(Press-News.org) Stereotypes of gay men as effeminate and weak and black men as threatening and aggressive can hurt members of those groups when white people evaluate them in employment, education, criminal justice and other contexts.
But the negative attributes of the two stereotypes can cancel one another out for gay black men in the employment context, according to research by a Princeton University graduate student in sociology, challenging the commonly held idea that membership in multiple marginalized groups leads to more discrimination than being a member of a single such group.
Sociologist David Pedulla asked 231 white participants in a nationwide survey to suggest a starting salary for an applicant for a fictional job as an assistant manager at a large retail store.
Each participant was shown one of four résumés, which were identical except for two items. Half used a white-sounding name, Brad Miller, and half used a black-sounding name, Darnell Jackson. In addition, half noted the applicant's role as president of the "Gay Student Advisory Council" in college while the other half listed his role as president of the "Student Advisory Council."
The result was that each participant suggested a starting salary for an applicant portrayed as a straight white man, a gay white man, a gay black man or a straight black man. Participants were also asked questions about the applicant that Pedulla used to measure how "threatening" they perceived the applicant to be.
The survey participants recommended lower starting salaries for straight black men and gay white men than for straight white men, indicating a salary penalty for being black or for being gay, Pedulla said.
"However, there is no salary penalty for gay black men, who receive higher salary recommendations than straight black men and salary recommendations on par with straight white men," Pedulla said. "There is some evidence that gay black men are perceived as less threatening than straight black men and that this difference accounts for a piece of the salary recommendation difference between these two groups."
The research is described in a paper titled "The Positive Consequences of Negative Stereotypes: Race, Sexual Orientation and the Job Application Process" that was published in March in Social Psychology Quarterly.
Robb Willer, an associate professor of sociology at Stanford University, said Pedulla's research is "cutting-edge theoretically."
"Several lines of work in the social sciences would suggest that membership in disadvantaged social categories combine in simple, straightforward ways," said Willer, whose research interests include status hierarchies. "But Pedulla's work suggests the process is more complex and that the contents of the stereotypes of different disadvantaged groups can counteract one another, leading to less total disadvantage than would have previously been expected."
Willer also noted the study was "highly rigorous."
"Survey experiments of this sort combine the descriptive strength with very high levels of control, allowing the researcher high confidence in making inferences of causality to larger populations," he said.
Tamar Kricheli-Katz, who is an assistant professor at the Buchman Faculty of Law and the Department of Sociology and Anthropology at Tel Aviv University in Israel, said it is important to note that being a member of two disadvantaged groups may not always be beneficial.
"The effect depends on the content of the contradicting stereotypes and on the context and its cultural meanings," said Kricheli-Katz, whose research interests include inequality, anti-discrimination law and employment law. "As a result, the same group of people (like black gay men) may be disadvantaged in some contexts while advantaged in others."
Along with exploring what other stereotypes might interact in unexpected ways, Pedulla said, "I would be interested in conducting an experimental audit study of real job openings in the labor market where the race and sexual orientation of the job applicants were experimentally manipulated."
INFORMATION:
The data collection for Pedulla's survey experiment was supported by Time-Sharing Experiments for the Social Sciences, which is funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF Grant 0818839, Jeremy Freese and James Druckman, Principal Investigators).
Negative stereotypes can cancel each other out on resumes
2014-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Penn Vet study reveals Salmonella's hideout strategy
2014-05-15
The body's innate immune system is a first line of defense, intent on sensing invading pathogens and wiping them out before they can cause harm. It should not be surprising then that bacteria have evolved many ways to specifically evade and overcome this sentry system in order to spread infection.
A study led by researchers in the University of Pennsylvania's School of Veterinary Medicine now reveals how some Salmonella bacteria hide from the immune system, allowing them to persist and cause systemic infection. The findings could help researchers craft a more effective ...
Research finds human impact may cause Sierra Nevada to rise, increase seismicity of San Andreas Fault
2014-05-15
RENO, Nev. – Like a detective story with twists and turns in the plot, scientists at the University of Nevada, Reno are unfolding a story about the rapid uplift of the famous 400-mile long Sierra Nevada mountain range of California and Nevada.
The newest chapter of the research is being published today in the scientific journal Nature, showing that draining of the aquifer for agricultural irrigation in California's Central Valley results in upward flexing of the earth's surface and the surrounding mountains due to the loss of mass within the valley. The groundwater subsidence ...
