(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Women face greater limits on their lifestyle and have more severe symptoms as a result of peripheral artery disease (PAD), but minimally invasive procedures used to unclog arteries are just as successful as in men.
The success of procedures, such as angioplasty or stent placement, in treating women with leg PAD was revealed in a Journal of the American College of Cardiology study.
The study provides a rare look at gender differences in PAD. PAD happens when fatty deposits build up in arteries outside the heart, usually the arteries supplying fresh oxygen and blood to the arms, legs and feet.
About 8 million Americans have peripheral artery disease, but PAD awareness among men and women is strikingly low compared with other cardiovascular diseases like hypertension and heart attacks.
"We found that women had excellent outcomes compared to men, even though they were older and had more severe disease," says senior study author P. Michael Grossman, M.D., an interventional cardiologist at the University of Michigan Frankel Cardiovascular Center and director of the cardiac catheterization laboratory at the Veterans Administration Ann Arbor Healthcare System.
Before treatment, women were at higher risk of amputation, and more likely to suffer from leg pain at rest or ulceration, called critical limb ischemia.
Fewer women complained of leg discomfort, fatigue or cramping with activity known as claudication, according to the study.
"The reasons for differences in symptoms are unclear, and deserve further study. It does indicate that we need to be vigilant in asking women about leg discomfort and screening women for PAD," says Grossman.
Researchers used Michigan's Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan Cardiovascular Consortium PVI registry, which collected data from 16 Michigan hospitals about percutaneous peripheral vascular intervention.
A total of 12,379 patients had lower extremity PVI from 2004 to 2009, and the overall procedural success rate of PVI was 79 percent for women compared to 81 percent for men. There was also no difference in heart attacks or strokes.
It was surprising, researchers say, to observe no gender-related differences in procedural success considering that women experienced more transfusions, vascular complications and embolisms.
"The data suggests women may benefit to a greater degree with an invasive percutaneous strategy for the management of PAD, particularly if complications can be avoided," says study author Elizabeth Jackson, M.D., cardiologist and director of the University of Michigan Women's Heart Program.
According to the study, women were less likely than men to be prescribed cholesterol-lowering statins and antiplatelet therapy before the procedure. "We need to work together to ensure all patients with PAD are prescribed these medications, particularly women," Jackson says.
Some patients need minimally invasive procedures to unclog arteries and restore blood flow, but lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, exercise and medications are known to slow or even reverse the symptoms of PAD.
INFORMATION:
Additional authors: Theodore Schreiber, M.D., Jeffrey R. Rubin, M.D., Robert Cuff, M.D., Katherine Gallagher, M.D., Peter K. Henke, M.D., and Hitinder Gurm, M.D.
Reference: "Impact of gender on morbidity and mortality rates following lower extremity interventions for peripheral arterial disease: Observations from the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan Cardiovascular Consortium," Journal of the American College of Cardiology, doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.03.036
Funding: Blue Cross Blue Shield Michigan.
Women and PAD: Excellent treatment outcomes in spite of disease severity
Study shows room for improvement in medical management of women with PAD
2014-05-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
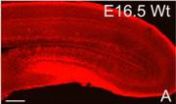
Cajal-Retzius cell loss and amyloidosis in Alzheimer's disease
2014-05-05
Cajal-Retzius cells are reelin-secreting neurons in the marginal zone of the neocortex and hippocampus. However, the relationship between Cajal-Retzius cells and Alzheimer's disease is unknown. Dr. Jinbo Deng and team from Henan University in China revealed that the number of Cajal-Retzius cells markedly reduced with age in both wild type and in mice over-expressing the Swedish double mutant form of amyloid precursor protein 695 (transgenic (Tg) 2576 mice). The decline in Cajal-Retzius cells in Tg2576 mice was found to occur concomitantly with the onset of Alzheimer's disease ...
New knowledge about muscular dystrophy
2014-05-05
The most common form of muscular dystrophy among adults is dystrophia myotonica type 1 (DM1), where approximately 1 in every 8000 is affected by the disease. The severity of the disease varies from mild forms to severe congenital forms. It is dominantly inherited and accumulates through generations, gaining increased severity and lowered age of onset. DM1 is characterised by accumulating toxic aggregates of ribonucleic acids (RNA) from a specific mutated gene (see figure 1).
When this RNA, which contains thousands of CUG nucleotide repeats, builds up in the cell, it attracts ...
