(Press-News.org) Coral Gables, Fla. (May 16, 2014) – Can psychological intervention help women adapt to the stresses of breast cancer? It appears that a brief, five-week psychological intervention can have beneficial effects for women who are dealing with the stresses of breast cancer diagnosis and surgery. Intervening during this early period after surgery may reduce women's distress and providing cognitive or relaxation skills for stress management to help them adapt to treatment.
Researchers at the University of Miami recruited 183 breast cancer patients from surgical oncology clinics in the Miami area in the weeks following surgery and prior to adjuvant treatment (chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and anti-hormonal therapy).
Women were randomized to one of three five-week groups: Cognitive Behavioral Training (e.g., changing thoughts about stressors and learning interpersonal skills), Relaxation Training (e.g., muscle relaxation and deep breathing), or a Health Education control group. At randomization and after women completed the 5-week group, researchers measured distress and life disruption, including mood, distress caused by breast cancer, disruption in social activities, and emotional well-being.
"We know from prior work at the University of Miami that a 10-week group combining cognitive behavioral and relaxation training improves quality of life for women in the early phases of breast cancer treatment. Since 10 weeks may be too long of a time commitment for most breast cancer patients, we wanted to test whether separate 5-week group versions of either cognitive behavioral training or relaxation training could have beneficial effects."
Researchers found that women who received the Cognitive Behavioral or Relaxation Training reported greater improvements in mood than women in the time-matched Health Education control group. Compared to the control group, women in the Cognitive Behavioral group also reported reduced breast cancer-specific distress (intrusive thoughts), as well as improved emotional-well-being, while women in the Relaxation group reported reduced disruptions in social activities.
In addition, women in the intervention groups showed greater improvements in stress management skills than those assigned to the Health Education control group. Women who received Cognitive Behavioral Training reported improvements in their sense of social support. Women who received Relaxation Training reported increased confidence in their ability to use the relaxation skills they had learned.
"Fine-grained analyses of the stress management skills women reported after the sessions were completed suggest that those in the cognitive behavioral training group were improving their sense of social support, which we know can improve mood and quality of life. On the other hand, women in the Relaxation Training group were improving their confidence in using skills such as muscle relaxation, breathing, and imagery. These skills may lower their day-to-day tension and anxiety, enabling them to enjoy more aspects of their social lives."
Future work by this group will investigate whether the Cognitive Behavioral and Relaxation Training interventions produce changes in stress hormone levels and measures of immune function and inflammatory processes over an extended follow-up period. Indicators of psychological and physiological well-being may provide a pathway through which these interventions could improve quality of life and health outcomes over the long-term survivorship period.
The findings were presented at the American Psychosomatic Society Meeting in San Francisco, California, on March 14, 2014.
INFORMATION:
Cognitive behavioral or relaxation training helps women reduce distress during breast cancer treatment
University of Miami researchers say confidence in stress management techniques improve after 5-week session
2014-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Spiders spin possible solution to 'sticky' problems
2014-05-16
Researchers at The University of Akron are again spinning inspiration from spider silk—this time to create more efficient and stronger commercial and biomedical adhesives that could, for example, potentially attach tendons to bones or bind fractures.
The Akron scientists created synthetic duplicates of the super-sticky, silk "attachment discs" that spiders use to attach their webs to surfaces. These discs are created when spiders pin down an underlying thread of silk with additional threads, like stiches or staples, explains Ali Dhinojwala, UA's H. A. Morton professor ...
With imprecise chips to the artificial brain
2014-05-16
This news release is available in German. Which circuits and chips are suitable for building artificial brains using the least possible amount of power? This is the question that Junior Professor Dr. Elisabetta Chicca from the Center of Excellence Cognitive Interaction Technology (CITEC) has been investigating in collaboration with colleagues from Italy and Switzerland.
Their surprising finding: Constructions that use not only digital but also analog compact and imprecise circuits are more suitable for building artificial nervous systems, rather than arrangements ...
