(Press-News.org) Most plants try to turn towards the sun. Scientists from the University of Gothenburg have worked with Finnish colleagues to understand how light-sensitive proteins in plant cells change when they discover light. The results have been published in the most recent issue of Nature.
The family of proteins involved is known as the "phytochrome" family, and these proteins are found in all plant leaves. These proteins detect the presence of light and inform the cell whether it is day or night, or whether the plant is in the shade or the sun.
"You can think of them as the plant's 'eyes'. Our study has shown how these eyes work at the molecular level," explains Sebastian Westenhoff at the Department of Chemistry and Molecular Biology at the University of Gothenburg.
Molecules change in the light
Most plants try to avoid the shade and grow towards the light, which enables them, among other things, to consume more carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. Proteins known as "phytochromes" control this process. The phytochromes in the plants are thus changed through the light radiation, and signals are passed onwards to the cells.
Phytochromes have, as do most other proteins, a three-dimensional molecular structure. Light is absorbed by the phytochromes and the structure of the protein changes.
The scientists have studied this structural change in phytochromes from bacteria, since it is possible to obtain sufficient material to work on from bacteria.
"We already knew that some form of structural change was taking place, since the light signals must be transferred onwards to the cell. What we didn't know, however, was how the structure changed, and this is what we have revealed. Nearly the complete molecule is rebuilt," says Sebastian Westenhoff.
More efficient crops
The discovery increases our understanding of how phytochromes work. This may, in turn, lead to new strategies in the development of more efficient crops, which may be able to grow where there is little light.
"Proteins are the factories and machines of life, and their structures change when they carry out their specific tasks. At the moment, it's usually not possible to determine these changes. But I believe that we can use similar experiments to determine many important structural changes in phytochromes and other proteins," says Sebastian Westenhoff.
New measurement method
A new measurement method that Sebastian Westenhoff has developed has made the study possible. This method is based on using laser light to initiate the structural change. X-rays are then used to image the structural change.
The project has its origin in an approach made by scientist Janne Ihalainen from the University of Jyväslkyla two years ago.
"He asked whether we could use my method on phytochromes, which he had recently started working on."
INFORMATION:
Link to the article: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13310
Contact:
Sebastian Westenhoff, Department for Chemistry and Molecular Biology
Tel: +46 31 786 3936, E-mail: sebastian.westenhoff@chem.gu.se
Light-sensitive 'eyes' in plants
2014-05-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study reveals potentially unnecessary radiation after suspected sports-related injury
2014-05-05
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA – A new study of Utah youth with suspected sports-related head injuries found that emergency room visits for children with sports-related head injuries have increased since the state's concussion law passed in 2011, along with a rise in head CT scans -- leading to potentially unnecessary radiation exposure.
The results were announced at the Pediatric Academic Societies conference in Vancouver, British Columbia in May by William McDonnell, M.D., J.D., associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Utah.
The study, completed by McDonnell ...
New research explores how smoking while pregnant leads to other diseases
2014-05-05
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA – While many parents-to-be are aware that the health of their baby starts before they've actually arrived into the world, recent research reveals that "harm" (i.e., tobacco smoke, dirty air, poor nutrition, even preeclampsia) may not present itself disease-wise until well into adulthood or when a second harmful "hit" triggers the individual's susceptibility.
The results were announced at the Pediatric Academic Societies conference in Vancouver, British Columbia in May by Lisa Joss-Moore, Ph.D., University of Utah Department of Pediatrics. ...
Uncorking East Antarctica yields unstoppable sea-level rise
2014-05-05
The melting of a rather small ice volume on East Antarctica's shore could trigger a persistent ice discharge into the ocean, resulting in unstoppable sea-level rise for thousands of years to come. This is shown in a study now published in Nature Climate Change by scientists from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK). The findings are based on computer simulations of the Antarctic ice flow using improved data of the ground profile underneath the ice sheet.
"East Antarctica's Wilkes Basin is like a bottle on a slant," says lead-author Matthias Mengel, ...
