(Press-News.org) SOUTH PLAINFIELD, NJ – May 16, 2014 – PTC Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ: PTCT) today announced that the results of a Phase 3 study of ataluren in patients with nonsense mutation cystic fibrosis (nmCF) were published in Lancet Respiratory Medicine. The results demonstrated positive trends in both the primary endpoint, lung function as measured by relative change in % predicted FEV1 (forced expiratory volume in one second) and in the secondary outcome measure, rate of pulmonary exacerbations. The collective data from this trial, including retrospective and subgroup analyses support the conclusion that ataluren was active and showed clinically meaningful improvements over placebo in these trials.
"The overall data from this trial are promising. Patients on ataluren experienced fewer pulmonary exacerbations and showed a stabilization in their FEV1 results, particularly in the subgroup of patients that did not use chronic inhaled aminoglycosides. Such stabilization of disease is an important clinical endpoint, particularly for this patient population that has one of the most severe forms of CF. CF patients with nonsense mutations do not produce any functional CFTR protein and therefore generally have a more severe form of cystic fibrosis. Current treatments for nonsense mutation cystic fibrosis focus on alleviating symptoms and reducing infections, whereas ataluren targets the underlying cause of disease," stated Michael Konstan, M.D., lead study investigator and Chairman of Pediatrics at from University Hospitals Rainbow Babies and & Children's Hospital in Cleveland, Ohio.
The Phase 3 double-blind, placebo-controlled study, which was conducted across 11 countries, compared ataluren (n=116) to placebo (n=116) in nmCF patients. The primary endpoint, the relative change from baseline in %-predicted FEV1 at 48 weeks, showed a positive trend favoring ataluren versus placebo, and a larger effect in patients not receiving chronic inhaled tobramycin. In the intent-to-treat population, there was a 3% difference in the relative change from baseline in %-predicted FEV1 between the ataluren and placebo groups at Week 48 (-2.5% change on ataluren vs. -5.5% change on placebo; p=0.12) which was not statistically significant. An analysis of the relative change from baseline in %-predicted FEV1 across all post-baseline study visits demonstrated an average difference between ataluren and placebo of 2.5% (-1.8% average change on ataluren vs. -4.3% average change on placebo; p= 0.048). There were 23% fewer pulmonary exacerbations in the ataluren group compared to placebo (p=0.0992). Further results from a post hoc analysis of the subgroup of patients not receiving chronic inhaled tobramycin showed a 5.7% difference in relative change from baseline in % predicted FEV1 favoring ataluren, with a mean change from baseline of -0.7% in the ataluren arm, and – 6.4% in the placebo arm (nominal p=0.0082). In addition, there were 40% fewer exacerbations in ataluren-treated patients in this subgroup. The outcomes observed in multiple endpoints between the subgroup of patients who were not prescribed chronic inhaled tobramycin and the subgroup of patients who were prescribed chronic inhaled tobramycin as well as post-hoc in vitro testing showing the interference of aminoglycoside antibiotics with ataluren activity support the hypothesis that inhaled tobramycin may interfere with ataluren's mechanism of action.
Safety results indicate that ataluren was generally well tolerated. The overall incidence of adverse events through Week 48 was similar in the ataluren and placebo groups, except for the occurrence of creatinine elevations that occurred more frequently in the ataluren group in connection with concomitant treatment with systemic aminoglycosides. Most treatment emergent adverse events were of mild (Grade 1) or moderate (Grade 2) severity, and no life-threatening adverse events were reported. Most serious adverse events reported in this study were CF pulmonary exacerbations and were considered unrelated to ataluren treatment. Eight patients in the ataluren arm and three patients in the placebo arm discontinued treatment due to an adverse event.
"We are very encouraged by the data from this trial. Given spirometry and pulmonary exacerbation results in the subgroup of patients not receiving chronic inhaled tobramycin, and a favorable safety profile, this study supports further clinical testing of ataluren as a potential first-in-class treatment for nmCF patients not receiving chronic inhaled tobramycin," stated Stuart W. Peltz, Ph.D., Chief Executive Officer of PTC Therapeutics, Inc. "We look forward to initiating a confirmatory ataluren trial in nmCF patients later this year."