A skeleton clue to early American ancestry
2014-05-15
This news release is available in Spanish and Arabic.
The discovery of a near-complete human skeleton in a watery cave in Mexico is helping scientists answer the question, "Who were the first Americans?" The finding, reported in the 16 May issue of the journal Science, sheds new light on a decades-long debate among archaeologists and anthropologists.
Deciphering the ancestry of the first people to populate the Americas has been a challenge.
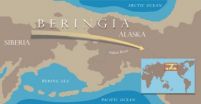
On the basis of genetics, modern Native Americans are thought to descend from Siberians who moved into eastern Beringia (the ...
Oldest most complete, genetically intact human skeleton in New World
2014-05-15
WASHINGTON (May 15, 2014)—The skeletal remains of a teenage female from the late Pleistocene or last ice age found in an underwater cave in Mexico have major implications for our understanding of the origins of the Western Hemisphere's first people and their relationship to contemporary Native Americans.
In a paper released today in the journal Science, an international team of researchers and cave divers present the results of an expedition that discovered a near-complete early American human skeleton with an intact cranium and preserved DNA. The remains were found surrounded ...
WSU anthropologist leads genetic study of prehistoric girl
2014-05-15
PULLMAN, Wash.—For more than a decade, Washington State University molecular anthropologist Brian Kemp has teased out the ancient DNA of goose and salmon bones from Alaska, human remains from North and South America, and human coprolites—ancient poop—from Oregon and the American Southwest.
His aim: use genetics as yet another archaeological record offering clues to the identities of ancient people and how they lived and moved across the landscape.
As head of the team studying the DNA of Naia, an adolescent girl who fell into a Yucatan sinkhole some 12,000 years ago, he ...
Genetic study helps resolve years of speculation about first people in the Americas
2014-05-15
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study could help resolve a longstanding debate about the origins of the first people to inhabit the Americas, researchers report in the journal Science. The study relies on genetic information extracted from the tooth of an adolescent girl who fell into a sinkhole in the Yucatan 12,000 to 13,000 years ago.
The girl's remains were found alongside those of ancient extinct beasts that also fell into the "inescapable natural trap," as researchers described the sinkhole. The team used radiocarbon dating and analyzed chemical signatures in bones and ...
Dating and DNA show Paleoamerican-Native American connection
2014-05-15
Eastern Asia, Western Asia, Japan, Beringia and even Europe have all been suggested origination points for the earliest humans to enter the Americas because of apparent differences in cranial form between today's Native Americans and the earliest known Paleoamerican skeletons. Now an international team of researchers has identified a nearly complete Paleoamerican skeleton with Native American DNA that dates close to the time that people first entered the New World.
"Individuals from 9,000 or more years ago have morphological attributes -- physical form and structure -- ...
Genetic study confirms link between earliest Americans and modern Native-Americans
2014-05-15
AUSTIN, Texas — The ancient remains of a teenage girl found in an underwater Mexican cave establish a definitive link between the earliest Americans and modern Native Americans, according to a new study released today in the journal Science.
The study was conducted by an international team of researchers from 13 institutions, including Deborah Bolnick, assistant professor of anthropology at The University of Texas at Austin, who analyzed DNA from the remains simultaneously with independent researchers at Washington State University and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
The ...
First 'heavy mouse' leads to first lab-grown tissue mapped from atomic life
2014-05-15
Scientists have created a 'heavy' mouse, the world's first animal enriched with heavy but non-radioactive isotopes - enabling them to capture in unprecedented detail the molecular structure of natural tissue by reading the magnetism inherent in the isotopes.
This data has been used to grow biological tissue in the lab practically identical to native tissue, which can be manipulated and analysed in ways impossible for natural samples. Researchers say the approach has huge potential for scientific and medical breakthroughs: lab-grown tissue could be used to replace heart ...
One of oldest human skeletons in North America is discovered
2014-05-15
Cave-diving scientist Patricia A. Beddows of Northwestern University is a member of an international team of researchers and cave divers this week announcing the discovery in an underwater Yucatán Peninsula cave of one of the oldest human skeletons found in North America.
Details of "Naia," a teenage girl who went underground to seek water and fell to her death in a large pit named Hoyo Negro ("black hole" in Spanish), will be published May 16 in the journal Science.
"The preservation of all the bones in this deep water-filled cave is amazing -- the bones are beautifully ...