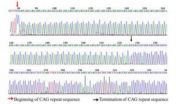
Genetic diagnosis can rule out a suspected Huntington's chorea patient
2014-05-05
Huntington's disease is an autosomal-dominant inherited neurodegenerative disease with a distinct phenotype, but the pathogenesis is unclear. Although patients with a family history have more typical clinical symptoms, signs, and pathological changes, as well as an unambiguous clinical diagnosis, other diseases with dance-like movements, e.g., dentatorubral-pallidoluy-sian atrophy, spinocerebellar ataxia type 17, Huntington's disease-like-2, and neuroferritinopathy, are difficult to identify and distinguish from Huntington's disease. By mutation screening for CAG repeats ...
Animal hoarding, a lesser-known problem for public health and welfare
2014-05-05
Animal hoarding is a psychiatric disorder that consists of accumulating large numbers of animals at home, usually cats and dogs, without providing them with a minimal standard of care. Researchers from IMIM (Hospital del Mar Research Institute) publish the first European study to provide data on this disorder, in the Journal Animal Welfare. The disorder is still largely unknown and has a negative effect on the health of both the people who suffer from it and the animals involved.
"This is the first step towards public recognition of this disorder, a disorder that constitutes ...
Nanoengineers develop basis for electronics that stretch at the molecular level
2014-05-05
Nanoengineers at the University of California, San Diego are asking what might be possible if semiconductor materials were flexible and stretchable without sacrificing electronic function?
Today's flexible electronics are already enabling a new generation of wearable sensors and other mobile electronic devices. But these flexible electronics, in which very thin semiconductor materials are applied to a thin, flexible substrate in wavy patterns and then applied to a deformable surface such as skin or fabric, are still built around hard composite materials that limit their ...
Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation implants its 1st world's smallest cardiac pacemaker
2014-05-05
MINNEAPOLIS, MN – May 1, 2014 – The Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation (MHIF) announced today the first implant of the world's smallest pacemaker at the Minneapolis Heart Institute. The device was implanted as part of a global clinical trial and the procedure was the first of its kind in the Midwest.
One-tenth the size of a conventional pacemaker, and comparable in size to a large vitamin, the Medtronic Micra™ Transcatheter Pacing System is delivered directly into the heart through a catheter inserted in the femoral vein. Once positioned, the pacemaker is securely ...
Penn study shows stimulant drug may help women cope with post-menopausal memory lapses
2014-05-05
NEW YORK – Menopausal women have long reported experiencing hot flashes, mood swings, night sweats and memory lapses, too.
A new study from researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania shows preliminary evidence that the psychostimulant drug lisdexamfetamine (LDX) can aid post-menopausal women by improving attention and concentration, organization, working memory and recall. The findings will be presented by C. Neil Epperson, MD, director of the Penn Center for Women's Behavioral Wellness, on Tuesday during the American Psychiatric ...
Inbred wolves struggle, moose proliferate at Isle Royale National Park
2014-05-05
During their annual Winter Study at Isle Royale National Park, scientists from Michigan Technological University counted nine wolves organized into one breeding pack and a second small group that is a remnant of a formerly breeding pack.
In the Isle Royale Wolf-Moose Study’s annual report released today, the researchers say that over the past three years, they have tallied the lowest numbers of wolves ever: nine in 2011–12, eight in 2012–13 and nine in 2013–14. During the same period, predation rates—the proportion of the moose population killed by wolves—also dropped ...
Infusion of young blood recharges brains of old mice, Stanford study finds
2014-05-05
STANFORD, Calif. — Something — or some things — in the blood of young mice has the ability to restore mental capabilities in old mice, a new study by Stanford University School of Medicine investigators has found.
If the same goes for humans, it could spell a new paradigm for recharging our aging brains, and it might mean new therapeutic approaches for treating dementias such as Alzheimer's disease.
In the study, to be published online May 4 in Nature Medicine, the researchers used sophisticated techniques to pin down numerous important molecular, neuroanatomical and ...
Compound Formula Rehmannia alleviates dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease
2014-05-05
Levodopa is the preferred treatment for Parkinson's disease in the clinic. However, long-term use of levodopa may lead to various motor complications, among which levodopa-induced dyskinesia is the most common, severely affecting patients' quality of life. Dr. Jiancheng He and co-workers from Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China established a model of Parkinson's disease dyskinesia in rats, and treated these animals with Compound Formula Rehmannia. They found that Compound Formula Rehmannia alleviates levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Women and PAD: Excellent treatment outcomes in spite of disease severityStudy shows room for improvement in medical management of women with PAD