INFORMATION:
ABOUT THE PHASE 3 TRIAL
The primary endpoint of the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was the relative change in % predicted FEV1 from baseline to Week 48 as assessed by spirometry. Spirometry was performed at screening, at randomization, and every eight weeks during the 48 week study duration. The secondary objective was rate of pulmonary exacerbations. Additional endpoints evaluated other aspects of patient function, drug activity, and safety. The 48-week trial enrolled 238 patients, ages six years and older, at 36 sites in 11 countries in North America and Europe. Patients were randomly assigned to one of two treatment arms: ataluren (10 mg/kg morning, 10 mg/kg midday, 20 mg/kg evening) or placebo (morning, midday, evening). Patients who completed the study were eligible to receive open-label ataluren in an ongoing extension study.
ABOUT CYSTIC FIBROSIS
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a disabling and life-threatening autosomal recessive disorder resulting
from mutations that cause dysfunction in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). In nmCF, an interruption in the genetic code - known as a nonsense mutation - prematurely halts the synthesis of CFTR, causing the protein to be short and non-functioning. Nonsense mutations are categorized as Class I mutations that result in little or no production of the CFTR protein. CF patients with Class I mutations typically experience more severe disease symptoms than those with other genotypes, including a shorter life span, a higher probability of end-stage lung disease, and a higher prevalence of pancreatic insufficiency. Approximately 10% of patients have CF due to a Class I nonsense mutation in at least one allele of the CFTR gene. Available therapies for treatment of lung manifestations of CF, such as inhaled antibiotics do not address the underlying defect. There are no marketed treatments that target the defect associated with CF caused by nonsense mutations.
ABOUT ATALUREN
Ataluren, an investigational new drug discovered and developed by PTC Therapeutics, is a protein restoration therapy designed to enable the formation of a functioning protein in patients with genetic disorders caused by a nonsense mutation. A nonsense mutation is an alteration in the genetic code that prematurely halts the synthesis of an essential protein. The resulting disorder is determined by which protein cannot be expressed in its entirety and is no longer functional, such as dystrophin in nmDMD. The development of ataluren has been supported by grants from Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Therapeutics Inc. (the nonprofit affiliate of the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation); Muscular Dystrophy Association; FDA's Office of Orphan Products Development; National Center for Research Resources; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy.
ABOUT PTC THERAPEUTICS, INC.
PTC is a biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery and development of orally administered, proprietary small molecule drugs that target post-transcriptional control processes. Post-transcriptional control processes regulate the rate and timing of protein production and are essential to proper cellular function. PTC's internally discovered pipeline addresses multiple therapeutic areas, including rare disorders, oncology and infectious diseases. PTC has developed proprietary technologies that it applies in its drug discovery activities and which form the basis for collaborations with leading biopharmaceutical companies. For more information on the company, please visit our website http://www.ptcbio.com.
Ataluren Phase 3 trial results in nonsense mutation cystic fibrosis
Data demonstrate positive trends in lung function and pulmonary exacerbations
2014-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Glasses-free 3-D projector
2014-05-16
Over the past three years, researchers in the Camera Culture group at the MIT Media Lab have steadily refined a design for a glasses-free, multiperspective, 3-D video screen, which they hope could provide a cheaper, more practical alternative to holographic video in the short term.
Now they've designed a projector that exploits the same technology, which they'll unveil at this year's Siggraph, the major conference in computer graphics. The projector can also improve the resolution and contrast of conventional video, which could make it an attractive transitional technology ...
Growing camelina and safflower in the Pacific Northwest
2014-05-16
A recent study published in Agronomy Journal provides information important to farmers growing oilseed crops. In the study, camelina and safflower were grown in three-year rotations with winter wheat and summer fallow. The study shows that using this rotation may require that no tillage should be done to the soil during the fallow year. Oilseed crops produce relatively little residue—organic material such as roots that hold the soil together. Even light tillage can disintegrate the soil.
A cooperative study by the USDA-ARS and Washington State University researched the ...
