(Press-News.org) Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) scientists at Massachusetts General Hospital have a potential solution for how to more effectively kill tumor cells using cancer-killing viruses. The investigators report that trapping virus-loaded stem cells in a gel and applying them to tumors significantly improved survival in mice with glioblastoma multiforme, the most common brain tumor in human adults and also the most difficult to treat.
The work, led by Khalid Shah, MS, PhD, an HSCI Principal Faculty member, is published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute. Shah heads the Molecular Neurotherapy and Imaging Laboratory at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Cancer-killing or oncolytic viruses have been used in numerous phase 1 and 2 clinical trials for brain tumors but with limited success. In preclinical studies, oncolytic herpes simplex viruses seemed especially promising, as they naturally infect dividing brain cells. However, the therapy hasn't translated as well for human patients. The problem previous researchers couldn't overcome was how to keep the herpes viruses at the tumor site long enough to work.
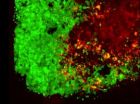
Shah and his team turned to mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)—a type of stem cell that gives rise to bone marrow tissue—which have been very attractive drug delivery vehicles because they trigger a minimal immune response and can be utilized to carry oncolytic viruses. Shah and his team loaded the herpes virus into human MSCs and injected the cells into glioblastoma tumors developed in mice. Using multiple imaging markers, it was possible to watch the virus as it passed from the stem cells to the first layer of brain tumor cells and subsequently into all of the tumor cells.
"So, how do you translate this into the clinic?" asked Shah, who also is an Associate Professor at Harvard Medical School.
"We know that 70-75 percent of glioblastoma patients undergo surgery for tumor debulking, and we have previously shown that MSCs encapsulated in biocompatible gels can be used as therapeutic agents in a mouse model that mimics this debulking," he continued. "So, we loaded MSCs with oncolytic herpes virus and encapsulated these cells in biocompatible gels and applied the gels directly onto the adjacent tissue after debulking. We then compared the efficacy of virus-loaded, encapsulated MSCs versus direct injection of the virus into the cavity of the debulked tumors."
Using imaging proteins to watch in real time how the virus combated the cancer, Shah's team noticed that the gel kept the stem cells alive longer, which allowed the virus to replicate and kill any residual cancer cells that were not cut out during the debulking surgery. This translated into a higher survival rate for mice that received the gel-encapsulated stem cells.
"They survived because the virus doesn't get washed out by the cerebrospinal fluid that fills the cavity," Shah said. "Previous studies that have injected the virus directly into the resection cavity did not follow the fate of the virus in the cavity. However, our imaging and side-by-side comparison studies showed that the naked virus rarely infects the residual tumor cells. This could give us insight into why the results from clinical trials with oncolytic viruses alone were modest."
The study also addressed another weakness of cancer-killing viruses, which is that not all brain tumors are susceptible to the therapy. The researchers' solution was to engineer oncolytic herpes viruses to express an additional tumor-killing agent, called TRAIL. Again, using mouse models of glioblastoma—this time created from brain tumor cells that were resistant to the herpes virus—the therapy led to increased animal survival.
"Our approach can overcome problems associated with current clinical procedures," Shah said. "The work will have direct implications for designing clinical trials using oncolytic viruses, not only for brain tumors, but for other solid tumors."
Further preclinical work will be needed to use the herpes-loaded stem cells for breast, lung and skin cancer tumors that metastasize to the brain. Shah predicts the approach will enter clinical trials within the next two to three years.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the James S. McDonnell Foundation and the National Institutes of Health.
Cited: Duebgen, M., et. al. Stem cells loaded with multimechanistic oncolytic herpes simplex virus variants for brain tumor therapy. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. June 2014. (Early access May 16, 2014)
Herpes-loaded stem cells used to kill brain tumors
2014-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ataluren Phase 3 trial results in nonsense mutation cystic fibrosis
2014-05-16
SOUTH PLAINFIELD, NJ – May 16, 2014 – PTC Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ: PTCT) today announced that the results of a Phase 3 study of ataluren in patients with nonsense mutation cystic fibrosis (nmCF) were published in Lancet Respiratory Medicine. The results demonstrated positive trends in both the primary endpoint, lung function as measured by relative change in % predicted FEV1 (forced expiratory volume in one second) and in the secondary outcome measure, rate of pulmonary exacerbations. The collective data from this trial, including retrospective and subgroup analyses ...
Glasses-free 3-D projector
2014-05-16
Over the past three years, researchers in the Camera Culture group at the MIT Media Lab have steadily refined a design for a glasses-free, multiperspective, 3-D video screen, which they hope could provide a cheaper, more practical alternative to holographic video in the short term.
