The Lancet: Antipsychotic medication associated with reduced rate of violent crime
2014-05-08
(Press-News.org) People who use antipsychotic medication (such as clozapine or risperidone) to treat psychiatric illness are nearly half as likely to commit a violent crime compared to when they are not using such medication, according to new results published in The Lancet. The use of mood stabilising drugs (such as lithium or carbamazepine) is also associated with a reduced rate of violent crime, although the reduction is less pronounced, and only in patients with bipolar disorder.
Antipsychotic and mood stabilising medication are used to treat a variety of disorders, but are most commonly associated with the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and related disorders that affect up to 2% of the general population. Although evidence suggests that people who use these medications are at less risk of relapse and re-hospitalisation for their illness, until now, there has been very little evidence for these drugs' effects on real-world adverse outcomes, such as reducing violent behaviour, despite increasing prescription rates in many countries.
In this study, a team of researchers in the UK and Sweden, led by Dr Seena Fazel of Oxford University, UK, used Swedish national health registries to study the psychiatric diagnoses, and any subsequent criminal convictions, in over 80,000 patients (40,937 men and 41,710 women) who were prescribed antipsychotic or mood stabilising medication, from 2006 to 2009.
In the three years studied, 6.5% (2657) of the men, and 1.4% (604) of women were convicted of a violent crime. Compared with periods when participants were not on medication, violent crime fell by 45% in patients receiving antipsychotics, and by 24% in patients prescribed mood stabilisers.
Although the two types of medication are often combined, the researchers found no evidence that combining the drugs has any further effect on reducing violent crime, and for patients prescribed mood stabilisers, the medication was associated with reductions in violent crime only in male patients with bipolar disorder.
Moreover, although antipsychotic and mood stabilising medications are generally associated with treatment of schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, the researchers found that many people in the study were prescribed these drugs for other disorders, such as depression or alcohol and drug misuse.
According to Dr Fazel, "Patients with psychiatric disorders are at risk of perpetrating violent acts, as well as being victims. Until now, we have not known whether antipsychotics and mood stabilizers reduce risks of violence. By comparing the same people when they are on medication compared to when they are not, our study provides evidence of potentially substantial reductions in risk of violence, and suggests that violence is to a large extent preventable in patients with psychiatric disorders."*
In a linked Comment, Professor Sheilagh Hodgins of Université de Montréal, Canada, and Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, writes that "[This] well executed study provides a basis for future clinical studies aiming to establish how antipsychotics and mood stabilisers can be used to reduce aggressive behaviour. The study illustrates again that de-identified data from national registers that were established for administrative reasons can be used by epidemiologists to identify potential strategies to reduce health-related social problems."
INFORMATION:
NOTES TO EDITORS:
The study was funded by The Wellcome Trust, the Swedish Prison and Probation Service, the Swedish Research Council, and the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare.
*Quotes direct from author and cannot be found in text of Article.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study suggests improved survivorship in the aftermath of the medieval Black Death
2014-05-08
Human mortality and survival may have improved in the generations following the Black Death, according to results published May 7, 2014, in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Sharon DeWitte from University of South Carolina.
As one of the most devastating epidemics in human history, the medieval Black Death (c. 1347-1351) killed tens of millions of Europeans. Previous studies have shown that the disease targeted elderly adults and sick or stressed people; however, not much is known about any substantial changes in the population, like overall health and mortality, before ...
Scientists focus on role of ventilation in preventing tuberculosis transmission
2014-05-08
Scientists studying the role of room ventilation in tuberculosis transmission found that students in Cape Town, South Africa, spend almost 60 percent of their day in poorly ventilated rooms, at risk of transmission, according to results published May 7, 2014, in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Eugene Richardson from Stanford University School of Medicine and colleagues. The researchers propose an increase in low-cost, WHO-compliant natural ventilation to facilitate healthy indoor environments and reduce risks.
Despite biomedical improvements to treat tuberculosis ...
A new tool to measure the speed of aging
2014-05-08
A physical test for measuring age shows wide differences between the rates of aging among different population groups, according to new research by demographers at the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis.