Lighting the way to graphene-based devices
2014-05-16
Graphene continues to reign as the next potential superstar material for the electronics industry, a slimmer, stronger and much faster electron conductor than silicon. With no natural energy band-gap, however, graphene's superfast conductance can't be switched off, a serious drawback for transistors and other electronic devices. Various techniques have been deployed to overcome this problem with one of the most promising being the integration of ultrathin layers of graphene and boron nitride into two-dimensional heterostructures. As conductors, these bilayered hybrids ...
Herpes-loaded stem cells used to kill brain tumors
2014-05-16
Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) scientists at Massachusetts General Hospital have a potential solution for how to more effectively kill tumor cells using cancer-killing viruses. The investigators report that trapping virus-loaded stem cells in a gel and applying them to tumors significantly improved survival in mice with glioblastoma multiforme, the most common brain tumor in human adults and also the most difficult to treat.
The work, led by Khalid Shah, MS, PhD, an HSCI Principal Faculty member, is published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute. Shah heads ...
Ataluren Phase 3 trial results in nonsense mutation cystic fibrosis
2014-05-16
SOUTH PLAINFIELD, NJ – May 16, 2014 – PTC Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ: PTCT) today announced that the results of a Phase 3 study of ataluren in patients with nonsense mutation cystic fibrosis (nmCF) were published in Lancet Respiratory Medicine. The results demonstrated positive trends in both the primary endpoint, lung function as measured by relative change in % predicted FEV1 (forced expiratory volume in one second) and in the secondary outcome measure, rate of pulmonary exacerbations. The collective data from this trial, including retrospective and subgroup analyses ...
Glasses-free 3-D projector
2014-05-16
Over the past three years, researchers in the Camera Culture group at the MIT Media Lab have steadily refined a design for a glasses-free, multiperspective, 3-D video screen, which they hope could provide a cheaper, more practical alternative to holographic video in the short term.
Now they've designed a projector that exploits the same technology, which they'll unveil at this year's Siggraph, the major conference in computer graphics. The projector can also improve the resolution and contrast of conventional video, which could make it an attractive transitional technology ...
Growing camelina and safflower in the Pacific Northwest
2014-05-16
A recent study published in Agronomy Journal provides information important to farmers growing oilseed crops. In the study, camelina and safflower were grown in three-year rotations with winter wheat and summer fallow. The study shows that using this rotation may require that no tillage should be done to the soil during the fallow year. Oilseed crops produce relatively little residue—organic material such as roots that hold the soil together. Even light tillage can disintegrate the soil.
A cooperative study by the USDA-ARS and Washington State University researched the ...
How Asian American 'tiger mothers' motivate their children
2014-05-16
An article titled "Why Chinese Mothers Are Superior," published in The Wall Street Journal in 2011, has continued to provoke a cultural debate among parents after self-proclaimed 'tiger mother' Amy Chua asserted that Asian American parenting methods produce more successful children. Researchers at Stanford University delved deeper into Chua's 'tiger mother' approach, and their research sheds light on key fundamental differences in parenting methods between Asian Americans and European Americans.
To reveal the cultural differences in parenting, the researchers compare ...
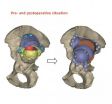
Ground breaking hip and stem cell surgery in Southampton
2014-05-16
Doctors and scientists in Southampton have completed their first hip surgery with a 3D printed implant and bone stem cell graft.
The 3D printed hip, made from titanium, was designed using the patient's CT scan and CAD CAM (computer aided design and computer aided manufacturing) technology, meaning it was designed to the patient's exact specifications and measurements.
The implant will provide a new socket for the ball of the femur bone to enter. Behind the implant and between the pelvis, doctors have inserted a graft containing bone stem cells.
The graft acts as ...
Fires continue in San Diego County, California
2014-05-16
Seven fires are still burning in San Diego County, California. Arson is suspected as the origin of these fires. Two teens have been arrested on suspicion of setting the fire that spread so ferociously across the county. All of California is experiencing exceptional, extreme or severe drought conditions. The wildfire area is in the second-most dangerous category--extreme drought conditions. California's governor has cited climate change as a factor in the fires, noting the last three years have been the driest in recorded history. Wildfire season used to start in late ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
[Press-News.org] Cognitive behavioral or relaxation training helps women reduce distress during breast cancer treatmentUniversity of Miami researchers say confidence in stress management techniques improve after 5-week session