How Asian American 'tiger mothers' motivate their children
2014-05-16
An article titled "Why Chinese Mothers Are Superior," published in The Wall Street Journal in 2011, has continued to provoke a cultural debate among parents after self-proclaimed 'tiger mother' Amy Chua asserted that Asian American parenting methods produce more successful children. Researchers at Stanford University delved deeper into Chua's 'tiger mother' approach, and their research sheds light on key fundamental differences in parenting methods between Asian Americans and European Americans.
To reveal the cultural differences in parenting, the researchers compare ...
Ground breaking hip and stem cell surgery in Southampton
2014-05-16
Doctors and scientists in Southampton have completed their first hip surgery with a 3D printed implant and bone stem cell graft.
The 3D printed hip, made from titanium, was designed using the patient's CT scan and CAD CAM (computer aided design and computer aided manufacturing) technology, meaning it was designed to the patient's exact specifications and measurements.
The implant will provide a new socket for the ball of the femur bone to enter. Behind the implant and between the pelvis, doctors have inserted a graft containing bone stem cells.
The graft acts as ...
Fires continue in San Diego County, California
2014-05-16
Seven fires are still burning in San Diego County, California. Arson is suspected as the origin of these fires. Two teens have been arrested on suspicion of setting the fire that spread so ferociously across the county. All of California is experiencing exceptional, extreme or severe drought conditions. The wildfire area is in the second-most dangerous category--extreme drought conditions. California's governor has cited climate change as a factor in the fires, noting the last three years have been the driest in recorded history. Wildfire season used to start in late ...
Skunk fire in Arizona
2014-05-16
The Skunk Fire in Arizona started with a lightning strike on Saturday, April 19. Currently over 10,000 acres have been affected. It is located in the San Carlos Apache Reservation. The terrain in the area is very steep with boulders making it difficult for firefighters to traverse the area to fight the fire. The fire continues to grow to the north, but fire activity in the south has been stopped. The fire is currently 20% contained.
The National Weather Service is forecasting winds of 7-12 mph with gusting to 25 mph. These conditions coupled with extremely dry fuels ...
Cause of death established
2014-05-16
Chamois (Rupicapra rupicapra) share their habitat with a number of other wild animals as well as with farm animals. Because of the risk of disease transmission between species, when dead or sick animals are discovered by hunters or foresters it is extremely important determining the causes. Early identification of the cause of disease or death can be crucial to prevent a wide-scale outbreak. The Pathological Laboratory at the Research Institute of Wildlife Ecology specializes in such cases.
Severe pneumonia as cause of death
Nineteen dead chamois from the region of ...
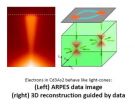
Fast and curious: Electrons hurtle into the interior of a new class of quantum materials
2014-05-16
As smartphones get smarter and computers compute faster, researchers actively search for ways to speed up the processing of information. Now, scientists at Princeton University have made a step forward in developing a new class of materials that could be used in future technologies.
They have discovered a new quantum effect that enables electrons — the negative-charge-carrying particles that make today's electronic devices possible — to dash through the interior of these materials with very little resistance.
The discovery is the latest chapter in the story of a curious ...
Researchers call for better ocean stewardship
2014-05-16
FORT LAUDERDALE-DAVIE, Fla. – It has been said that we know more about the surface of the moon than we do about our own planet's oceans. That especially applies to the deepest parts of our oceans – depths that are 200 meters or deeper.
Researchers from organizations around the world who specialize in studying and exploring the deepest regions of our oceans have come together to pen a cautionary tale that urges we take a critical look at how we're treating our seas.
"We need to consider the common heritage of mankind - when do we have the right to take something that ...
Molecules involved in rheumatoid arthritis angiogenesis identified
2014-05-16
Two protein molecules that fit together as lock and key seem to promote the abnormal formation of blood vessels in joints affected by rheumatoid arthritis, according to researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine, who found that the substances are present at higher levels in the joints of patients affected by the disease.
Their results are reported in the journal Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
"Our results show, for the first time, that these two proteins – a receptor and its corresponding binding protein - play a key role in the progression ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
[Press-News.org] Ataluren Phase 3 trial results in nonsense mutation cystic fibrosisData demonstrate positive trends in lung function and pulmonary exacerbations