Dual method to remove precancerous colon polyps may substantially reduce health-care costs
2014-05-05
Chicago, IL (May 5, 2014) — A surgical method combining two techniques for removing precancerous polyps during colonoscopies can substantially reduce the recovery time and the length of hospital stays, potentially saving the health-care system millions of dollars, according to research presented today at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
"Not only did we find that patients were discharged a day and a half earlier, we discovered other benefits, which could transform our approach to removing difficult colon polyps," said Jonathan Buscaglia, MD, the study's lead researcher ...
Women and PAD: Excellent treatment outcomes in spite of disease severity
2014-05-05
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Women face greater limits on their lifestyle and have more severe symptoms as a result of peripheral artery disease (PAD), but minimally invasive procedures used to unclog arteries are just as successful as in men.
The success of procedures, such as angioplasty or stent placement, in treating women with leg PAD was revealed in a Journal of the American College of Cardiology study.
The study provides a rare look at gender differences in PAD. PAD happens when fatty deposits build up in arteries outside the heart, usually the arteries supplying fresh ...
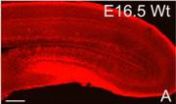
Cajal-Retzius cell loss and amyloidosis in Alzheimer's disease
2014-05-05
Cajal-Retzius cells are reelin-secreting neurons in the marginal zone of the neocortex and hippocampus. However, the relationship between Cajal-Retzius cells and Alzheimer's disease is unknown. Dr. Jinbo Deng and team from Henan University in China revealed that the number of Cajal-Retzius cells markedly reduced with age in both wild type and in mice over-expressing the Swedish double mutant form of amyloid precursor protein 695 (transgenic (Tg) 2576 mice). The decline in Cajal-Retzius cells in Tg2576 mice was found to occur concomitantly with the onset of Alzheimer's disease ...
New knowledge about muscular dystrophy
2014-05-05
The most common form of muscular dystrophy among adults is dystrophia myotonica type 1 (DM1), where approximately 1 in every 8000 is affected by the disease. The severity of the disease varies from mild forms to severe congenital forms. It is dominantly inherited and accumulates through generations, gaining increased severity and lowered age of onset. DM1 is characterised by accumulating toxic aggregates of ribonucleic acids (RNA) from a specific mutated gene (see figure 1).
When this RNA, which contains thousands of CUG nucleotide repeats, builds up in the cell, it attracts ...
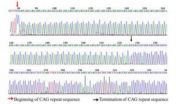
Genetic diagnosis can rule out a suspected Huntington's chorea patient
2014-05-05
Huntington's disease is an autosomal-dominant inherited neurodegenerative disease with a distinct phenotype, but the pathogenesis is unclear. Although patients with a family history have more typical clinical symptoms, signs, and pathological changes, as well as an unambiguous clinical diagnosis, other diseases with dance-like movements, e.g., dentatorubral-pallidoluy-sian atrophy, spinocerebellar ataxia type 17, Huntington's disease-like-2, and neuroferritinopathy, are difficult to identify and distinguish from Huntington's disease. By mutation screening for CAG repeats ...
Animal hoarding, a lesser-known problem for public health and welfare
2014-05-05
Animal hoarding is a psychiatric disorder that consists of accumulating large numbers of animals at home, usually cats and dogs, without providing them with a minimal standard of care. Researchers from IMIM (Hospital del Mar Research Institute) publish the first European study to provide data on this disorder, in the Journal Animal Welfare. The disorder is still largely unknown and has a negative effect on the health of both the people who suffer from it and the animals involved.
"This is the first step towards public recognition of this disorder, a disorder that constitutes ...
Nanoengineers develop basis for electronics that stretch at the molecular level
2014-05-05
Nanoengineers at the University of California, San Diego are asking what might be possible if semiconductor materials were flexible and stretchable without sacrificing electronic function?
Today's flexible electronics are already enabling a new generation of wearable sensors and other mobile electronic devices. But these flexible electronics, in which very thin semiconductor materials are applied to a thin, flexible substrate in wavy patterns and then applied to a deformable surface such as skin or fabric, are still built around hard composite materials that limit their ...