A strong handshake can say a lot about a person—it can indicate power, confidence, health, or aggression. Now scientists say that the strength of a person's grasp may also be one of the most useful ways to measure people's true age.
In a new study published today in the journal PLOS ONE, IIASA researchers Serguei Scherbov and Warren Sanderson (also at ...
UH Rainbow study finds rising incidence of acute pancreatitis in hospitalized children
2014-05-08
The largest investigation to date has found a significant increase in the number of acute pancreatitis (AP) cases in hospitalized children in the United States.
The new study, in the "PLOS ONE" journal found a 51 percent increase in the primary diagnosis of AP from 2000 to 2009. The number increased from 6,350 in 2000 to 9,561 in 2009.
The study looked at hospitalization records of patients 20 years old and younger using a federal children's inpatient database. From 2000 to 2009, they identified 55,012 cases of AP in hospitalized children ages 1 – 20.
According ...
Study finds genetic patterns in preeclampsia
2014-05-08
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Different manifestations of preeclampsia, such as early vs. late timing or typical vs. high severity, appear to have distinct genetic underpinnings, suggesting that they may need to be studied and treated differently. That and several other insights are described in a newly published comprehensive review of genetic studies of the condition, which produces life-threatening complications such as high-blood pressure in as many as 8 percent of pregnancies in the United States.
"There are probably very different phenotypes of preeclampsia ...
Experts say 'insourcing' innovation may be the best approach to transforming health care
2014-05-08
Philadelphia - A group of health care and policy experts from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania is urging health care institutions to look more to their own in-house personnel, including physicians and nurses, as a source of new ideas for improving how care is delivered. The practice – referred to as insourcing – relies on an organization's existing staff to drive needed transformations. The team also suggests a four-stage design process which, when adopted internally, may help organizations implement more efficient health care delivery solutions. ...
New order of marine creatures discovered among sea anemones
2014-05-08
A deep-water creature once thought to be one of the world's largest sea anemones, with tentacles reaching more than 6.5 feet long, actually belongs to a new order of animals. The finding is part of a new DNA-based study led by the American Museum of Natural History that presents the first tree of life for sea anemones, a group that includes more than 1,200 species. The report, which is published today in the journal PLOS ONE, reshapes scientists' understanding of the relationships among these poorly understood animals.
"The discovery of this new order of Cnidaria—a phylum ...
Recent Ebola outbreak highlights need for better global response
2014-05-08
WHAT:In an invited perspective article on the Ebola outbreak under way in West Africa, Heinz Feldmann, M.D., Ph.D., of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) emphasizes the need for scientists to make their data available to colleagues in real-time to improve the public health response to outbreaks. He cites past responses to influenza and SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) outbreaks as successful examples of global information sharing. Rapid diagnoses are key to controlling outbreaks of deadly viruses such as Ebola, for which no therapies are available. The immediate ...
Malaria severity not determined solely by parasite levels in blood
2014-05-08
WHAT:
Although malaria kills some 600,000 African children each year, most cases of the mosquito-borne parasitic disease in children are mild. Repeated infection does generate some immunity, and episodes of severe malaria are unusual once a child reaches age 5. However, the relative contributions of such factors as the level of malaria-causing parasites in a person's blood—parasite density—to disease severity and to development of protective immunity are not well understood.
To clarify these issues, researchers from the United States and Tanzania regularly examined 882 ...
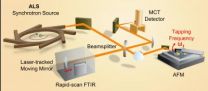
Berkeley Lab develops nanoscope to probe chemistry on the molecular scale
2014-05-08
For years, scientists have had an itch they couldn't scratch. Even with the best microscopes and spectrometers, it's been difficult to study and identify molecules at the so-called mesoscale, a region of matter that ranges from 10 to 1000 nanometers in size. Now, with the help of broadband infrared light from the Advanced Light Source (ALS) synchrotron at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), researchers have developed a broadband imaging technique that looks inside this realm with unprecedented sensitivity and range.
By ...