-cell organisms.
This lack of microbial representation leaves a world of untapped genetic potential undiscovered, according to an exhaustive survey conducted by UBC researchers of on-going genomics projects. The survey results are published in the May issue of Trends in Ecology and Evolution.
"We're still mostly analyzing the same well-known eukaryotic ...
Deep origins to the behavior of Hawaiian volcanoes
2014-04-30
Kīlauea volcano, on the Big Island of Hawai'i, typically has effusive eruptions, wherein magma flows to create ropy pāhoehoe lava, for example. However, Kīlauea less frequently erupts more violently, showering scoria and blocks over much of the surface of the island. To explain the variability in Kīlauea's eruption styles, a team including Bruce Houghton, the Gordon Macdonald Professor of Volcanology in Geology and Geophysics at the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa (UHM) School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) and colleagues from ...
New tool for Joint Lab to investigate the chemistry of nature
2014-04-30
This news release is available in German. HZB-scientist Emad Aziz, who leads the Joint lab between HZB and Freie Universität Berlin, has developed and installed a new tool to investigate ultrafast dynamics in solutions and at interfaces with the use of ultrashort Laser pulses. Liquid phases are a natural environment for many interesting processes in chemistry and biology, and short light pulses allow insights into electronic and structural dynamics of molecules and molecular complexes. In particular, photoelectron spectroscopy with extreme ultraviolet (XUV) radiation ...
Harnessing magnetic vortices for making nanoscale antennas
2014-04-30
UPTON, NY—Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory are seeking ways to synchronize the magnetic spins in nanoscale devices to build tiny yet more powerful signal-generating or receiving antennas and other electronics. Their latest work, published in Nature Communications, shows that stacked nanoscale magnetic vortices separated by an extremely thin layer of copper can be driven to operate in unison, potentially producing a powerful signal that could be put to work in a new generation of cell phones, computers, and other applications.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Mouse study points to potentially powerful tool for treating damaged heartsMay also lead to new insights into congenital heart defects