(Press-News.org) The sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 6:07 a.m. EDT on May 8, 2014, and NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, captured images of it. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event may impact Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, the U.S. government's official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings.
This flare is classified as an M5.2-class flare. M class flares are on the order of a tenth as strong as the most intense flares, the X-class flares.
Updates will be provided as needed.
INFORMATION:
What is a solar flare and what is M-class?
For answers to these and other space weather questions, please visit the Spaceweather Frequently Asked Questions page: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sunearth/spaceweather/index.html
Mid-level solar flare erupts from the sun
Flare captured by NASA's SDO mission
2014-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
JCI online ahead of print table of contents for May 8, 2014
2014-05-08
Leptin-dependent regulation of reproduction
Individuals that lack the adipose-derived hormone leptin fail to complete puberty and are infertile. Leptin-deficient mice recapitulate human phenotypes; however, it is not clear how leptin and leptin signaling impact the reproductive axis. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Vincent Prevot and colleagues at INSERM U837 evaluated leptin deficient animals and determined that leptin acts directly on neurons in the preoptic region of the hypothalamus that synthesize nitric oxide to regulate peripheral levels ...
Regenerating plastic grows back after damage
2014-05-08
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Looking at a smooth sheet of plastic in one University of Illinois laboratory, no one would guess that an impact had recently blasted a hole through it.
Illinois researchers have developed materials that not only heal, but regenerate. Until now, self-repairing materials could only bond tiny microscopic cracks. The new regenerating materials fill in large cracks and holes by regrowing material.
Led by professor Scott White, the research team comprises professors Jeffry S. Moore and Nancy Sottos and graduate students Brett Krull, Windy Santa Cruz and ...
Extinct kitten-sized hunter discovered
2014-05-08
A Case Western Reserve University student and his mentor have discovered an ancient kitten-sized predator that lived in Bolivia about 13 million years ago—one of the smallest species reported in the extinct order Sparassodonta.
Third-year undergraduate student Russell Engelman and Case Western Reserve anatomy professor Darin Croft made the finding by analyzing a partial skull that had been in a University of Florida collection more than three decades.
The researchers report their finding in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology online at: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/02724634.2013.827118#.U2p8-S8njhM.
"The ...
Fueling aviation with hardwoods
2014-05-08
A key challenge in the biofuels landscape is to get more advanced biofuels—fuels other than corn ethanol and vegetable oil-based biodiesel—into the transportation pool. Utilization of advanced biofuels is stipulated by the Energy Independence and Security Act; however, current production levels lag behind proposed targets. Additionally, certain transportation sectors, such as aviation, are likely to continue to require liquid hydrocarbon fuels in the long term even as light duty transportation shifts to alternative power sources. A multi-university team lead by George ...
Chemotherapy timing is key to success
2014-05-08
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- MIT researchers have devised a novel cancer treatment that destroys tumor cells by first disarming their defenses, then hitting them with a lethal dose of DNA damage.
In studies with mice, the research team showed that this one-two punch, which relies on a nanoparticle that carries two drugs and releases them at different times, dramatically shrinks lung and breast tumors. The MIT team, led by Michael Yaffe, the David H. Koch Professor in Science, and Paula Hammond, the David H. Koch Professor in Engineering, describe the findings in the May 8 online ...
Climate change may worsen summertime ozone pollution
2014-05-08
Ozone pollution across the continental United States will become far more difficult to keep in check as temperatures rise, according to new research results.
The study shows that Americans face the risk of a 70 percent increase in unhealthy summertime ozone levels by 2050.
The results appear online this week in a paper in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, published by the American Geophysical Union.
The work was funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the U.S. Department of Energy.
Warmer temperatures and other changes in the atmosphere ...
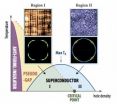
Scientists find solution to 2 long-standing mysteries of cuprate superconductivity
2014-05-08
UPTON, NY—Scientists seeking to understand the intricacies of high-temperature superconductivity—the ability of certain materials to carry electrical current with no energy loss—have been particularly puzzled by a mysterious phase that emerges as charge carriers are added that appears to compete with superconductivity. It's also been a mystery why, within this "pseudogap" phase, the movement of superconducting electrons appears to be restricted to certain directions. So exploring the pseudogap and whether and how it affects the movement of electrons has been a pivotal challenge. ...
'Rice theory' explains north-south China cultural differences, study shows
2014-05-08
A new cultural psychology study has found that psychological differences between the people of northern and southern China mirror the differences between community-oriented East Asia and the more individualistic Western world – and the differences seem to have come about because southern China has grown rice for thousands of years, whereas the north has grown wheat.
"It's easy to think of China as a single culture, but we found that China has very distinct northern and southern psychological cultures and that southern China's history of rice farming can explain why people ...
Exploring the magnetism of a single atom
2014-05-08
Magnetic devices like hard drives, magnetic random access memories (MRAMs), molecular magnets, and quantum computers depend on the manipulation of magnetic properties. In an atom, magnetism arises from the spin and orbital momentum of its electrons. 'Magnetic anisotropy' describes how an atom's magnetic properties depend on the orientation of the electrons' orbits relative to the structure of a material. It also provides directionality and stability to magnetization. Publishing in Science, researchers led by EPFL combine various experimental and computational methods to ...
Plant hormone has dual role in triggering flower formation, Penn study finds
2014-05-08
Flowers aren't just pretty to look at, they are how plants reproduce. In agricultural plants, the timing and regulation of flower formation has economic significance, affecting a crop's yield.
A new paper by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania published in the journal Science has revealed that a plant hormone once believed to promote flower formation in annual plants also plays a role in inhibiting flowers from forming. The dual role of this hormone, gibberellin, could be exploited to produce higher-yielding crop plants.
The study was led by Nobutoshi Yamaguchi ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
People’s gut bacteria worse in areas with higher social deprivation
Unique analysis shows air-con heat relief significantly worsens climate change
Keto diet may restore exercise benefits in people with high blood sugar
Manchester researchers challenge misleading language around plastic waste solutions
Vessel traffic alters behavior, stress and population trends of marine megafauna
Your car’s tire sensors could be used to track you
Research confirms that ocean warming causes an annual decline in fish biomass of up to 19.8%
Local water supply crucial to success of hydrogen initiative in Europe
New blood test score detects hidden alcohol-related liver disease
High risk of readmission and death among heart failure patients
Code for Earth launches 2026 climate and weather data challenges
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
Have abortion-related laws affected broader access to maternal health care?
Do muscles remember being weak?
Do certain circulating small non-coding RNAs affect longevity?
How well are international guidelines followed for certain medications for high-risk pregnancies?
New blood test signals who is most likely to live longer, study finds
Global gaps in use of two life-saving antenatal treatments for premature babies, reveals worldwide analysis
Bug beats: caterpillars use complex rhythms to communicate with ants
High-risk patients account for 80% of post-surgery deaths
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
New method to remove toxic PFAS chemicals from water
The nanozymes hypothesis of the origin of life (on Earth) proposed
Microalgae-derived biochar enables fast, low-cost detection of hydrogen peroxide
Researchers highlight promise of biochar composites for sustainable 3D printing
Machine learning helps design low-cost biochar to fight phosphorus pollution in lakes
Urine tests confirm alcohol consumption in wild African chimpanzees
[Press-News.org] Mid-level solar flare erupts from the sunFlare captured by NASA's SDO mission