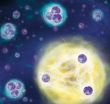
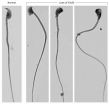
(Press-News.org) Eight years ago Rudolf Grimm's research group was the first to observe an Efimov state in an ultracold quantum gas. The Russian physicist Vitali Efimov theoretically predicted this exotic bound state of three particles in the 1970s. He forecast that three particles would form a bound state due to their quantum mechanical properties, under conditions when a two-body bound state would be absent. What is even more astounding: When the distance between the particles is increased by factor 22.7, another Efimov state appears, leading to an infinite series of these states. Until now this essential ingredient of the famous scenario has remained elusive and experimentally proving the periodicity of the famous scenario has presented a challenge. "There have been some indications that particles continuously create three-body states if the distance is increased by this factor," says Rudolf Grimm from the Institute of Experimental Physics of the University of Innsbruck and the Institute of Quantum Physics and Quantum Optics of the Austrian Academy of Sciences. "Proving the scenario was very difficult but we have finally been successful."
Bound in great distance
Ultracold quantum gases are highly suited for studying and observing quantum phenomena of particle systems experimentally as the interaction between atoms are well tunable by a magnetic field. However, Rudolf Grimm's research group got very close to the limits of what is possible experimentally when they had to increase the distance between the particles to one micrometer to be able to observe the second Efimov state. "This corresponds to 20,000 times the radius of a hydrogen atom," explains Grimm. "Compared to a molecule, this is a gigantic structure." This meant that the physicists had to be particularly precise with their work. What greatly helped the researchers in Innsbruck was their extensive experience with ultracold quantum gases and their great technical expertise. Their final result shows that the second Efimov state is larger than the first one by a factor of 21.0 with a measurement uncertainty of 1.3. "This small deviation from the factor 22.7 may be attributed to the physics beyond the ideal Efimov state, which is also an exciting topic," explains Rudolf Grimm.
New research area
The scientific community's interest in this phenomenon lies in its universal character. The law is equally applicable to nuclear physics, where strong interaction is responsible for the binding of particles in the atomic nucleus, and to molecular interactions that are based on electromagnetic forces. "Interaction between two particles and between many particles is well studied," says Grimm. "But we still need to investigate and learn about phenomena that arise from the interaction between only a few particles. The Efimov states are the basic example for this." The joint work of Rudolf Grimm's team and the British theoretical physicist Jeremy M. Hutson has been supported by the Austrian Science Fund. The results are now published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
INFORMATION: END
Quantum trimer -- from a distance
The mysterious Efimov scenario
2014-05-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify link between colon cancer and metabolism
2014-05-13
HEIDELBERG, 13 May 2014 – More than 60 years ago Otto Warburg recognized that cancer cells differ from normal cells in the metabolic pathway they use for the oxidation of sugar. Rather than the typical series of oxidative steps that take place in the citric acid cycle, cancer cells metabolize sugar via the glycolytic pathway irrespective of whether oxygen is present or not. In The EMBO Journal, researchers in the United States report that the reason for this difference in colon cancer is changes in the Wnt signaling pathway, an essential communication pathway operating ...
Dangerous nitrogen pollution could be halved
2014-05-13
Ambitious mitigation efforts, however, could decrease the pollution by 50 percent. The analysis is the very first to quantify this.
"Nitrogen is an irreplaceable nutrient and a true life-saver as it helps agriculture to feed a growing world population – but it is unfortunately also a dangerous pollutant," says Benjamin Bodirsky, lead-author of the study. In the different forms it can take through chemical reactions, it massively contributes to respirable dust, leads to the formation of aggressive ground-level ozone, and destabilizes water ecosystems. Damages in Europe ...
Male infertility: It's all about the package
2014-05-13
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – Infertility is generally thought of as a woman's problem. In fact, more than 3 million men across America also experience it. Today, researchers from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) describe a key event during sperm development that is essential for male fertility. A team led by CSHL Professor Alea Mills explains how a protein controls DNA packaging to protect a man's genetic information.
The sperm is a simple delivery vehicle for a man's genetic information. The highly specialized cell is little more than a DNA bundle powered by molecular ...
Concerns raised over EU ban on ditching unwanted fish
2014-05-13
New rules banning fishermen from throwing away unwanted fish they have caught could harm wildlife – and fail to improve fish stocks, a University of Strathclyde report has found.
The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, suggests new reforms to the European Union's Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) – ending the practice of throwing away unwanted fish caught at sea – may have unintended consequences. The new CFP took effect on 1 January 2014 and will phase out the discarding of fish between 2015 and 2019.
The aim is to improve fish stocks – but Professor ...
Researchers identify genetic marker linked to OCD
2014-05-13
A group of researchers led by Johns Hopkins scientists say they have identified a genetic marker that may be associated with the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), whose causes and mechanisms are among the least understood among mental illnesses.
The results of the research are published online May 13 by the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
"If this finding is confirmed, it could be useful," says study leader Gerald Nestadt, M.D., M.P.H., a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and director of ...
Humans and companion animals harbor the same types of MRSA infections
2014-05-13
A shared population of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria circulates both in humans and companion animals, according to a study published this week in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Our study demonstrates that humans and companion animals readily exchange and share MRSA bacteria from the same population," says senior author Mark Holmes, senior lecturer in preventive veterinary medicine at the University of Cambridge in England. MRSA naturally lives on the skin and also causes difficult-to-treat ...
E-cigarettes and mental health
2014-05-13
Researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine report that people living with depression, anxiety or other mental health conditions are twice as likely to have tried e-cigarettes and three times as likely to be current users of the controversial battery-powered nicotine-delivery devices, as people without mental health disorders.
They are also more susceptible to trying e-cigarettes in the future in the belief that doing so will help them quit, the scientists said. The FDA has not approved e-cigarettes as a smoking cessation aid.
The study will ...
Novel target found for chemotherapy-resistant leukemia cells
2014-05-13
Researchers at Children's Hospital Los Angeles have discovered that by targeting a particular receptor, chemotherapy-resistant cancer cells can be killed in an acute form of childhood leukemia, offering the potential for a future treatment for patients who would otherwise experience relapse of their disease.
Nora Heisterkamp, PhD, and colleagues at The Saban Research Institute of Children's Hospital Los Angeles have discovered that by targeting the B-cell activating receptor (BAFF-R), chemotherapy-resistant precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells (pre-B ALL) can ...
Older, sicker men with early-stage prostate cancer do not benefit from aggressive treatment
2014-05-13
Treating older men with early-stage prostate cancer who also have other serious underlying health problems with aggressive therapies such as surgery or radiation therapy does not help them live longer and, in fact, can be detrimental, according to a study by UCLA researchers.
The study followed the cases of more than 140,500 men aged 66 and older diagnosed with early-stage prostate cancer between 1991 and 2007 from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Medicare database. Men who also suffered from multiple major medical conditions such as a history of ...
Study: Former prisoners, parolees turn to emergency departments for care
2014-05-12
AURORA, Colo. (May 12, 2014) – Being released from prison or jail is a difficult time for the millions of Americans returning to their communities from correctional facilities. Add to the list of challenges a high risk of winding up in the emergency department or the hospital. That's according to a new study from the University of Colorado School of Medicine.
The study, published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, provides support for efforts to improve access to insurance and readily available health care for this vulnerable group.
"This study comes at a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
[Press-News.org] Quantum trimer -- from a distanceThe mysterious Efimov scenario