Now they've designed a projector that exploits the same technology, which they'll unveil at this year's Siggraph, the major conference in computer graphics. The projector can also improve the resolution and contrast of conventional video, which could make it an attractive transitional technology ...
Growing camelina and safflower in the Pacific Northwest
2014-05-16
A recent study published in Agronomy Journal provides information important to farmers growing oilseed crops. In the study, camelina and safflower were grown in three-year rotations with winter wheat and summer fallow. The study shows that using this rotation may require that no tillage should be done to the soil during the fallow year. Oilseed crops produce relatively little residue—organic material such as roots that hold the soil together. Even light tillage can disintegrate the soil.
A cooperative study by the USDA-ARS and Washington State University researched the ...
How Asian American 'tiger mothers' motivate their children
2014-05-16
An article titled "Why Chinese Mothers Are Superior," published in The Wall Street Journal in 2011, has continued to provoke a cultural debate among parents after self-proclaimed 'tiger mother' Amy Chua asserted that Asian American parenting methods produce more successful children. Researchers at Stanford University delved deeper into Chua's 'tiger mother' approach, and their research sheds light on key fundamental differences in parenting methods between Asian Americans and European Americans.
To reveal the cultural differences in parenting, the researchers compare ...
Ground breaking hip and stem cell surgery in Southampton
2014-05-16
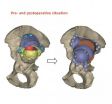
Doctors and scientists in Southampton have completed their first hip surgery with a 3D printed implant and bone stem cell graft.
The 3D printed hip, made from titanium, was designed using the patient's CT scan and CAD CAM (computer aided design and computer aided manufacturing) technology, meaning it was designed to the patient's exact specifications and measurements.
The implant will provide a new socket for the ball of the femur bone to enter. Behind the implant and between the pelvis, doctors have inserted a graft containing bone stem cells.
The graft acts as ...
Fires continue in San Diego County, California
2014-05-16
Seven fires are still burning in San Diego County, California. Arson is suspected as the origin of these fires. Two teens have been arrested on suspicion of setting the fire that spread so ferociously across the county. All of California is experiencing exceptional, extreme or severe drought conditions. The wildfire area is in the second-most dangerous category--extreme drought conditions. California's governor has cited climate change as a factor in the fires, noting the last three years have been the driest in recorded history. Wildfire season used to start in late ...
Skunk fire in Arizona
2014-05-16
The Skunk Fire in Arizona started with a lightning strike on Saturday, April 19. Currently over 10,000 acres have been affected. It is located in the San Carlos Apache Reservation. The terrain in the area is very steep with boulders making it difficult for firefighters to traverse the area to fight the fire. The fire continues to grow to the north, but fire activity in the south has been stopped. The fire is currently 20% contained.
The National Weather Service is forecasting winds of 7-12 mph with gusting to 25 mph. These conditions coupled with extremely dry fuels ...
Cause of death established
2014-05-16
Chamois (Rupicapra rupicapra) share their habitat with a number of other wild animals as well as with farm animals. Because of the risk of disease transmission between species, when dead or sick animals are discovered by hunters or foresters it is extremely important determining the causes. Early identification of the cause of disease or death can be crucial to prevent a wide-scale outbreak. The Pathological Laboratory at the Research Institute of Wildlife Ecology specializes in such cases.
Severe pneumonia as cause of death
Nineteen dead chamois from the region of ...
Fast and curious: Electrons hurtle into the interior of a new class of quantum materials
2014-05-16
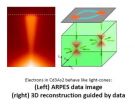
As smartphones get smarter and computers compute faster, researchers actively search for ways to speed up the processing of information. Now, scientists at Princeton University have made a step forward in developing a new class of materials that could be used in future technologies.
They have discovered a new quantum effect that enables electrons — the negative-charge-carrying particles that make today's electronic devices possible — to dash through the interior of these materials with very little resistance.
The discovery is the latest chapter in the story of a curious ...
Researchers call for better ocean stewardship
2014-05-16
FORT LAUDERDALE-DAVIE, Fla. – It has been said that we know more about the surface of the moon than we do about our own planet's oceans. That especially applies to the deepest parts of our oceans – depths that are 200 meters or deeper.
Researchers from organizations around the world who specialize in studying and exploring the deepest regions of our oceans have come together to pen a cautionary tale that urges we take a critical look at how we're treating our seas.
"We need to consider the common heritage of mankind - when do we have the right to take something that ...